|
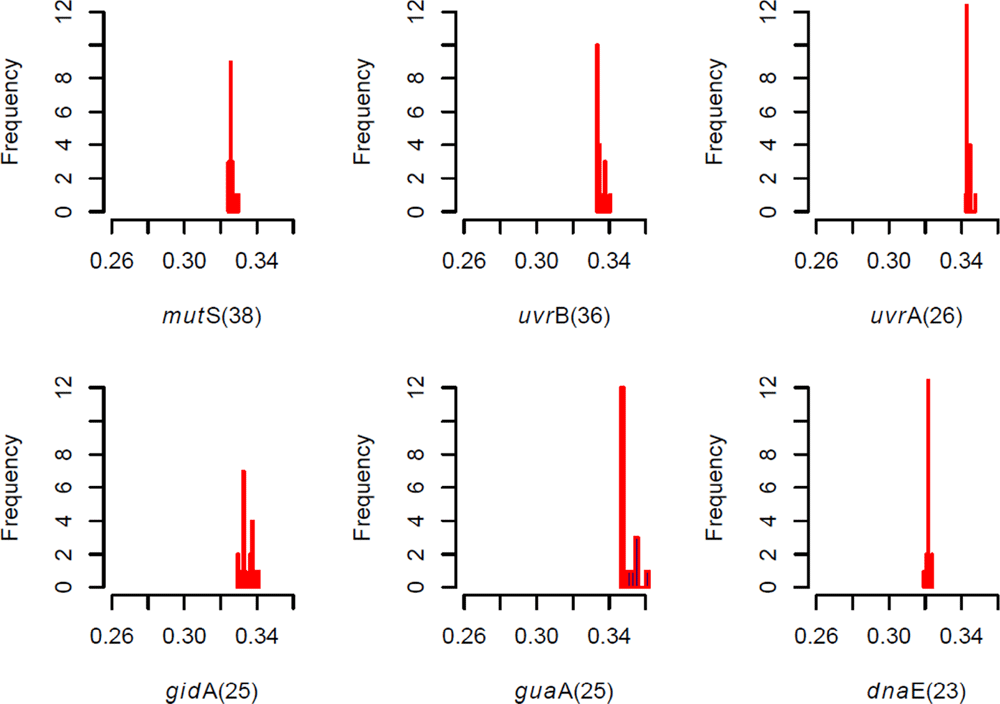
dnaE_ | Cj0718 | DNA polymerase III subunit alpha | It is a main replicative polymerase(Catalyses DNA-template-directed extension of the 3’- end of a DNA strand by one nucleotide at a time) | Purine metabolism, pyrimidine metabolism, metabolic pathways, DNA replication, mismatch repair and homologous recombination |
|
gidA_ | Cj1188c | tRNA uridine 5-carboxymethylaminomethyl modification enzyme | Involved in the modification of the wobble third base in tRNAs (5- carboxymethylaminomethyl modification (mnm(5)s(2)U) of the wobble uridine base in some tRNAs; also known as a glucose-inhibited cell division protein A) | tRNA modification and regulation |
|
guaA_ | Cj1248 | Probable GMP synthase
(glutamine-hydrolysing) | Purine ribonucleotide biosynthesis | Purine metabolism |
|
gyrA_ | Cj1027c | DNA gyrase subunit A | Negatively supercoils closed circular double-stranded DNA or prevents from super-coiling that is deleterious to bacterial survival | Direct DNA repair mechanism |
