Keywords
mouse phenotyping, Crb1/rd8 mutation, retina degeneration,
mouse phenotyping, Crb1/rd8 mutation, retina degeneration,
Retinal degeneration in mice occurs in many forms, many of which can be attributed to mutations in specific genes. Some of the reported types of retinal degeneration display a similar phenotype, characterised by the presence in the fundus of white spots of different shapes and sizes1–3. One of the causative mutations for retinal degeneration in the mouse is the spontaneous single nucleotide deletion rd8 in the Crb1 gene, situated on chromosome 11,4. It has been previously reported that the C57BL/6N strain, derived from the unaffected C57BL/6J strain, often presents typical retinal white spots (flecks) caused by the Crb1/rd8 mutation4. These have been described as dysplastic lesions affecting the retinal region between the inner and the outer nuclear layer and are mainly localised in the inferior part of the retina5,6. The observed phenotype is considered a possible confounding factor that could mask a phenotype with a similar appearance but a different causative gene mutation (Figure 1). This is of particular importance considering that the C57BL/6N line is a widely used commercial line and is the background strain used for the generation of gene-targeted mice in several mouse mutagenesis/phenotyping programmes, including the International Knockout Mouse Consortium (IKMC) and the International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium (IMPC).
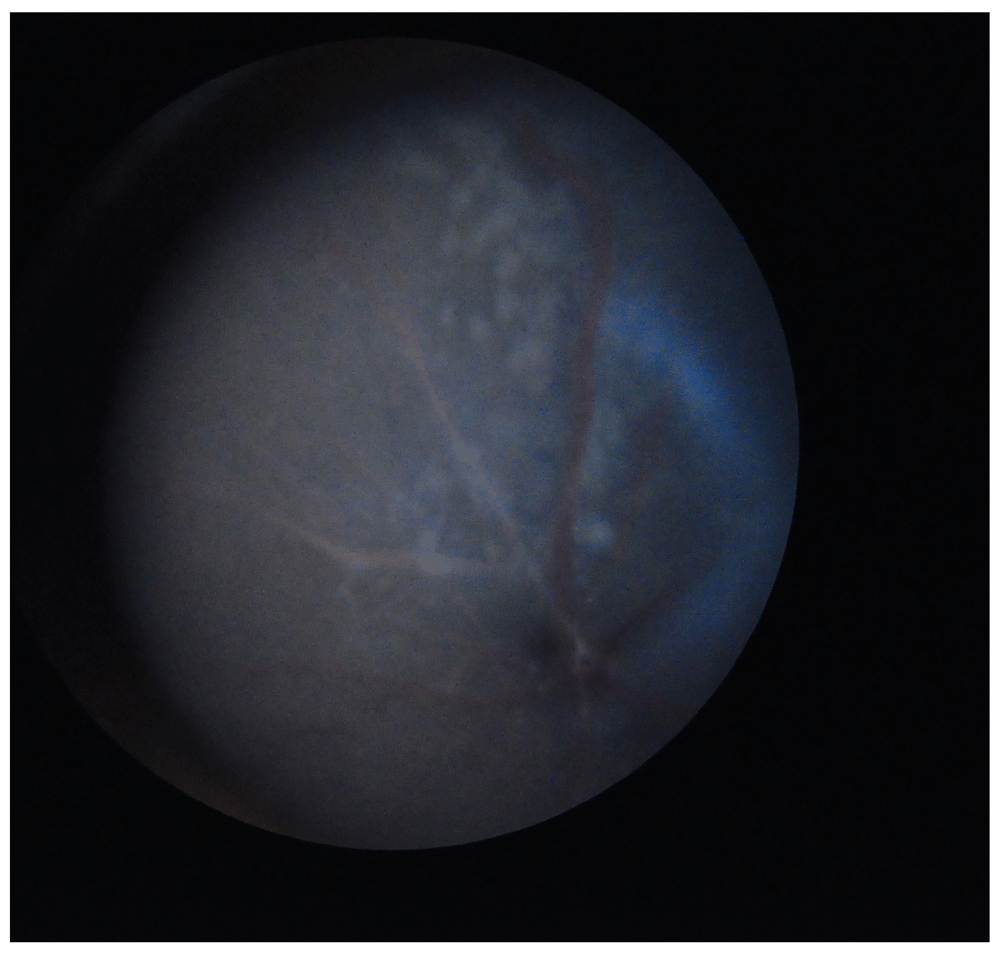
The flecks appear in the superior hemicycle of the fundus because the image is inverted by the ophthalmoscope.
