Keywords
Pan-genomic, core-genome, unique gene, Serratia plymuthica, genome sequencing, comparative genomic
Pan-genomic, core-genome, unique gene, Serratia plymuthica, genome sequencing, comparative genomic
Serratia plymuthica bacteria have been isolated from many environmental sources and are found associated with diverse plants1–5. Many strains of this species have been reported to have the ability to inhibit the growth of plant-pathogenic fungi and stimulate plant growth6–9. UBCF_13 is one strain of this species. It has ability to inhibit Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, a species of post-harvest pathogenic fungi that causes anthracnose disease in various plants10.
Here, we report the complete genome sequence of this bacterium, constructed using Illumina sequencing technology. Our dataset may be useful as a comparative genome for evolutionary and speciation studies, as well as for the analysis of protein-coding RNA, biosynthetic gene clusters and may also useful for further study such as the regulation of gene expression in relation to the antifungal activity of this bacterium.
S. plymuthica strain UBCF_13 was isolated from phylloplane of Brassica juncea L. in 2012 from District of Solok, Province of West Sumatera, Indonesia10. The bacterium was cultivated in Luria–Bertani (LB) broth at 27°C for 16 hours with 150 rpm. The genomic DNA was extracted using the method of Chen and Kuo (1993)11, followed by degrading residual RNA by RNAse. Library preparation and sequencing was done by Novogen (Hong Kong). Sequencing was performed using Illumina NovaSeq 6000 (Illumina NovaSeq 6000 Sequencing System, RRID:SCR_016387).
Continuous short reads of 150 bp were merged into a single dataset. The dataset was obtained by using combination of map-based gene references and de novo assembly that was performed in Geneious software (Geneious, RRID:SCR_010519)12. The annotation in genome submission was carried out using NCBI Prokaryotic Genomes Automatic Annotation Pipeline (PGAP)13. The annotated genome sequence of UBCF_13 has been deposited in the NCBI GenBank under accession number CP068771.
Comparative genomics analysis was carried out using genome sequences of UBCF_13 from this research and 17 whole sequenced genomes of other Serratia plymuthica strains retrieved from NCBI’s GenBank. The genomes were reannotated using the Prokka software tool (Prokka, Galaxy Version 1.14.6+galaxy0) (Prokka, RRID:SCR_014732)14,15 that is available from the NCBI. Identification of genes shared between the strains, and ‘presence-absence gene set’ was carried out using Roary; Galaxy Version 3.13.0+galaxy1, (Roary, RRID:SCR_018172)16 with a threshold similarity of 70%.
Genes that exist in all the strains are the core-genome. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using Maximum Likelihood based inference of large phylogenetic trees-RAxML, Galaxy Version 8.2.4+galaxy2 (RAxML, RRID:SCR_006086)17 based on multialignment of concatenate core-genome. Phandango (Phandango, RRID:SCR_015243)18 was used to view the resulted output graphs.
The translated protein coding genes of UBCF_13 was used for identification of cluster of orthologous groups (COG). This was obtained from NCBI BLAST+rpsblast (Galaxy Version 2.10.1+galaxy0)19 and eggNOG Mapper (Galaxy Version 2.0.1+galaxy1) (eggNOG, RRID:SCR_002456)20. The result of COG identification was classified based on the categories in COG database NCBI21.
The whole genome sequencing reads of Serratia plymuthica UBCF_13 were assembled into a single circular 5.46 Mb chromosome with overall GC content of 56.2% (Table 1). S. plymuthica has a genome size in the range 5.40–5.70 Mb. The GC content percentage is 55.70–56.60. Based on genome reannotation by Prokka, it was found different number of CDS in each genome S. plymuthica (Table 1). All of the compared S. plymuthica genomes shared a highly conserved genomic architecture as inferred from synteny of protein coding orthologs.
