Keywords
Whole Exome Sequencing, Lamellar ichthyosis, chr22q12, genodermatosis, TGM1
Whole Exome Sequencing, Lamellar ichthyosis, chr22q12, genodermatosis, TGM1
Autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis (ARCI), a heterogeneous disorder of cornification of skin, encompasses three clinical subtypes: lamellar ichthyosis (LI; OMIM 242300); congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma (CIE; OMIM 242100); and harlequin ichthyosis (HI; OMIM 242500)1. LI has an incidence of approximately 1 in 250,000. Over 115 mutations in TGM1 and less frequent ones in six other genes (NIPAL4z, ALOX12B, CGI-58, FLJ39501, ICHYN and ABCA12) have been associated with the LI/CIE phenotypic spectrum worldwide2,3. Overlapping phenotypes and the non-specificity of the conventional histopathology, makes clinical diagnosis challenging in many cases and inaccurate in some4. Whole exome sequencing has become a useful diagnostic aid for genetic disorders including multigene dermatoses such as epidermolysis bullosa5,6 and acrokeratosis verruciformis7.
Two, 8 and 6-year-old, siblings born out of a non-consanguineous marriage (Figure 1a) presented with hyperpigmented fish-like scales all over the body including face and flexures ectropion, loss of lateral half of eyebrows and alopecia along the scalp margins (Figure 1b–1e). Both siblings were heat intolerant, photosensitive and hypohidrotic. Born uneventfully vaginally they were encased in a collodion membrane which was shed within a week of birth. There was no family history of any dermatoses. Slit lamp examination revealed bilateral keratitis. Karyotyping of their parents and the siblings performed previously revealed duplication of the chromosome arm on 22q12+ in the father and two siblings. The patients were put on daily oral (5 mg) isotretinoin after analysing their lipid profile.
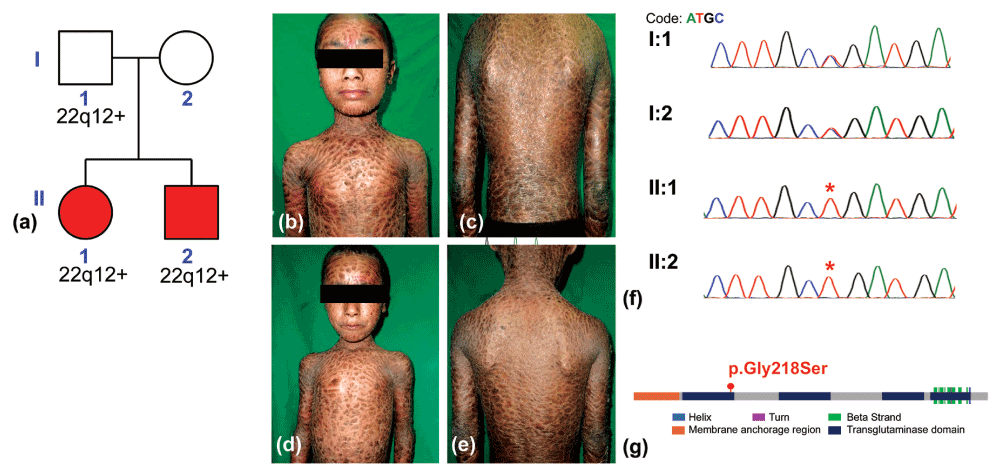
a) Pedigree of the family; (b), (c) and (d), (e) correspond to the ventral and dorsal views of siblings II:1, and II:2 respectively and shows hyperpigmented fish-like scales all over the body including face and flexures, ectropion, loss of lateral half of eyebrows and hair along scalp margins. Panel (f) shows the chromatogram from capillary sequencing for the parents and siblings, while panel (g) shows the domain organization of the protein and the location of the p.Gly218Ser variation with respect to the protein domains.
