Keywords
Stand-alone PV, Photovoltaic system, Solar cell, MATLAB simulation
This article is included in the Energy gateway.
This article is included in the Solar Fuels and Storage Technologies collection.
Stand-alone PV, Photovoltaic system, Solar cell, MATLAB simulation
The world’s population continues to grow, passing the seven billion mark in 2012.1 With seven billion people on the planet, existing resources for food, housing, universal health care, and carbon-based energy will be severely stretched.2 Developing economically and environmentally viable renewable energy technologies to meet the energy needs of the growing population is perhaps the most important of all the challenges we face.3 Photovoltaic () solar modules generate electrical energy that is highly desirable due to their natural advantages such as environmentally friendly and silent operation, long-term performance, and reliability.4 solar modules must be affordable, highly efficient, and made from readily available, abundant resources to be economically feasible.5 Stand-alone operation islanding system relies heavily on batteries to supply the required amount of electricity.6 Normally, the batteries in these systems are charged during peak solar hours, and the stored energy is used when needed.7 The solar irradiance changes throughout the day, and this irregular pattern affects the output.8 Various forecasting techniques are developed in the literature to calculate solar irradiance.9–13 Recently, Javed et al. applied the stand-alone systems to a hybrid home storage system with a battery and a supercapacitor.6 Since irradiation is irregular during the day, the charge and discharge patterns of a battery change rapidly. This circumstance degrades battery performance, shortens battery life, and increases battery replacement costs.14–16 As shown in Figure 1, a typical stand-alone system includes a generator, a storage battery, a converter, a charge controller, an inverter, alternating current ( and/or direct current (DC) loads, and an attenuation load.17 There is no connection between a stand-alone system and the power grid. A generator usually consists of a generator array composed of multiple modules, each of which consists of numerous solar cells. When the output of the generator exceeds the required demand, the battery stores the excess energy and releases it when the output of the generator is insufficient. The load demand of a islanding system can take various forms, including and/or 18–20 The power conditioning unit serves as an interface between all components of the system, providing control and protection. The converter, the charge controller, and the inverter are the most commonly used components in the power conditioning unit. Additionally, the reducing load is required to absorb any excess energy created when the PV generator’s output exceeds the load requirement and the storage batteries are simultaneously completely charged.
In this study, a stand-alone solar cell was enhanced to better understand the system operation. modeling and simulation were performed using MATLAB software (Version: R2017a, RRID: SCR_001622). In order to determine a regional action plan that can manage different renewable energy techniques, Beccali et al.21 used ELECTRE. Goletsis et al.22 used an energy planning approach to evaluate energy projects. Topcu and Ulengin23 developed energy scenarios based on environmental, economic, physical, political, and other uncontrollable factors. Ribeiro et al.24 developed a multi-criteria decision analysis ranking tool for different scenarios. This classification system is based on technical, economic, environmental, quality of life and labor market factors. The purpose of this research is to model, simulate, and evaluate islanding systems in order to increase the operational efficiency of such systems in different large and simple projects.