Over the last 5 years of phenotyping mice through the IMPC pipeline at MRC Harwell, we have observed the presence of fundus flecks in both the knockout lines and in the C57BL/6NTac wild type mice. The number of affected individuals for each knockout line generated has been variable, as has the number of flecks present in each individual. As a result of such variability, the probability that the flecking in the mutant line is a phenotype attributable to the gene mutations rather than the background strain effect becomes questionable. To correctly interpret similar phenotypes in the knockout lines and exclude the contribution of Crb1/rd8 -related flecks, we have created a scoring system to allow us to fully categorise the lesions present in the C57BL/6NTac mice in a systematic manner in order to provide a comprehensive background strain reference. The flecks scoring system takes into account the position of the flecks in the superior and inferior retinal hemicycle, as the retina is not uniformly affected by the phenotype5. As an innovative approach, we also scored the number of flecks in each hemicycle as a measure of the phenotypic penetrance. In addition, in order to determine any sexual dimorphism, we applied our scoring system to both males and females.
194 C57BL/6NTac males and 200 females were screened at 15 weeks of age. Animals were housed in IVC cages from birth under 12-hour-on/12-hour-off cyclic lighting, at controlled temperature (21 ± 2°C) and humidity (55 ± 10%) conditions. The mice had free access to water (25 p.p.m. chlorine) and were fed ad libitum on a commercial diet (SDS Rat and Mouse No.3 Breeding diet RM3). All procedures and animal studies were carried out in accordance with the Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986, UK, SI 4 2012/3039) and with the NC3R’s ARRIVE guidelines All animal work reported in this article has been optimised to minimise the animals’ suffering and unnecessary procedures.
For the fundus examination an Omega 180 ophthalmoscope (Heine Ltd, USA) and a Superfield NC lens (Volk Optical Inc., USA) were used. Each eye pupil was dilated using a drop of 1% w/v Minims Tropicamide (Bausch & Lomb Inc., USA) and the observation was performed after 2 minutes. Images of the fundus were acquired by the use of a topical endoscopy fundus imaging (TEFI) camera.
The examinations were conducted by trained technicians on both eyes and the flecks on individual eyes were evaluated according to an in-house scoring system (Figure 2), taking into account their position in the fundus with respect to the optic nerve head (superior or inferior) and their number (with respect to the retinal surface covered by the flecks) as a measure of the severity grade. Therefore, the combination of both the position and the severity grade formed a scoring category for each eye.
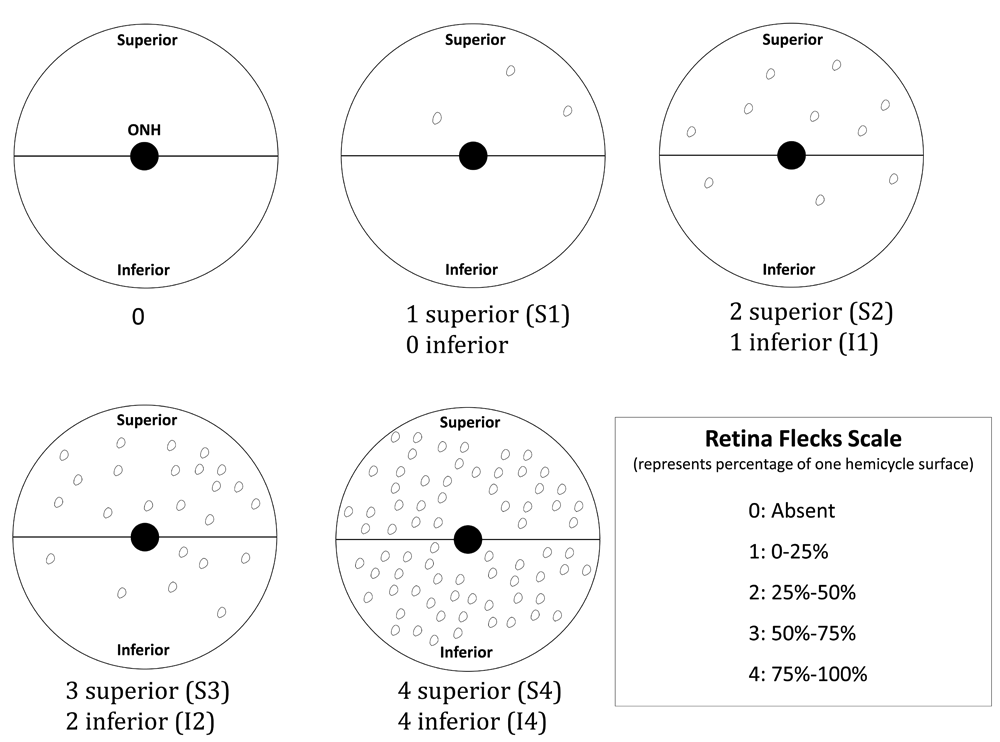
The retinal fundus has been divided into two hemicycles: inferior and superior. In each one of the hemicycles the percentage of the surface that is covered by flecks represents the severity grade within a range of 25% for each level. The combination of the position, superior (S) or inferior (I), and the severity grade (from 0 to 4) represents the flecks score.