|
gyrB_ | Cj0003 | DNA gyrase subunit B | Negatively super-coils closed circular double-stranded DNA | Direct DNA repair mechanism |
|
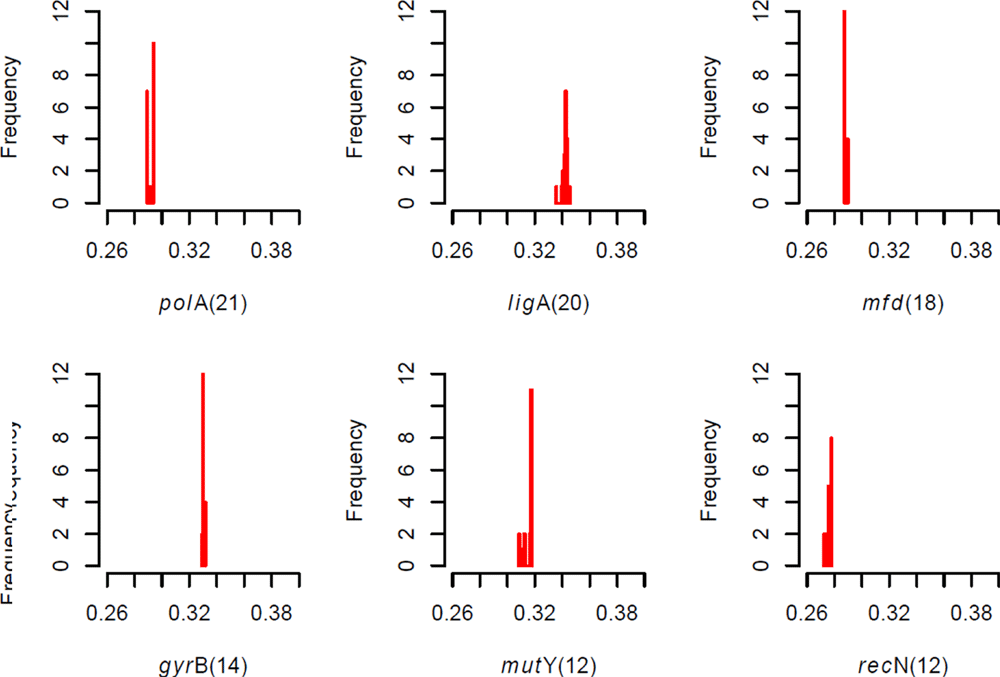
ligA | Cj0586 | NAD-dependent DNA ligase | Catalyses the formation of phosphodiester linkages and is essential for DNA replication and repair of damaged DNA (between 5’-phosphoryl and 3’-hydroxyl groups in double-stranded DNA using NAD as a coenzyme and as the energy source for the reaction) | Direct DNA repair mechanism, DNA replication, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair and mismatch repair |
|
mfdrepair | Cj1085c | Transcription-repair coupling factor | Prevents or corrects mutagenic nucleotides by removing them from DNA strands during replication | Nucleotide excision repair – DNA |
|
mutS | Cj1052c | Recombination and DNA strand exchange inhibitor protein | Involved in blocking homologous recombination and inhibits DNA strand exchange (has ATPase activity stimulated by recombination intermediates) | Mismatch excision repair – DNA repair |
