Keywords
Aeromonas hydrophila, bivalent vaccine, monovalent vaccine, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Streptococcus agalactiae.
This article is included in the Agriculture, Food and Nutrition gateway.
Vaccination is an effective and alternative means of disease prevention, however, it cannot be conducted on the offspring of fish. For this process to take place, the transfer of maternal immunity should be implemented. This study aims to determine the effectiveness of transferring immunity from the broodstock to the offspring using a polyvalent vaccine against Aeromonas hydrophila, Streptococcus agalactiae, and Pseudomonas fluorescens in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus.
Nile tilapia broodstock with an average weight of 203g (±SD 23) was reared in spawning ponds until mass spawning and harvested one week post-spawning for vaccination. After being vaccinated according to the treatment, each fish broodstock was reared in 3x3 m cages installed in an earthen pond with a density of 20 broodstock, consisting of 15 females and 5 males. The vaccine used was a formalin-killed whole-cell vaccine at a density of 1010 cfu/mL injected intramuscularly (i.m.) at a dose of 0.4 mL/kg fish. Nile tilapia was injected with a vaccine used as a treatment. Example include A. hydrophila monovalent (MA), S. agalactiae monovalent (MS), P. fluorescens monovalent (MP), A. hydrophila and S. agalactiae bivalent (BAS), A. hydrophila and P. fluorescens bivalent (BAP), P. fluorescens and S. agalactiae bivalent (BPS), and A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens polyvalent vaccines (PAPS). While the control was fish that were injected with a PBS solution. The broodstock’s immune response was observed on the 7th, 14th, 21st, and 28th days, while the immune response and challenge test on the offspring was conducted on the 10th, 20th, 30th, and 40th day during the post-hatching period. The parameters observed consisted of total leukocytes, phagocytic activity, antibody titer, lysozyme, and relative survival percentage (RPS).
The application of PAPS in broodstock could significantly induce the best immune response and immunity to multiple diseases compared to other treatments. The RPS of the PAPS was also higher than the other types of vaccines. This showed that the transfer of immunity from the broodstock to the Nile tilapia offspring could protect it against bacterial diseases such as A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens.
The application of polyvalent vaccine A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, P. fluorescens vaccines increased the broodstock’s immune response and it was transferred to their offsprings. Polyvalent vaccines derived from maternal immunity can protect offspring from disease up to 30 days of age. They were able to produce tilapia seeds that are immune to diseases caused by A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens.
Aeromonas hydrophila, bivalent vaccine, monovalent vaccine, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Streptococcus agalactiae.
There are various phrase modifications, as well as italicizing letters and refining figure and table captions. There is a more extensive explanation of the serum dilution procedure, as well as the use of positive and negative controls in the agglutination test, under the research methods section. It was also made clear that the agglutination test used serum extracted from offspring blood. It was also stated that the challenge test included three different species of bacteria at the same time, namely A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens. We did make changes to the figures and tables in the updated text. There are improvements to the captions of the figures in the research results, specifically in Figures 1-4, as well as enhancements in Tables 1 and 2. The role of the Polivalent vaccine derived from maternal immunity is explained in the discussion, which can protect offspring from disease attacks up to 30 days of age, while after 40 days of age offsprings rely solely on immune responses transferred naturally from their parents/broodstocks or begin to produce their immune responses. It is stated in the conclusion section that the use of polyvalent vaccines through maternal immunity can protect offspring from disease up to 30 days of age.
To read any peer review reports and author responses for this article, follow the "read" links in the Open Peer Review table.
Tilapia was originally considered to be more resistant to bacterial, parasitic, fungus, and viral diseases than other species of cultivated fish. However, they are found to be susceptible to bacterial and parasitic diseases1–3, particularly during the offspring phase4. Globally, the control of bacterial disease mostly uses antibiotics that are proven not environmentally friendly5–7. Some common diseases of tilapia found in several Southeast Asian countries including Indonesia are Streptococcus agalactiae, Aeromonas hydrophila, Edwardsiella ictaluri, Flavobacterium columnaris, and Pseudomonas fluorescens infections8–10. In addition to the bacterial disease, a new disease has emerged called Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV) disease whose specific host is tilapia, causing disease outbreaks with high mortality rates in several Southeast Asian countries such as Thailand11 and Malaysia12.
Among the various methods of disease control, vaccination is one of the most effective ways, which is commonly used5,13–16. The administration of vaccines is meant to produce antibodies that could improve the immunity of tilapia3,5. Unfortunately, they could not be administered to the offspring of fish because the organs that form the immune response are not yet fully developed, therefore they are unable to produce antibodies7,13–17. Tilapia fry was not able to produce their own immune system at the age of less than 21 days18, Immune systems of Xenopus laevis develop within 2 weeks of age19, while Indian major carp develop within 3 weeks of age20.
An effective solution to the aforementioned issue is the application of maternal immunity transfer. This is the transfer of immunity from broodstock to offspring, by which immunoglobulin (IgM type) are transferred through eggs19,21,22. Maternal immunity has been shown to improve the fish offspring’s immunity against pathogens in the early phases of their lives23–26.
This process is usually carried out using monovalent vaccines27–30. However, a polyvalent vaccine would be more effective because it could control multiple diseases3,31,32 especially using a formalin-killed vaccine with low production cost compared to other types of vaccines3. Though the effectiveness has been known, the application of polyvalent vaccines to confer maternal immunity in offspring has not been extensively investigated, particularly in Nile tilapia (O. niloticus).