All observational data were recorded on a Microsoft Office Excel spreadsheet, and counts and percentage calculations were performed. Where different flecking scores were obtained for the left and right eye of the same animal, the eye with the most severe grade was used for the percentage calculations.
As shown in Table 1, the total percentage of affected males was higher than that of affected females (14.4% of males and 5% of females). Further categorising the flecks according to our scoring system, we observed that the males were still the most affected in the score classes ranging from I1 to I3 (Figure 3), with a symmetrical distribution of the frequencies centred in the I2 class (25–50% of inferior retina surface) in both sexes (8.2% of males and 3.0% of females). In the sample, there were no males affected in the class I4 (75 to 100% of inferior retina surface), whilst only one female (0.5% of the total) presented that severity grade. We mentioned above that the presence of this kind of flecks has already been associated with the inferior hemicycle of the fundus by other authors, a fact supported by our data that show just one male in the S3 (50–75% of superior retina surface) class of flecking.
For each flecks class, the percentage relative to the total number of animals in each sex group has been calculated.
| Flecks class | Males affected | Females affected | % of males affected | % of females affected |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | 4 | 1 | 2.1 | 0.5 |
| I2 | 16 | 6 | 8.2 | 3.0 |
| I3 | 7 | 2 | 3.6 | 1.0 |
| I4 | 0 | 1 | 0.0 | 0.5 |
| S1 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| S2 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| S3 | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.0 |
| S4 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Total | 28 | 10 | 14.4 | 5.0 |
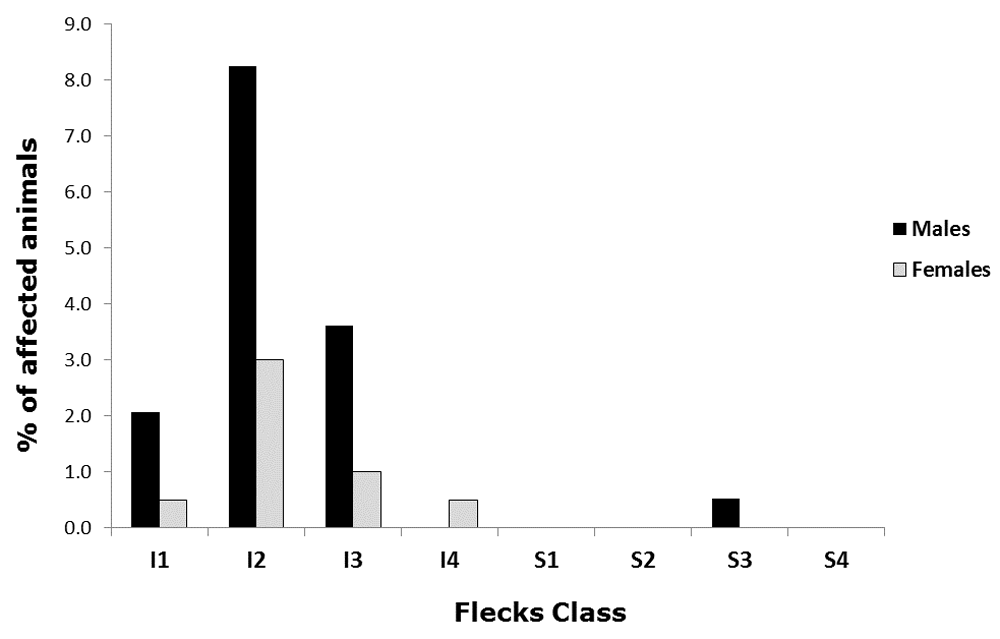
The chart shows the percentage distribution of the flecks in the retinal fundus of males (black columns) and females (white columns) C57BL/6NTac mice. The horizontal categories represent the flecks class as previously explained in Figure 2.