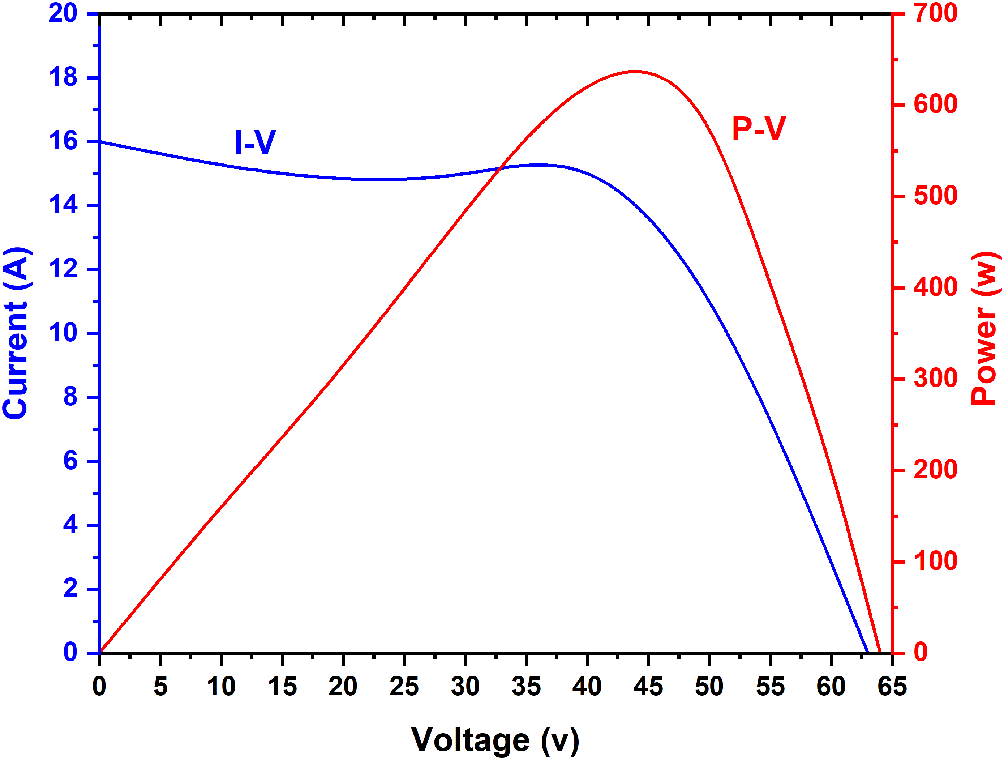
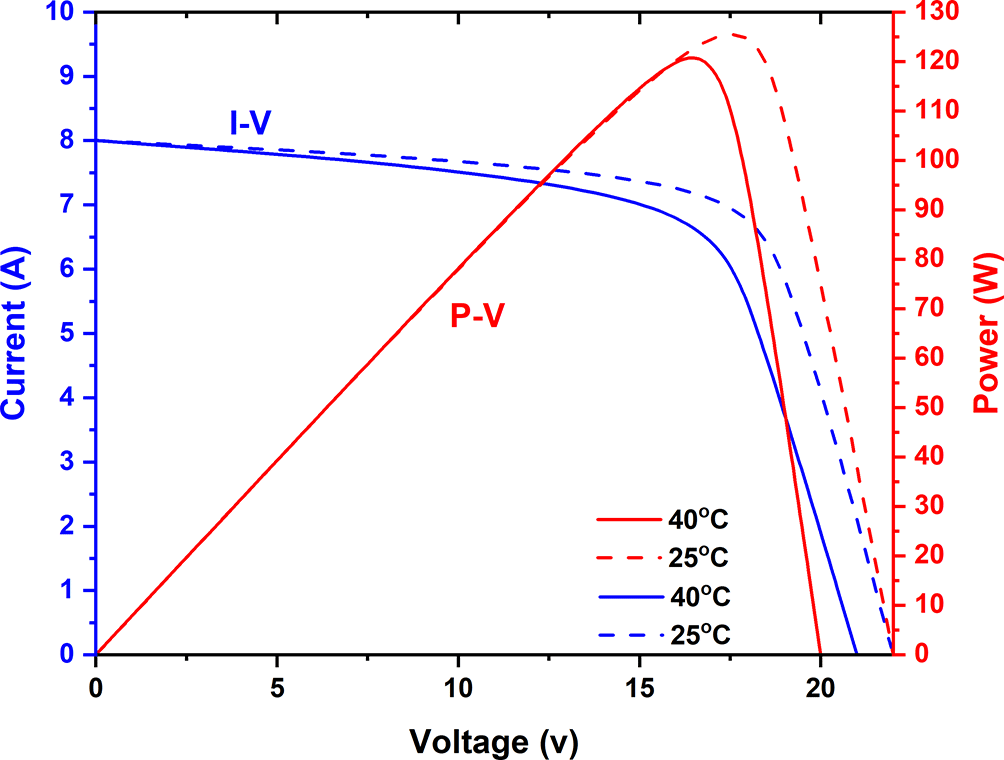
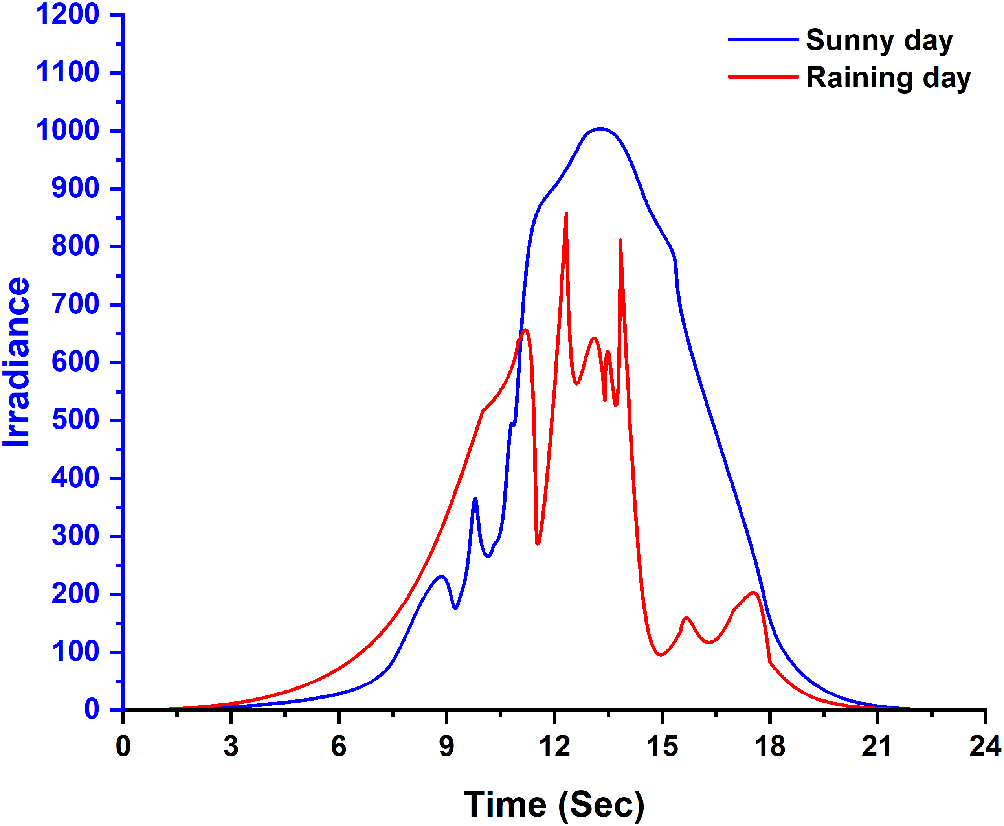
One of the most important tasks to achieve the best design is to decide on the evaluation criteria for building a stand-alone system for a given site.25 In this text, the steps to model a stand-alone system using the MATLAB software of the Simulink portal are explained. At an irradiance of 1000 W/m2, a multi-crystalline system, namely the Kyocera KC130GT, was used with 36 individual cells connected with two bypass diodes to prevent the breakdown and reverse voltage of the system, thus avoiding the generation of a negative voltage (see Figure 2). The terminal voltages of the panel varied, and the P-V and I-V characteristics were measured as in the model in Figure 3. The temperature was set to 25 or 40 °C for the simulation process. The battery is a necessary part of the modelling of the islanding system. Therefore, it is connected to a parallel resistor of 8.64 Ω and a 12 V voltage source. The battery is controlled by a charge controller with pulse width modulation (PWM). The PWM simulation was performed at 5 kHz, an 8.02 A saturation current, and a 21.7 volt voltage at a duty cycle of 0.5 for 1 second. To make the simulation more accurate, solar irradiance data for the city of Baghdad was used for a sunny day and a rainy day on February 2, 2022 and February 5, 2022, respectively. This in turn incorporated the weather effect into the experimental work to be studied by the model system.