The transfer of maternal immunity using polyvalent vaccine for S. agalactiae, Lactococcus garvieae, and Enterococcus faecalis has been studied by Abu-elala et al.33, and three vaccine strains for S. agalactiae by Nurani et al.34. The types of bacterial diseases studied in the aforementioned studies are very limited even though Nile tilapia often suffer from them in fish farms and hatcheries35. Besides being infected by S. agalactiae29,34–36, Nile tilapia are often infected by A. hydrophila9,35,37 and P. fluorescens37,38 leading to high mortality, including in Indonesia. Therefore, this study aimed to examine maternal immunity transfer using the polyvalent vaccine for S. agalactiae, A. hydrophila, and P. fluorescens (PAPS). It was expected that the broodstock could pass their immunity to their offspring, making them resistant to the three diseases (A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens bacteria), and also the production of tilapia offspring could also be increased. Furthermore, this study aimed to determine the effectiveness of the transfer of immunity induced by PAPS against A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens from the Nile tilapia (O. niloticus) broodstock to their offspring and the protection against S. agalactiae, A. hydrophila, and P. fluorescens infections.
Nile tilapia broodstock, obtained from the Ompo Inland Hatchery, Soppeng, Indonesia, with an average weight of 203g (±SD 23) were used as experimental animal. They were kept in spawning ponds (25X30X1.2 LxWxD) and fed ad libitum with pellets that have a protein content of 30% in the mornings and afternoons. Also, 25% of the water was replaced daily. One week after the fish spawned, they were harvested and a large number of Nile tilapia broodstock at gonad developmental stage 2 were obtained.
Pure isolates of the A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens bacteria were obtained from the Research and Development of Fish Disease Control Installation, Ministry of Marine Affairs and Fisheries, Depok, Indonesia. Vaccine production was carried out by harvesting bacteria aged 24 hours, which were cultured on TSA media. The yields were then put into 100 mL of PBS with a bacterial density of 1010 cfu/mL measured by the McFarland method. Further, it was killed with formalin according to the results of Amrullah et al.39, S. agalactiae and P. fluorescens were inactivated in 1% formalin, while A. hydrophila was inactivated with 0.6%39. Later, stirred and incubated for 24 hours at 4°C. After 24 hours of incubation, a vaccine safety test was carried out using the sterilization method. Finally, the vaccine was diluted at a dose of 107 cfu/mL and was ready to be used for the vaccination of tilapia broodstock.
The vaccine treatments consist of (1) a monovalent vaccine against A. hydrophila (MA), (2) a monovalent vaccine against P. fluorescens (MP), (3) a monovalent vaccine against S. agalactiae (MS), (4) a bivalent vaccine against A. hydrophila, P. fluorescens and (BAP), (5) a bivalent vaccine against A. hydrophila and S. agalactiae (BAS), (6) a bivalent vaccine against P. fluorescens and S. agalactiae (BPS), (7) a polyvalent vaccine against A. hydrophila, P. fluorescens and S. agalactiae (PAPS), and (8) the control, fish injected with PBS solution. However, only the female broodstock was vaccinated.
The vaccination method used was intramuscular (i.m.)40,41 by injecting between the first and second scales of the dorsal fin and was administered at a dose of 0.4 mL/kg of fish (±0.08 mL/fish). After the fish were vaccinated, a booster with the same dose as the initial vaccination was later administered on the 7th day. The fish were anesthetized using MS-222 (Sigma) before injection.
The gonad developmental stage 2 fish post-vaccination were reared using 3×3 m cages and installed in dirt ponds 25×30×1.2 (L×W×D). Furthermore, 20 broodstock were reared per cage, consisting of 15 females and 5 males. The fish were fed with pellets at a dose of 4%/day in the morning, at midday, and in the afternoon. The water was replaced daily at a rate of 5%/day. The fish would spawn after being reared for approximately 4 weeks.
Following vaccinations, the fish’s immune response was observed on the 7th, 14th, 21st, and 28th day by collecting caudal vein blood samples. The immune response parameters were the antibody titer using the direct agglutination method42, total leukocyte9,34,43, phagocytic44,45 and lysozyme activities27,34,45,46.
Random blood sampling from the offspring was conducted on each treatment group on the 10th, 20th, 30th, and 40th day post-hatching period. Serum was collected by grinding 5 offspring in effendorf tube for 5 µL with PBS-tween at a ratio of 4:1. It was then centrifuged at 6000 rpm. Furthermore, the serum in the second layer of the centrifugation result was harvested and stored at 47°C for 30 minutes to inactivate the complements47. It was then stored for agglutination titer and lysozyme activity. The direct agglutination test on both broodstocks and offspring was carried out by adding 25 µL PBS into the microplate from the 1st to 12th wells. A total of 25 µL of test fish serum based on treatment was added to the 1st well (positive control) and 2nd well. Furthermore, multilevel dilutions were carried out starting from the 2nd well to the 11th well, while the 12th well was not added with serum (negative control). Furthermore, 25 µL of whole cell antigen of bacteria A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, P. fluorescens was added to each of the 1st to 12th wells48. The microtiter containing antibodies and antigens was then incubated overnight at room temperature and the agglutinating titer was calculated.
The offspring challenge test was conducted on the 10, 20, 30, and 40 days after hatching. It was carried out by dividing the fish into 7 groups based on the type of vaccine administered plus one unvaccinated. Challenge tests on all treatments were carried out using three types of pathogenic bacteria; A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens. This test was carried out by placing 20 offsprings into containers containing 4 liters of water and then they were immersed for 24 h in water containing pathogenic bacteria at a dose of 2.1×108 cfu/mL according to their relative treatments, each conducted triplicate. To observe the effectiveness of the vaccine, the relative percentage survival (RPS) was calculated49,50 on the 14th day post-challenge test.