|
mutY_ | Cj1620c | Probable A/G-specific adenine glycosylase | Corrects incorrectly paired bases during DNA replication and involved in recombinational repair | Base excision repair – DNA repair |
|
ogt
| Cj0836 | Methylated-DNA-protein-cysteine methyltransferase | Direct DNA repair by alkylation reversal | Direct DNA repair |
|
polA | Cj0338c | DNA polymerase I | Has 3’-5’ exonuclease, 5’-3’ exonuclease and 5’-3’polymerase activities, primarily functions to fill gaps during DNA replication and repair | Replication and DNA repair |
|
pyrC_ | Cj0259 | Dihydroorotase Pyrimidine | ribonucleotide biosynthesis: catalyses the formation of N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate from (S)-dihydroorotate in pyrimidine biosynthesis | Pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis |
|
pyrG_ | Cj0027c | CTP synthetase | Catalyses the ATP-dependent amination of UTP to CTP with either Lglutamine or ammonia as the source of nitrogen | Pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis |
|
recA_ | Cj1673c | Recombinase A | Involved in recombinational repair of DNA damage. Catalyses the hydrolysis of ATP in the presence of single-stranded DNA, the ATP-dependent uptake of single stranded DNA by duplex DNA, and the ATP-dependent hybridisation of homologous single-stranded DNAs | Recombinational repair |
|
recJ_ | Cj0028 | Putative single-stranded-DNAspecific exonuclease | Synthesis and modification of macromolecules - DNA replication, restriction/modification, recombination and repair | Recombinational repair |
|
recN | Cj0642 | Putative DNA repair protein | DNA repair protein | Recombinational repair |
|
recR | Cj1263 | Recombination protein | Involved in a recombinational process of DNA repair | Recombinational repair |
|