With this study we make available both the observational data on the retinal flecks in C57BL/6NTac mice determined by the use of our scoring system, and the scoring system itself. Our findings, using a large population of wild type mice, provide a reference baseline that could significantly contribute to the further evaluation of Crb1 mutations-based eye morphology phenotypes. In addition to the flecks distribution data, the scoring system used represents a reliable quantitative method to evaluate the degree of flecking of an affected mouse retina and to make the comparison process between two or more strains (or treatment groups) more accurate and manageable.
Dataset 1: Flecks scores raw data. A spreadsheet with the raw data related to the manual scoring of flecks made by the trained technicians, according to our in-house scoring system. The spreadsheet contains one column related to the animal ID and one column with the score class for males and females. The score class represents the combination of the position, superior (S) or inferior (I), and the severity grade (from 0 to 4) as described in Figure 2.
DC: Score system design, data analysis, article writing, charts and preparation of figures. HC: Score system design, article review. SW: Article review
The research described in this manuscript was funded by the National Institutes for Health (U54HG006348) and by the Medical Research Council Strategic Award (53650).
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
We wish to thank Sharon Clementson-Mobbs, Russell Joynson and Clare Norris (MRC Harwell Institute, Mary Lyon Centre) for their precious contribution with fundus examination. We wish also to thank Dr Debora Bogani (MRC Harwell Institute), for her generous contribution to the manuscript reviewing process.
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Is the work clearly and accurately presented and does it cite the current literature?
Partly
Is the study design appropriate and is the work technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of methods and analysis provided to allow replication by others?
Partly
If applicable, is the statistical analysis and its interpretation appropriate?
Partly
Are all the source data underlying the results available to ensure full reproducibility?
No
Are the conclusions drawn adequately supported by the results?
Yes
References
1. Simon MM, Greenaway S, White JK, Fuchs H, et al.: A comparative phenotypic and genomic analysis of C57BL/6J and C57BL/6N mouse strains.Genome Biol. 2013; 14 (7): R82 PubMed Abstract | Publisher Full TextCompeting Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Retinal physiopathology, notably in diseases which main symptoms are not visual, as Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy or Down Syndrome, using immunohistology, microscopy, electrophysiology and retinal imaging (TEFI, OCT). In parallel, I have been supervising visual phenotyping at the Mouse Clinic Institute, notably for the Eumodic and IMPC program, thus facing the common problem of C57Bl/6N users described and quantified here.
Is the work clearly and accurately presented and does it cite the current literature?
Yes
Is the study design appropriate and is the work technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of methods and analysis provided to allow replication by others?
Yes
If applicable, is the statistical analysis and its interpretation appropriate?
Yes
Are all the source data underlying the results available to ensure full reproducibility?
Yes
Are the conclusions drawn adequately supported by the results?
Partly
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: My expertise is molecular neurobiology and genetics of blindness using mouse and rat models to decipher and understand the phototransduction cascade. I was the first to molecularly identify the members of the arrestin superfamily and other key signal transduction proteins in the retina by creating genetically engineered knockout mice for the cone arrestin and to address the phototransduction shutoff in cones. We identified and characterized a serious degeneration with Crb1 on the knockout Grk1 because of a C57Bl/6N background (Pak JS, Lee EJ, Craft CM.The retinal phenotype of Grk1-/- is compromised by a Crb1 rd8 mutation.Mol Vis. 2015 Nov 30;21:1281-94.PMID:26664249
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |
|
Version 1 31 Mar 17 |
read | read |
Click here to access the data.
Spreadsheet data files may not format correctly if your computer is using different default delimiters (symbols used to separate values into separate cells) - a spreadsheet created in one region is sometimes misinterpreted by computers in other regions. You can change the regional settings on your computer so that the spreadsheet can be interpreted correctly.
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Comments on this article Comments (0)