In general, the different types of vaccines at each period of post-vaccination had a significant effect (P<0.05) on the broodstock's total leukocyte (Figure 1), and phagocytic activity (Figure 2). The follow-up test showed that the fish vaccinated with PAPS had the highest total leukocyte (7.56–10.70×106 cell/mm3) and phagocytic activity (8.33–19.33%), followed by those vaccinated with bivalent and monovalent vaccines, while the lowest was found in control (total leukocyte was 7.40–7.86×106 cell/mm3, phagocytic activity was 9.00–9.33%).
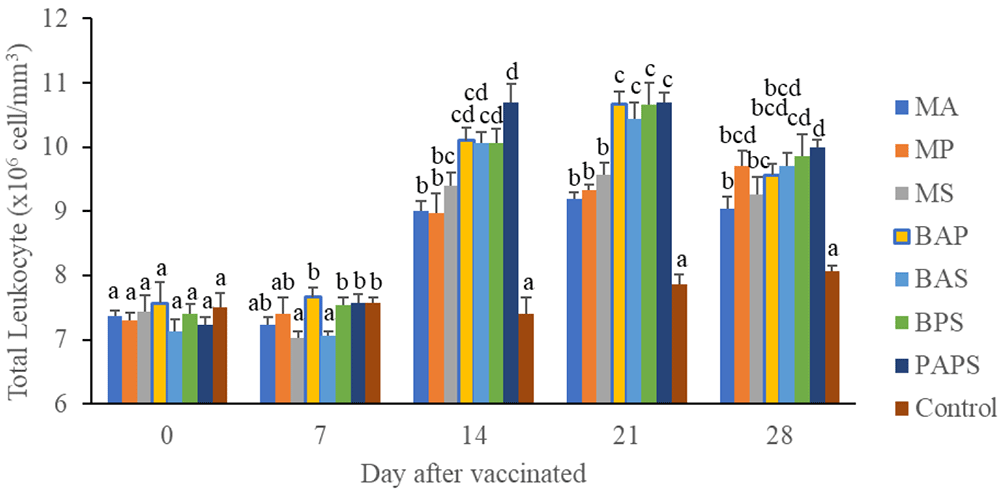
MA: A. hydrophila monovalent, MS: S. agalactiae monovalent, MP: P. fluorescens monovalent, BAS: A. hydrophila and S. agalactiae bivalent, BAP: A. hydrophila and P. fluorescens bivalent, BPS: P. fluorescens and S. agalactiae bivalent, and PAPS: A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens polyvalent vaccines. Values with different superscripts a,b indicate that their corresponding means are significantly different (P<0.05) according to one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s test.
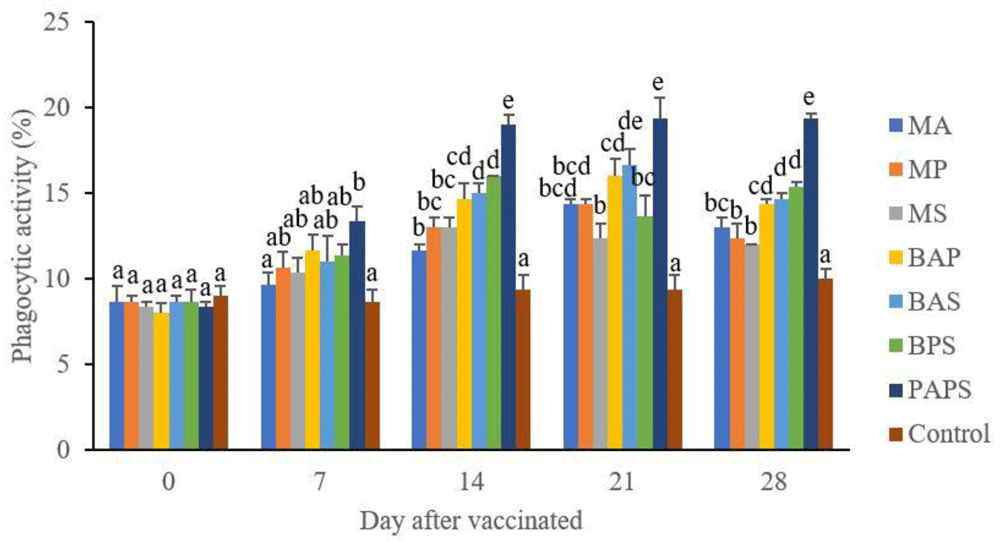
MA: A. hydrophila monovalent, MS: S. agalactiae monovalent, MP: P. fluorescens monovalent, BAS: A. hydrophila and S. agalactiae bivalent, BAP: A. hydrophila and P. fluorescens bivalent, BPS: P. fluorescens and S. agalactiae bivalent, and PAPS: A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens polyvalent vaccines. Values with different superscripts a,b indicate that their corresponding means are significantly different (P<0.05) according to one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s test.
The broodstock’s antibody (Table 1) increased, especially after the booster, except in the unvaccinated fish. After the peak, the broodstock’s immune response remained high up to day 28 even though there was a tendency for it to decrease. All the types of vaccines at each point of time had a significant effect (P<0.05) on the agglutination titer in the broodstock. The Duncan’s follow-up test showed that the vaccinated broodstock had a higher agglutination titer than the unvaccinated fish. Also, the highest significant value was found in the vaccinated fish with PAPS (1.67–6.67), followed by those vaccinated with the bivalent and monovalent vaccines, while the lowest was in the control (1.33–1.67). Offspring from unvaccinated broodstocks have native immunity, hence in the agglutination test occurs agglutination, but it is very low and does not show an increase, and has not been able to control infections.