rplB_ | Cj1704c | 50S ribosomal protein L2 | One of the primary rRNA-binding proteins; required for association of the 30S and 50S subunits to form the 70S ribosome, for tRNA binding and peptide bond formation | Ribosomal gene |
|
rpoB_ | Cj0479 | DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta’ | RNA synthesis, RNA modification and DNA transcription | RNA polymerase |
|
rpoD_ | Cj1001 | RNA polymerase sigma factor | Sigma factors are initiation factors that promote the attachment of RNA polymerase to specific initiation sites and are then released; this is the primary sigma factor of bacteria | RNA polymerase |
|
ruvA | Cj0799c | Holliday junction DNA helicase | Plays an essential role in ATPdependent branch migration of the Holliday junction | Branch migration repair mechanism |
|
ssb
| Cj1071 | Single-stranded DNA-binding protein | Binds to single stranded DNA and may facilitate the binding and interaction of other proteins to DNA | Other repair mechanisms |
|
uvrA_ | Cj0342c | Excinuclease ABC subunit A uvrA is an ATPase and a DNAbinding protein. | A damage recognition complex composed of two uvrA and two uvrB subunits scans DNA for abnormalities | Nucleotide excision repair |
|
uvrB Nucleotide excision repair | Cj0680c | Excinuclease ABC subunit B | The UvrABC repair system catalyzes the recognition and processing of DNA lesions | The beta hairpin of the Uvr-B subunit is inserted between the strands, where it probes for the presence of a lesion |
|
xseA | Cj0325 | Exo-deoxyribonuclease VII large subunit | Bi-directionally degrades single stranded DNA into large acid insoluble oligonucleotides | Mismatch excision repair :Repair, ribosomal and nucleotide metabolic genes employed for MLST typing of other bacterial species |
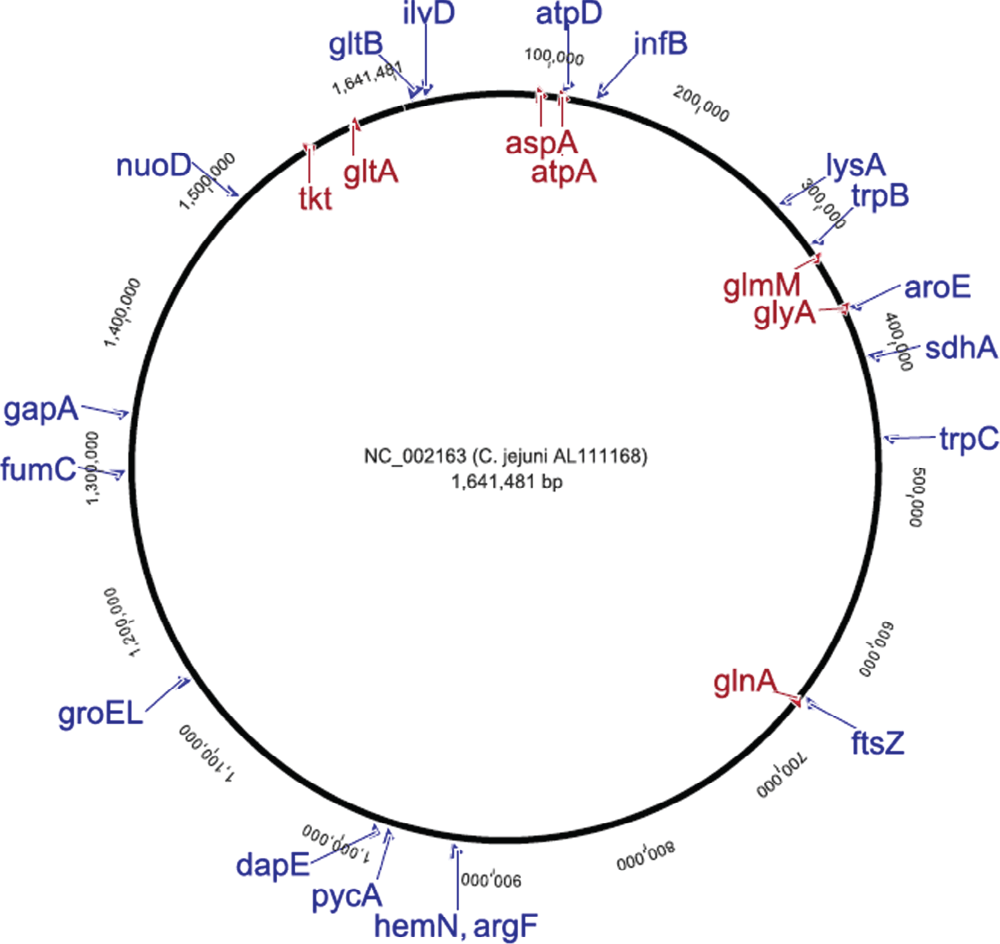
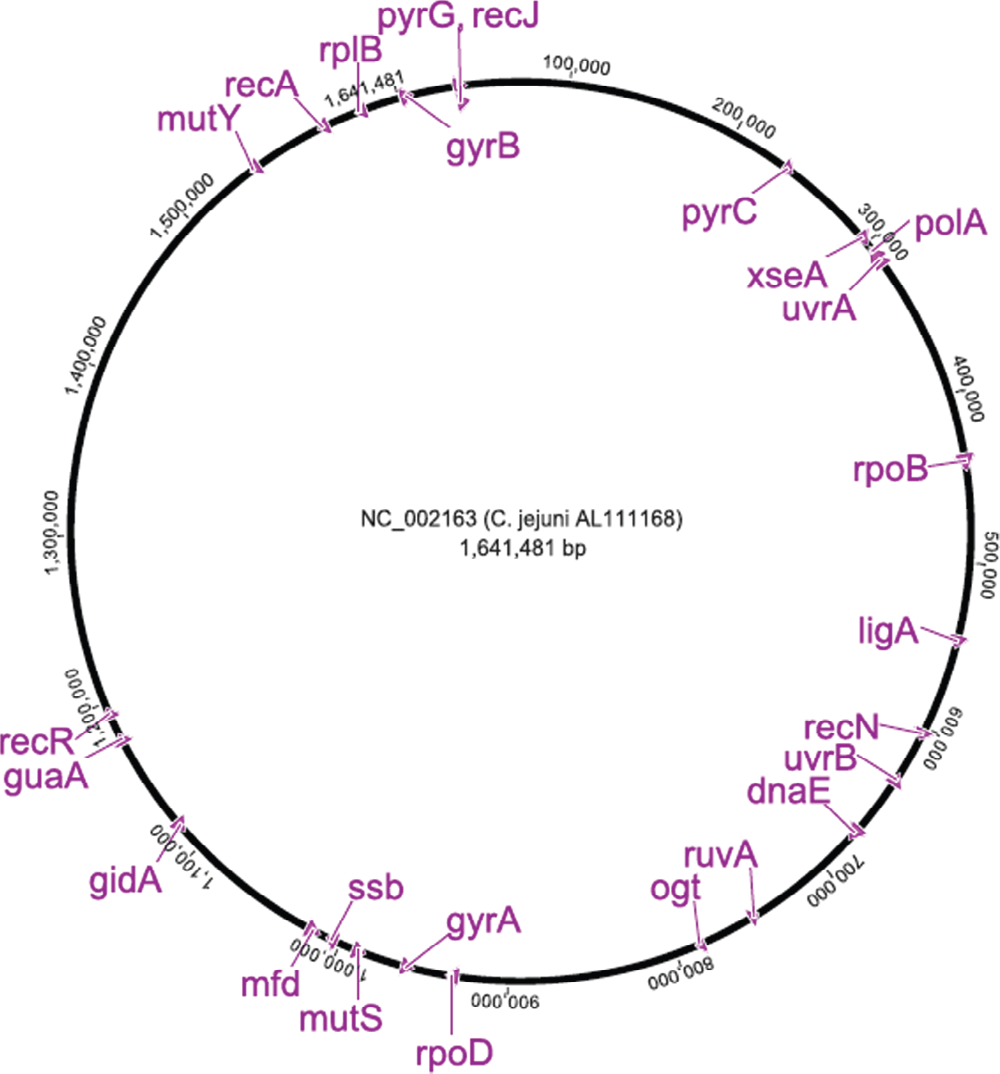
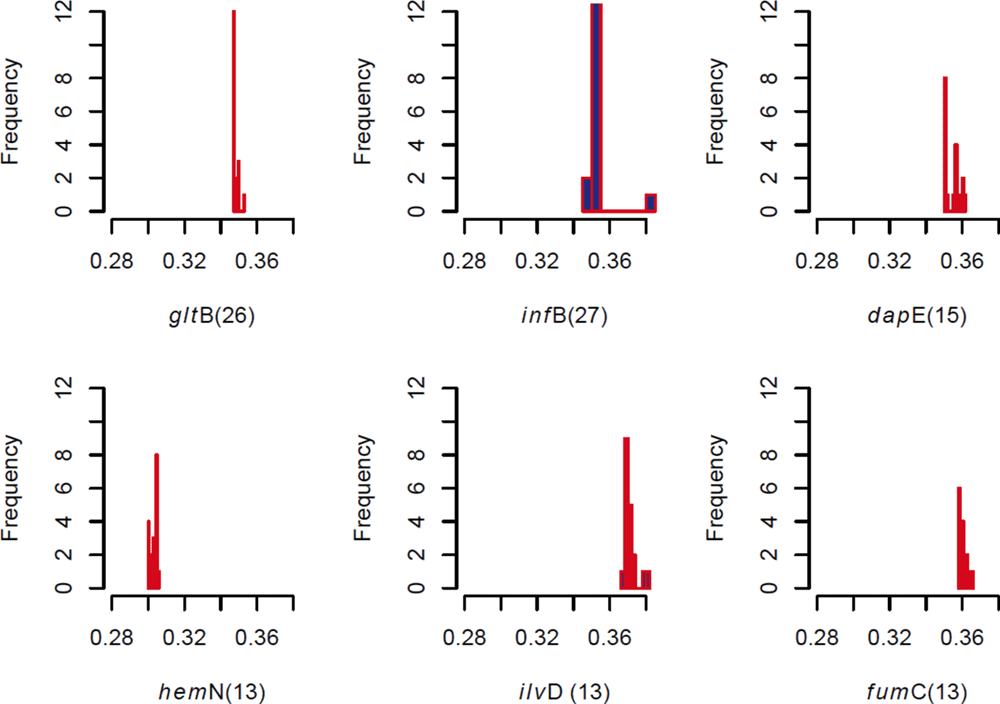
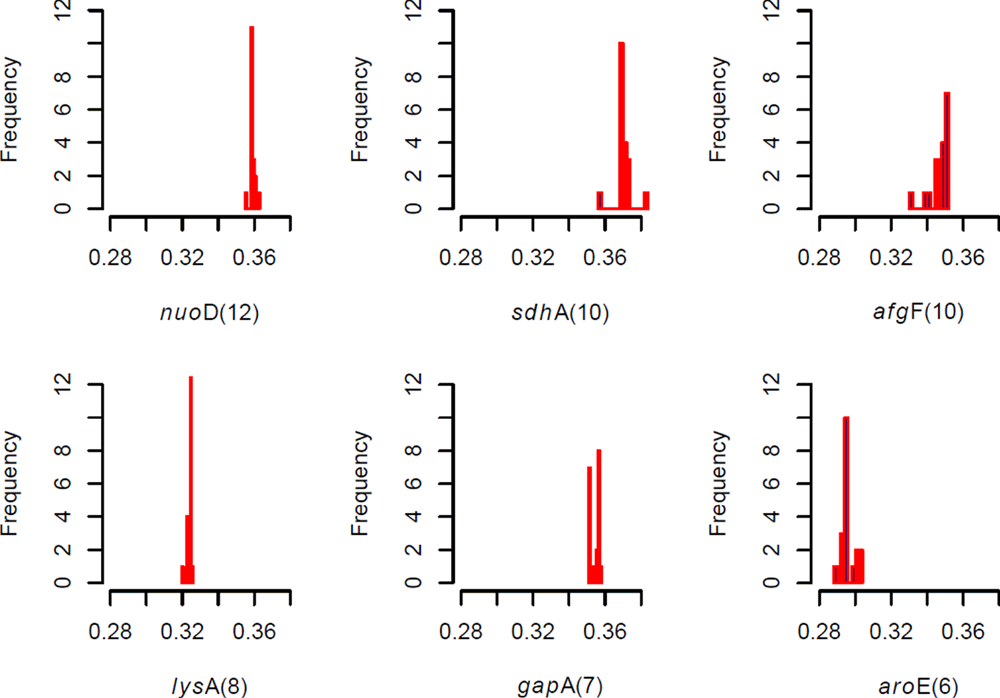
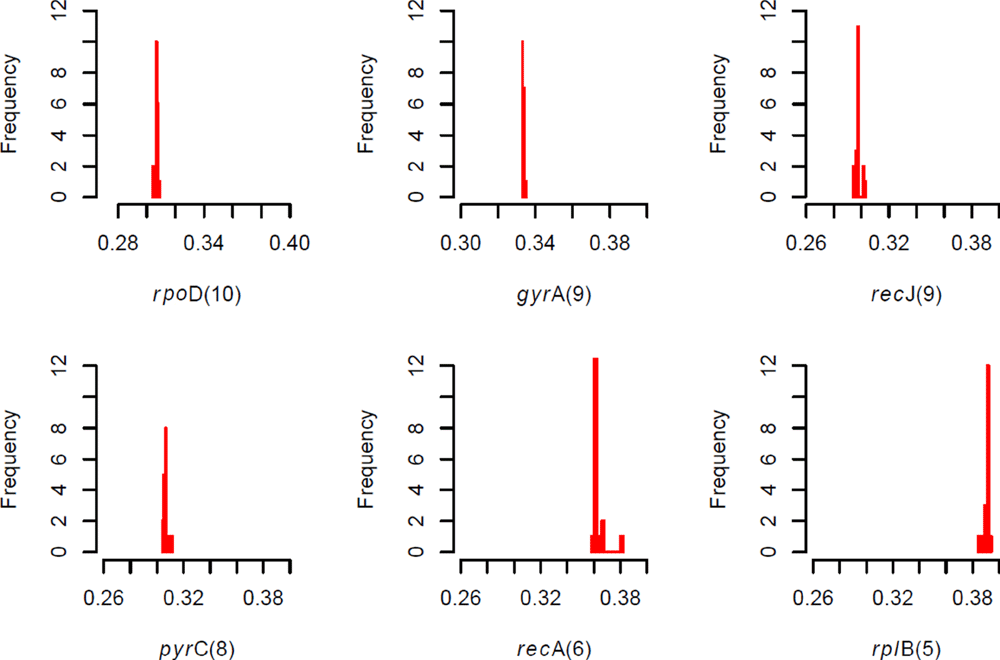
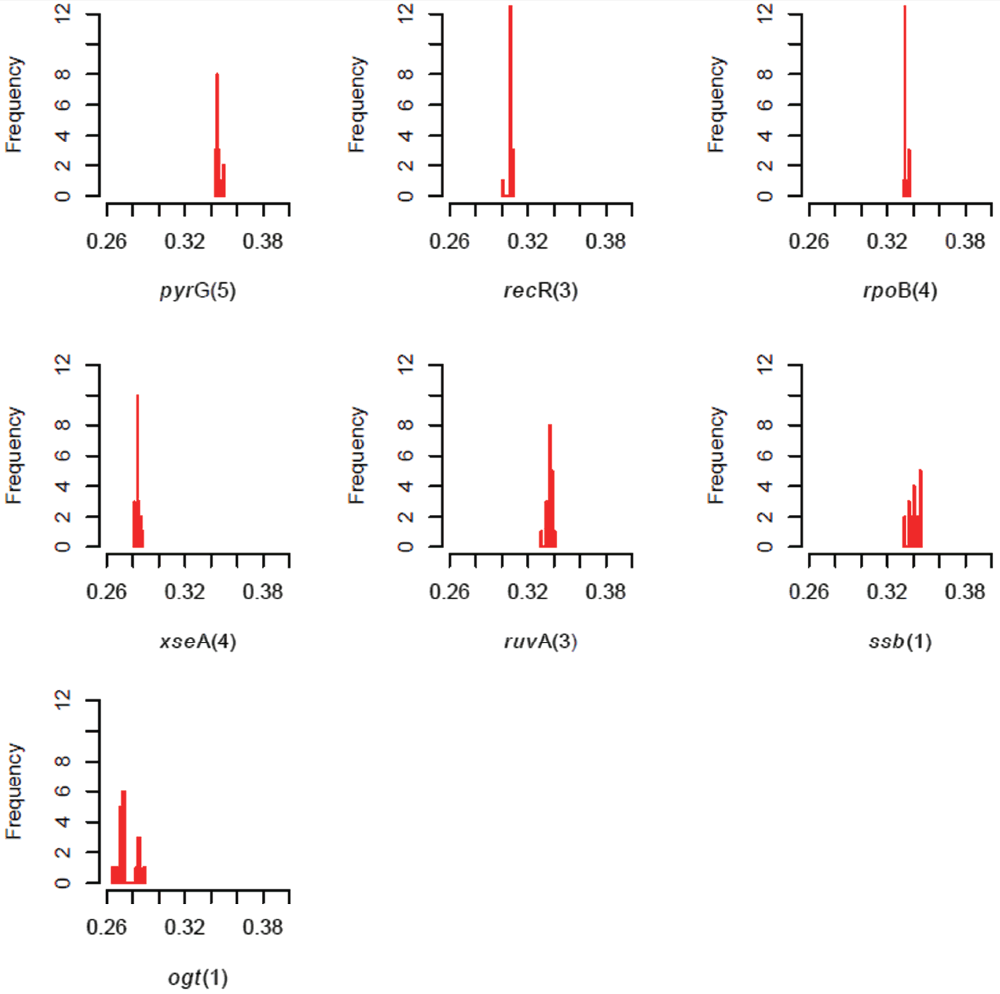
Comments on this article Comments (0)