Figure 1A shows the phylogenetic tree of 18 strains S. plymuthica. The phylogenetic tree shows that S. plymuthica UBCF_13 is in same cluster with strain AS9, PRI-2C, NCTC8015, and NCTC8900. The strain PRI-2C is reclassified and transferred to the species S. inhibens22. The pangenome was performed together with other strains in order to obtain further insight into specific features in the UBCF_13. It was found 3315 belong to the core-genome shared by the 18 strains evaluated. The genome of the UBCF_13 harbors 488 unique genes, of which 300 genes are only contained by this strain. The presence-absence gene set was shown in file supplementary data 1
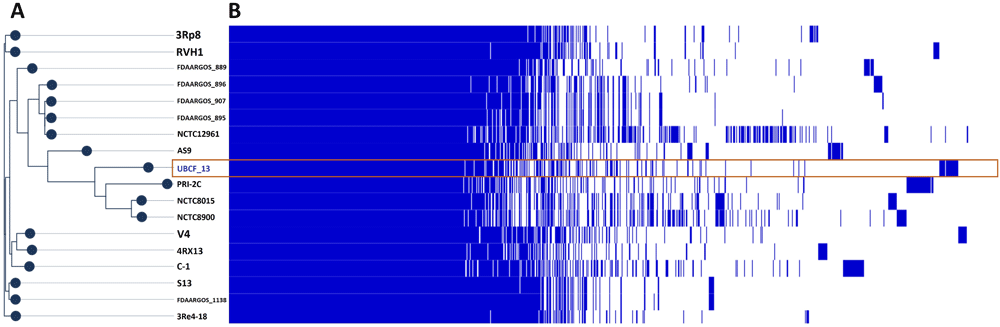
(a) Phylogenetic of 18 strains S. plymuthica based on concatenate core-genome multialignment; and (b) visualization of presence (blue bar)-absence (white bar) gene in each of the strains.
Functional categories of the CDS in S. plymuthica UBCF_13 based on the Cluster of Orthologous Groups (COG) categories are shown in Table 2. The list of UBCF_13 COG and its function classification based on COG database was shown in extended dataset 223.
Data from Serratia plymuthica UBCF_13 is available at NCBI under Bio-Project PRJNA692765, including the complete genome with annotation at GenBank accession CP068771, and the read data in the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database under the accession number SRR15012717.
Dataset 1:
Dryad: Gene presence absence in Serratia plymuthica strains. https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.1zcrjdfsj24
This project contains the following extended data;
Gene_presence_absence_in_Serratia_plymuthica_strains.csv (This data shows gene presence or absence across strain Serratia plymuthica species. It contains a list of coding protein gene (CDS) name and region where the gene exist in each genome (locus_tag). The region/locus where the CDS are existing has a specific tag for each genome, whereas the number after locus names represents the order of CDS in each genome. This data could be used to identify conserved and unique genes in Serratia plymuthica.)
Readme_Gene_presence_absence_in_Serratia_plymuthica_strains.txt (This text file provides information about the above data)
Dataset 2:
Dryad: Classification of the UBCF_13 COG based on COG database in NCBI https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.sn02v6x4g23
This project contains the following extended data;
Classification_of_the_UBCF_13_COG_based_on_COG_database_in_NCBI.csv (This data contains information about the assignment of Clusters of Orthologous Gene (COG) for each coding protein gene in Serratia plymuthica UBCF_13 and their functional classification based on COG database in NCBI)
Data are available under the terms of the Creative Commons Zero "No rights reserved" data waiver (CC0 1.0 Public domain dedication).
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Is the rationale for creating the dataset(s) clearly described?
No
Are the protocols appropriate and is the work technically sound?
No
Are sufficient details of methods and materials provided to allow replication by others?
No
Are the datasets clearly presented in a useable and accessible format?
No
References
1. Hennessy RC, Dichmann SI, Martens HJ, Zervas A, et al.: Serratia inhibens sp. nov., a new antifungal species isolated from potato (Solanum tuberosum).Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2020; 70 (7): 4204-4211 PubMed Abstract | Publisher Full TextCompeting Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Comparative genomics
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
|
Version 1 18 Aug 21 |
read |
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Comments on this article Comments (0)