MA: A. hydrophila monovalent, MS: S. agalactiae monovalent, MP: P. fluorescens monovalent, BAS: A. hydrophila and S. agalactiae bivalent, BAP: A. hydrophila and P. fluorescens bivalent, BPS: P. fluorescens and S. agalactiae bivalent, and PAPS: A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens polyvalent vaccines. Values with different superscripts a,b indicate that their corresponding means are significantly different (P<0.05) according to one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s test.
| Type of vaccine | Agglutination titer (log2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day after vaccinated (day) | |||||
| 0 | 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | |
| MA | 1.67±0.33a | 2.00±0.00a | 3.33±0.33a | 3.67±0.3bc | 3.67±0.33bc |
| MP | 1.67±0.33a | 2.67±0.33a | 3.67±0.33a | 3.33±0.33bc | 3.33±0.33b |
| MS | 1.33±0.33a | 2.33±0.33a | 3.33±0.33a | 3.00±0.00b | 3.33±0.33b |
| BAP | 2.00±0.58a | 2.33±0.33a | 4.33±0.33ab | 4.33±0.33c | 4.67±0.33bc |
| BAS | 1.67±0.33a | 2.33±0.33a | 4.33±0.33ab | 4.33±0.33c | 4.33±0.88bc |
| BPS | 1.67±0.67a | 2.33±0.33a | 4.33±0.33ab | 4.33±0.33c | 5.00±0.58c |
| PAPS | 1.67±0.33a | 3.67±0.33b | 5.33±0.33b | 6.67±0.33d | 6.67±0.33d |
| Control | 1.67±0.33a | 1.67±0.33a | 1.33±0.33a | 1.33±0.33a | 1.67±0.33a |
Based on the effect of the vaccine on the broodstock’s immune response, the agglutination titer in the offspring from the vaccinated broodstock at ages 10, 20, 30, and 40 days was higher than unvaccinated (P<0.05). The follow-up test showed that PAPS was more effective in increasing the agglutination titer in the offspring (6.33–3.00) than the bivalent and monovalent vaccines. The results showed that the administration of vaccines in tilapia broodstock had a significant effect on the maternal immunity transfer to the offsprings that were up to 30 days old (Table 2).
MA: A. hydrophila monovalent, MS: S. agalactiae monovalent, MP: P. fluorescens monovalent, BAS: A. hydrophila and S. agalactiae bivalent, BAP: A. hydrophila and P. fluorescens bivalent, BPS: P. fluorescens and S. agalactiae bivalent, and PAPS: A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens polyvalent vaccines. Values with different superscripts a,b indicate that their corresponding means are significantly different (P<0.05) according to one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s test.
| Type of vaccine | Agglutination titer (log2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day post-hatching (day) | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | |
| MA | 4.00±0.58ab | 3.67±0.33bc | 1.67±0.33a | 1.33±0.33a |
| MP | 4.00±0.00ab | 3.67±0.33bc | 1.67±0.33a | 1.33±0.33a |
| MS | 3.67±0.33b | 3.33±0.33b | 2.33±0.33ab | 1.33±0.33a |
| BAP | 4.67±0.33ab | 4.67±0.33c | 2.33±0.33ab | 1.67±0.33a |
| BAS | 5.00±0.58c | 4.33±0.33bc | 2.33±0.33ab | 1.67±0.33a |
| BPS | 4.33±0.33ab | 4.33±0.33bc | 2.33±0.33ab | 1.33±0.33a |
| PAPS | 6.33±0.33d | 5.67±0.33d | 3.00±0.33b | 1.67±0.33a |
| Control | 1.67±0.33a | 1.67±0.33a | 1.67±0.33a | 1.33±0.33a |
The lysozyme activity of broodstock vaccinated with PAPS (29.87–103.08 U/mL) was higher than other vaccines, and the lowest was in broodstock that was not vaccinated (27.65–33.89 U/mL) (P<0.05) (Figure 3). Generally, the offspring from the broodstock vaccinated with PAPS had a higher lysozyme activity (77.81–43.11 U/mL) than those of other treatments (P<0.05) up to the 30th day, the lowest was in the control (20.29–20.24 U/mL) The results showed that the application of PAPS in tilapia broodstock could increase lysozyme activity transferred to the offsprings (Figure 4).