Considering the diagnosis of LI, whole exome sequencing was attempted. Genomic DNA (gDNA) was isolated from 5 ml of blood8 of each of the affected children after obtaining written informed consent conforming to the institutional ethical committee approvals (Dr. D.Y. Patil Vidyapeeth, Pune. Approval number DYPV/EC/178/14 ). The whole exome capture and library preparation (Nextera expanded exome, Illumina Inc., USA) were carried out according to the manufacturer’s instructions and followed by high throughput sequence generation on Hiseq 2500 with default 101 paired end single index sequence by synthesis chemistry (Illumina Inc., USA). The raw sequence reads were trimmed at a Phred score of 30 leaving over 44.9 and 33.45 million reads respectively for the two siblings. The variations were called against the hg19 version of the human genome using standard GATK-Picard pipeline with Burrows-Wheeler Alignment according to GATK best practice9. The variants from the genomes of both siblings were further analysed using ANNOVAR10 for coding region and also screened using the NCBI-Clinvar database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/). Analysis revealed a homozygous p.Gly218Ser variation in TGM1 previously reported to be associated with autosomal recessive non-syndromic ichthyosis in an isolated Finnish population11. The variant mapped to the transglutaminase domain in the protein (Figure 1g) and was also predicted to be pathogenic by both SIFT (Sorts Intolerant From Tolerant)15 and PolyPhen216 (Polymorphism Phenotyping v2). This variation was further validated in parents and both siblings by site-specific PCR using a forward primer CTTCTCCTGGGGTCAGGCA and reverse primer GAGAAGTCCCAGGCTCCATC (Sigma Aldrich). The PCR was done using taq polymerase (Invitrogen, USA, Cat. No. 10342053) according to the manufacturer supplied protocol with a Tm of 60.5°C. The PCR products were size selected and gel purified (2% agarose) using qiaquick gel extraction kit (QIAGEN, NL) and performed capillary sequencing (Applied Biosystems) performed using manufacturer instruction. Analysis revealed the variant was heterozygous in parents, while homozygous in both affected siblings (Figure 1f).
Follow up after two years of low dose isotretinoin, titrated intermittently, revealed complete subsidence of ectropion, eclabium and alopecia with residual fine scales.
ARCI is a rare disorder with an estimated prevalence of 1 per 200,000 population in Europe and 1 per 200,000–300,000 population in the United States. Neonates with LI typically present with a collodion membrane which dries and peels away and is replaced by brown, plate-like scales over the entire body. Disease course ranges from very mild to severe, latter entailing ectropion, eclabium, scarring supraciliary and scalp alopecia, and palmoplantar hyperkeratosis11.
DNA based molecular diagnosis is crucial in ichthyosis as it provides a firm basis for genetic counseling of affected individuals and families, and also permits prenatal diagnosis. In a cohort of 520 independent families with ARCI, mutations were identified by direct sequencing of the 6 ARCI genes identified to date in 78% of patients: 32% harbored mutations in TGM1, 16% in NIPAL4, 12% in ALOX12B, 8% in CYP4F22, 5% in ABCA12, and 5% in ALOXE3. Whole exome sequencing may fill in the diagnostic lacuna of at least 22% of the patients who failed in this study to exhibit mutations in any of the known ARCI genes, indicating the existence of additional loci, such as 2 loci on chromosome 12p11.2-q1312. The 22q12+ duplication is known to cause cat eye syndrome, which has a range of potential morbidities with the occurrence of characteristic triad of iris coloboma, aural tags and/or pits and anal atresia14, though none of these features were present in the father or the children.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported concurrence of a potentially benign 22q12+ duplication and LI, both of which are extremely rare individually. The mother of the siblings is now pregnant and the present finding will be used to help screen the foetus prenatally.
Written informed consent for publication of their clinical details and clinical images was obtained from the parent of the patients.
The raw exome sequencing data are available at the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra), accession numbers SRX1096915 (II:1) and SRX1096920 (II:2).
AG, YKS and KD identified the patient, took the biopsies for histopathology and sent the blood for DNA analyses. They helped in writing the initial case report as well as editing and formatting the manuscript. SKV, RJ, VD and AV isolated the DNA, performed the quality checks, prepared the exome capture and sequencing library, performed the exome sequencing. SKV performed data quality checks on the reads, reference alignments, variant call and computational prioritisation of the variants, designed and performed the validation experiments. SS and VS conceptualised and oversaw the DNA isolation, quality checks, exome sequencing, exome sequence analysis and validation and contributed to writing the manuscript.
Authors acknowledge funding from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India through Grant No. BSC0122 (CARDIOMED).
I confirm that the funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Authors acknowledge Dr. Vamsi Y Krishna for critical comments and members of VS, SS labs and the GUaRDIAN Consortium for their help and support.
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |
|
Version 1 31 Jul 15 |
read | read |
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Comments on this article Comments (0)