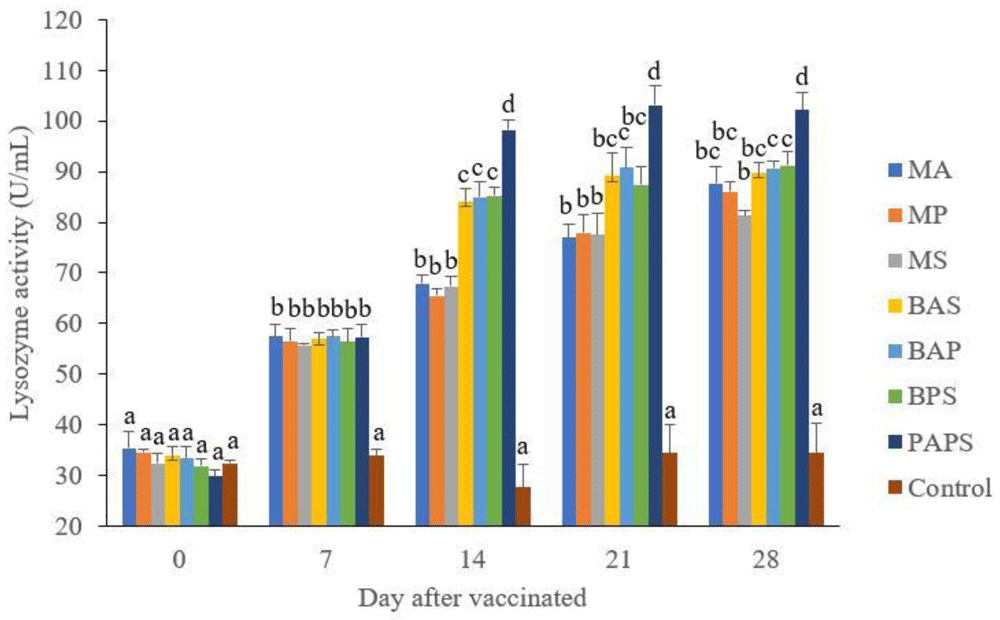
MA: A. hydrophila monovalent, MS: S. agalactiae monovalent, MP: P. fluorescens monovalent, BAS: A. hydrophila and S. agalactiae bivalent, BAP: A. hydrophila and P. fluorescens bivalent, BPS: P. fluorescens and S. agalactiae bivalent, and PAPS: A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens polyvalent vaccines. Values with different superscripts a,b indicate that their corresponding means are significantly different (P<0.05) according to one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s test.
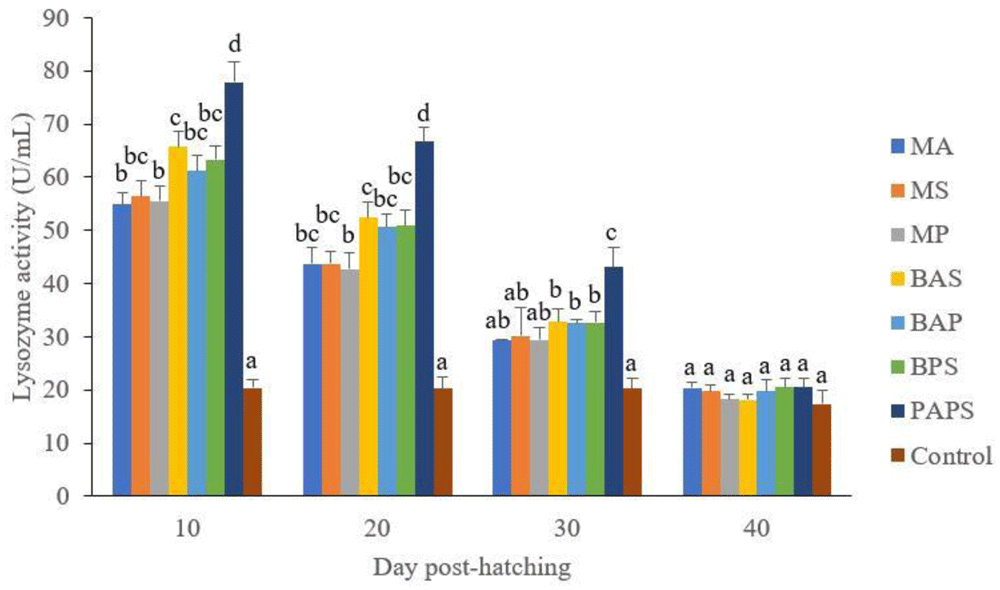
MA: A. hydrophila monovalent, MS: S. agalactiae monovalent, MP: P. fluorescens monovalent, BAS: A. hydrophila and S. agalactiae bivalent, BAP: A. hydrophila and P. fluorescens bivalent, BPS: P. fluorescens and S. agalactiae bivalent, and PAPS: A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens polyvalent vaccines. Values with different superscripts a,b indicate that their corresponding means are significantly different (P<0.05) according to one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s test.
Offsprings that were 10, 20, 30, and 40 days old from the vaccinated broodstock had higher RPS than those from the unvaccinated broodstock after being challenged with bacteria. The offsprings from the broodstock that were vaccinated with PAPS had the highest RPS when challenged with 3 bacteria simultaneously (a combination between A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens) (Table 3) up to day 30. The RPS of the offspring vaccinated with PAPS were 86,11% (10 days old), 78,95% (20 days old) and 56,41% (30 days old). The immune response generated through maternal immunity only lasts up to 30 days and in the end, the immune response will be formed by the body of the offspring itself.
The offspring were produced by broodstock vaccinated with various types of vaccines through intramuscular (i.m.) injection (mean±SE).
Efforts to produce seeds that are immune to several diseases were the best alternative to increasing Nile tilapia production. Furthermore, PAPSs for A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens were able to improve the broodstock’s immune response which was then transferred to the offspring. This process was carried out in order to produce offspring that possess both lysozyme and antibodies and a high survival rate post-challenge test using pathogenic bacteria. This was better than the other treatments that made use of the bivalent and monovalent vaccines.
The results from the observation of the broodstock for 28 days showed that the total leukocyte (Figure 1), phagocytic (Figure 2), antibody titer (Table 1), and lysozyme activity (Figure 3), started to increase in week two post-vaccination. The broodstock vaccinated with PAPS showed a higher increase in the immune response compared to the others that were vaccinated with the bivalent, monovalent vaccines, and was the lowest in the unvaccinated broodstock28,30,33,34,51. This showed that PAPS could increase the Nile tilapia broodstock’s immune response better than the other treatments.
The offspring produced from the broodstock that were vaccinated with PAPS had the highest antibodies (Table 2) and lysozyme activity (Figure 4) up to the 30th day post-hatching period and was the lowest in the offsprings from the unvaccinated broodstock (P<0.05). This demonstrated that their strong immune response was transferred to their offsprings27–29,33,34,52 through the egg yolk53.
The results from the challenge test using pathogenic bacteria (Table 3) showed that the offsprings that were produced using PAPS had a higher RPS compared to those from the offsprings produced from broodstocks that were treated using the monovalent and bivalent vaccines (P<0.05). This further showed that the vaccine treatment had adequately protected the fish from bacterial diseases with an RPS that was greater than 60% up to the 30th day post-hatching period49. RPS of the offspring vaccinated with formalin-inactivated vaccine in this study was higher at same time and lasted longer than the findings of Nurani et al.34 on days 10 and 20, closely similar to the Sukenda et al.18 and Pasaribu et al.54, but higher on day 20. The high RPS in the offspring during the challenge test using pathogenic bacteria in PAPS treatment was due to the broodstock’s high number of leukocytes, phagocytic activity, the amount of antibody, and lysozyme activity transferred to the offsprings for protection against diseases. Meanwhile, in the control (unvaccinated), it only relies on immunity transferred naturally from the broodstock, whereas in the vaccinated broodstock, the offspring also get immunity from the broodstock which is induced by the vaccine. The existence of vaccine induction in the broodstocks can increase the total leukocytes, phagocytic activity, antibodies, and lysozyme activity of the offspring which are higher than the offspring produced from unvaccinated broodstocks. Thus, in the challenge test, the immune response of the vaccinated offspring is sufficient to control bacterial attacks, while the control offspring have not been able to control bacterial attacks. Compared to the Abu-elala et al.33 study, the offspring immune response RPS was higher and could last up to 3 months, whereas in this study, the PAPS RPS vaccine was lower and only lasted up to days 30. Indicating that the role of the maternal immunity-derived polyvalent vaccine can protect the offspring from disease attack up to 30 days of age thus after 40 days of age the seeds only rely on the immune response naturally transferred from the mother or begin to produce their own immune response. The low RPS of the PAPS vaccine therefore requires improvement in the application of the maternal immunity method, such as the use of adjuvants, the use of quality tilapia broodstock, proper nutrition in terms of quality and quantity, and the application of biosecurity in the hatchery33.
The role of leukocytes which consist of neutrophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes, is to infiltrate the infected area for rapid protection55, stimulating the production of antibodies through the recognition of foreign bodies, including vaccines and pathogens during the challenge test in this study. The phagocytic activity occurs during phagocytosis, which involves antibodies and complements during opsonization. Furthermore, the total leukocyte parameter increases in line with other immune responses, such as the antibacterial lysozyme, which triggers the complement system and phagocytic cells56–58. It encourages phagocytosis by activating leukocytes and polymorphonuclear macrophages or through opsonization59. The high number of leukocytes and a large amount of lysozyme in the treatment using PAPS which is similar to an infection by a pathogen indicated the success of PAPS in triggering the fish’s immune system when developing an immune response.
The offsprings produced by the broodstock that were vaccinated with PAPS were protected from infections by A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens. However, the monovalent vaccines only protected the offsprings from one type of bacteria. This is one of the advantages of applying PAPS. The results of this study revealed that the application of PAPS produced broodstock and offspring with better immune responses than the bivalent and monovalent vaccines. Therefore, the development of a polyvalent vaccine is more prudent than that of bivalent or monovalent because of its ability to target more than one species of bacteria31,51,52,60–63. The use of this type of vaccine caused the fish to respond to multiple antigens and form an immune response, thereby making it a strategic method in controlling bacterial diseases commonly found in culture and breeding environments33,34,52,64. Additionally, the application of polyvalent vaccines is more practical than the monovalent containing only one type of antigen. This showed that PAPS provided the most effective protection against diseases caused by pathogenic bacteria that often affect fishes, and thus is an ideal candidate for developing a polyvalent vaccine against bacterial infection.
The results show that the application of the polyvalent vaccine against A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens increased the antibody, lysozyme, total leukocytes, and phagocytic activity in Nile tilapia broodstock which was transferred to their offsprings, leading to a high RPS during the challenge test. Polyvalent vaccines derived from maternal immunity can protect offspring from disease up to 30 days of age. Therefore, it is possible to produce seeds of Nile tilapia that are immune to diseases caused by A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens. This process could be carried out through the vaccination of the broodstocks using a polyvalent vaccine against A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens.
Research using fish in Indonesia has not been regulated and therefore it does not require animal ethics. However, this research has received approval from the Ministry of Education and Culture of the Republic of Indonesia (No.: 004/PL.22.7.1/SP-PG/2019). In addition, this study applies the principle of the International Animal Welfare standards including the assurance of fish welfare during maintenance and the use of drugs during sampling.
OSF: Underlying data for ‘Transfer of maternal immunity using a polyvalent vaccine and offspring protection in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus’. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/cnqdg65
The project contains the following underlying data:
Data on broodstock immune response, offspring immune response, and offspring RPS in tilapia, O. niloticus can be accessed on OSF
Data are available under the terms of the Creative Commons Zero "No rights reserved" data waiver (CC0 1.0 Public domain dedication).
Special gratitude also goes to the Director of Pangkep State Polytechnique of Agriculture, South Sulawesi, Indonesia for allowing the sample analysed in the laboratory.
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Health of Aquaculture Organisms
Is the work clearly and accurately presented and does it cite the current literature?
Yes
Is the study design appropriate and is the work technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of methods and analysis provided to allow replication by others?
Yes
If applicable, is the statistical analysis and its interpretation appropriate?
Yes
Are all the source data underlying the results available to ensure full reproducibility?
Yes
Are the conclusions drawn adequately supported by the results?
Yes
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Health of Aquaculture Organisms
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Aquatic animal health, microbiology
Is the work clearly and accurately presented and does it cite the current literature?
Yes
Is the study design appropriate and is the work technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of methods and analysis provided to allow replication by others?
Yes
If applicable, is the statistical analysis and its interpretation appropriate?
Yes
Are all the source data underlying the results available to ensure full reproducibility?
Yes
Are the conclusions drawn adequately supported by the results?
Yes
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: fish immunology, fish diseases, aquaculture, aquaculture extension
Is the work clearly and accurately presented and does it cite the current literature?
Yes
Is the study design appropriate and is the work technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of methods and analysis provided to allow replication by others?
Partly
If applicable, is the statistical analysis and its interpretation appropriate?
Yes
Are all the source data underlying the results available to ensure full reproducibility?
Yes
Are the conclusions drawn adequately supported by the results?
Yes
References
1. Shirajum Monir M, Yusoff SM, Mohamad A, Ina-Salwany MY: Vaccination of Tilapia against Motile Aeromonas Septicemia: A Review.J Aquat Anim Health. 32 (2): 65-76 PubMed Abstract | Publisher Full TextCompeting Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Aquatic animal health, microbiology
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|
Version 4 (revision) 10 Nov 23 |
read | ||
|
Version 3 (revision) 09 Mar 23 |
read | ||
|
Version 2 (revision) 15 Jun 22 |
read | ||
|
Version 1 24 Sep 21 |
read | read | |
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
I highly appreciate the reviewer's comments and suggestions to improve the quality of the paper. Our responses to comments and suggestions from reviewers ... Continue reading Indriyani Nur, Halu Oleo University, Kendari, Indonesia
I highly appreciate the reviewer's comments and suggestions to improve the quality of the paper. Our responses to comments and suggestions from reviewers can be seen in the table below:
Reviewer
1. Please, describe how to collect eggs after spawning and hatching the eggs
Author
Spawning and hatching of eggs were carried out naturally in ponds (cages), hence there is no post-spawning and hatching egg collection.
Reviewer
2. Please, describe in more detail the agglutination test, such as (1) the serum dilution in each well, (2) how about wells for positive and negative control?
Author
Methods, Broodstock and larvae immune response, Para-2
The direct agglutination test on both broodstocks and offspring was carried out by adding 25 µL PBS into the microplate from the 1st to 12th wells. A total of 25 µL of test fish serum based on treatment was added to the 1st well (positive control) and 2nd well. Furthermore, multilevel dilutions were carried out starting from the 2nd well to the 11th well, while the 12th well was not added with serum (negative control). Furthermore, 25 µL of whole cell antigen of bacteria A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens were added to each of the 1st to 12th wells. The microtiter containing antibodies and antigens was then incubated overnight at room temperature and the agglutinating titer was calculated.
Reviewer
3. Make sure the information/symbol in the legend is the same as what is written in the caption figure or table.
Author
Thanks for the suggestion, we will modify it accordingly.
. Please refer to the results (Figure 1, 2, 3, 4)
Reviewer
4. What are the units for agglutination titer in Tables 1 and 2?
Author
Agglutination titer (log2). Please see the results (Table 1 and Table 2)
Reviewer
5. On the 40th day, the observed parameters in all treatments were not significant, what does that mean for offspring?
Author
6. In the Discussion section (Paragraph 4)
Indicating the role of the Polivalent vaccine derived from maternal immunity can protect the offspring from disease attacks up to 30 days of age thus after the seeds are 40 days old the seeds only rely on the immune response transferred naturally from the mother or begin to produce their immune response.
Reviewer
7. There are several sentences that need to be revised according to the comments on the manuscript.
Is the work clearly and accurately presented and does it cite the current literature?
Author
Thank you for the suggestion, We will correct it accordingly
Reviewer
8. -Abstract, background
For this process to take place, the transfer of maternal
immunity must be implemented.
Author
..........should be..............
Reviewer
9. -Abstract, methods
Nile tilapia broodstock, with an average weight of 203g (±SD 23 g) was injected with a vaccine used as a treatment.
Author
Thanks for the suggestion, we will modify it accordingly.
..........203g (±SD 23)................
Reviewer
10. -Abstract, methods
The broodstock’s immune response
was observed on the 7th, 14th, 21st, and 28th day,
Author
Thank you for the suggestion, We will correct it accordingly (..days..)
Reviewer
11. - Methods, Experimental Animal, Para-1
They were kept in spawning ponds (25X30X1.2 LxWxD)
and fed ad libitum with pellets that
Author
We will correct it accordingly (ad libitum)
Reviewer
12. Methods, Broodstock and larvae immune response, Para-2
Random blood sampling from the offspring was conducted
on each treatment group
(Reviewer: Blood or serum?)
Author
The blood was collected from offspring, In the next stage, the serum will be separated from the blood for the agglutination titer (antibody) test.
Reviewer
13. -Methods, Challenge procedures, Para-1
The offspring challenge test was conducted on the 10, 20, 30,
and 40 days old during the post-hatching period.
Author
Thanks for the suggestion, we will modify it accordingly (after hatching.)
Reviewer
14. -Methods, Challenge procedures, Para-1
This test was carried out by placing 20 offsprings ............water containing pathogenic bacteria at a dose of 2.1×108 cfu/mL............
(Reviewer: Seperately or together?)
Author
Challenge tests were conducted with 3 types of bacteria simultaneously; A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens.
Reviewer
15. -Result,
What is the unit of agglutination titer?
Author
Thanks for the suggestion, we will modify it accordingly
(Agglutination titer, log2)
Reviewer
16. Conclusion
The results show that the application of the polyvalent vaccine against A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens increased the antibody, lysozyme, total leukocytes, and phagocytic activity in Nile tilapia broodstock which was transferred to their offsprings, leading to a high RPS during the challenge test. hingga umur 30 hari. Therefore, it is possible to produce seeds of Nile tilapia that are immune to diseases caused by A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens. This process could be carried out through the vaccination of the broodstocks using a polyvalent vaccine against A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens.
(Reviewer: Can provide protection to offspring for how long?)
Author
Thanks for the suggestion, we will modify it accordingly
.....................Polyvalent vaccines derived from maternal immunity can protect offspring from disease up to 30 days of age. .....................................................
I highly appreciate the reviewer's comments and suggestions to improve the quality of the paper. Our responses to comments and suggestions from reviewers can be seen in the table below:
Reviewer
1. Please, describe how to collect eggs after spawning and hatching the eggs
Author
Spawning and hatching of eggs were carried out naturally in ponds (cages), hence there is no post-spawning and hatching egg collection.
Reviewer
2. Please, describe in more detail the agglutination test, such as (1) the serum dilution in each well, (2) how about wells for positive and negative control?
Author
Methods, Broodstock and larvae immune response, Para-2
The direct agglutination test on both broodstocks and offspring was carried out by adding 25 µL PBS into the microplate from the 1st to 12th wells. A total of 25 µL of test fish serum based on treatment was added to the 1st well (positive control) and 2nd well. Furthermore, multilevel dilutions were carried out starting from the 2nd well to the 11th well, while the 12th well was not added with serum (negative control). Furthermore, 25 µL of whole cell antigen of bacteria A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens were added to each of the 1st to 12th wells. The microtiter containing antibodies and antigens was then incubated overnight at room temperature and the agglutinating titer was calculated.
Reviewer
3. Make sure the information/symbol in the legend is the same as what is written in the caption figure or table.
Author
Thanks for the suggestion, we will modify it accordingly.
. Please refer to the results (Figure 1, 2, 3, 4)
Reviewer
4. What are the units for agglutination titer in Tables 1 and 2?
Author
Agglutination titer (log2). Please see the results (Table 1 and Table 2)
Reviewer
5. On the 40th day, the observed parameters in all treatments were not significant, what does that mean for offspring?
Author
6. In the Discussion section (Paragraph 4)
Indicating the role of the Polivalent vaccine derived from maternal immunity can protect the offspring from disease attacks up to 30 days of age thus after the seeds are 40 days old the seeds only rely on the immune response transferred naturally from the mother or begin to produce their immune response.
Reviewer
7. There are several sentences that need to be revised according to the comments on the manuscript.
Is the work clearly and accurately presented and does it cite the current literature?
Author
Thank you for the suggestion, We will correct it accordingly
Reviewer
8. -Abstract, background
For this process to take place, the transfer of maternal
immunity must be implemented.
Author
..........should be..............
Reviewer
9. -Abstract, methods
Nile tilapia broodstock, with an average weight of 203g (±SD 23 g) was injected with a vaccine used as a treatment.
Author
Thanks for the suggestion, we will modify it accordingly.
..........203g (±SD 23)................
Reviewer
10. -Abstract, methods
The broodstock’s immune response
was observed on the 7th, 14th, 21st, and 28th day,
Author
Thank you for the suggestion, We will correct it accordingly (..days..)
Reviewer
11. - Methods, Experimental Animal, Para-1
They were kept in spawning ponds (25X30X1.2 LxWxD)
and fed ad libitum with pellets that
Author
We will correct it accordingly (ad libitum)
Reviewer
12. Methods, Broodstock and larvae immune response, Para-2
Random blood sampling from the offspring was conducted
on each treatment group
(Reviewer: Blood or serum?)
Author
The blood was collected from offspring, In the next stage, the serum will be separated from the blood for the agglutination titer (antibody) test.
Reviewer
13. -Methods, Challenge procedures, Para-1
The offspring challenge test was conducted on the 10, 20, 30,
and 40 days old during the post-hatching period.
Author
Thanks for the suggestion, we will modify it accordingly (after hatching.)
Reviewer
14. -Methods, Challenge procedures, Para-1
This test was carried out by placing 20 offsprings ............water containing pathogenic bacteria at a dose of 2.1×108 cfu/mL............
(Reviewer: Seperately or together?)
Author
Challenge tests were conducted with 3 types of bacteria simultaneously; A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens.
Reviewer
15. -Result,
What is the unit of agglutination titer?
Author
Thanks for the suggestion, we will modify it accordingly
(Agglutination titer, log2)
Reviewer
16. Conclusion
The results show that the application of the polyvalent vaccine against A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens increased the antibody, lysozyme, total leukocytes, and phagocytic activity in Nile tilapia broodstock which was transferred to their offsprings, leading to a high RPS during the challenge test. hingga umur 30 hari. Therefore, it is possible to produce seeds of Nile tilapia that are immune to diseases caused by A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens. This process could be carried out through the vaccination of the broodstocks using a polyvalent vaccine against A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, and P. fluorescens.
(Reviewer: Can provide protection to offspring for how long?)
Author
Thanks for the suggestion, we will modify it accordingly
.....................Polyvalent vaccines derived from maternal immunity can protect offspring from disease up to 30 days of age. .....................................................