In this paper, the electrical energy generated from the used panels was determined, taking into account the losses in power through the entire system. According to the design and simulation in this research, two different weather conditions during February 2, 2022 and February 5, 2022 were used as minimum data to find out the optimal parameters of the system as a home stand alone solar system. This system facilitates the process of calculating the amount of power expected to be supplied to the beneficiary throughout the year under different environmental conditions. In order to achieve the load requirements, the current, voltage, and power characteristics must be studied. The overall I-V and P-V characteristics of the modelled solar array are plotted in Figure 4. The highest values of the resulting power were about 119 and 125 Watts at 25 °C and 40 °C, respectively, as shown in Figure 5. From the characteristics of the I-V and P-V plots, it is possible to understand the dependence of the cell temperature on the material from which the cells are made, including multi-crystalline materials, and how much it is affected mainly by temperature, which in turn is stimulated by the presence of a potential difference applied to its ends. The voltage and current characteristics of the panels have a clear impact on the amount of power produced when using a PWM charge controller. Whereas stand-alone systems operate at 11-14 V, when a PWM charge controller is connected and the battery provides a 12 V operating voltage, hybrid systems operate at 12 V.
By simulating the main components of the stand-alone system, the solar irradiance data were used, as shown in Figure 6. The state of charge of the battery increased during the period 10:00 am–14:00 pm, as shown in Figure 7. The photovoltaic model was equipped with an 8.02 A saturation current and 21.7 volts. During the period of sunny hours, the load consumes part of the power, and the excess is stored in the battery (charging). When the solar radiation was low, it was noticed that the load removed power from the battery. The load would be disconnected from the battery as soon as the charge rate was below 30%. On February 2, 2022 (the sunny day), the state of charge of the applied battery dropped from 75% to 55% as it supplied power to the load. Then the panels were able to supply the loading power with the required energy. In the case of February 5, 2022 (the rainy day), the battery’s state of charge gave the same indication. But the panels were not able to supply the same quantity of the required power because of the lower irradiation amount. As a result, the simulated system performed significantly better during the sunny day conditions. Whereas the battery reached 95% as a maximum value of state of charge at the end of a sunny day, it ended the day at 82%. This was much better than the other day, which reached 58% at the end of the day.
Stand-alone modeling and simulation system with its components were presented using MATLAB and the SIMULINK portal. The simulation proved the effect of the amount of radiation projected and the weather condition on the amount of power generated by the system. The voltage and current characteristics of the panels had a clear impact on the amount of power produced when using a PWM charge controller. The simulated model in this research can be considered a system capable of sensing different conditions with the presence or absence of light at different temperatures. Also, it can be concluded from this research that the optimum size of the system corresponding to the capacity of the battery is a matter that must be taken into account carefully because of its impact on improving the efficiency of the solar system. It is also worth noting that the cost of the stand-alone system modelled in this research is very low. But if this system is implemented in larger projects, the cost will be five times what it was in this research due to the high prices of photovoltaic panels, batteries, and fuel. Finally, monitoring the temperatures, matching the voltage with the appropriate charger controller, and selecting solar panels made of optimal materials can raise the efficiency of the solar system and make it useful in more applications.
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Is the work clearly and accurately presented and does it cite the current literature?
Partly
Is the study design appropriate and is the work technically sound?
Partly
Are sufficient details of methods and analysis provided to allow replication by others?
Partly
If applicable, is the statistical analysis and its interpretation appropriate?
Partly
Are all the source data underlying the results available to ensure full reproducibility?
Partly
Are the conclusions drawn adequately supported by the results?
Partly
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Optimal design and of the standalone PV system, Parameter extraction of the PV models, MOO, and MCDM.
Is the work clearly and accurately presented and does it cite the current literature?
Partly
Is the study design appropriate and is the work technically sound?
Partly
Are sufficient details of methods and analysis provided to allow replication by others?
Partly
If applicable, is the statistical analysis and its interpretation appropriate?
Not applicable
Are all the source data underlying the results available to ensure full reproducibility?
No
Are the conclusions drawn adequately supported by the results?
Partly
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Solar photovoltaic, PV performance analysis, hybrid photovoltaic and thermal collector, solar thermal collector
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
|
Version 2 (revision) 05 Feb 24 |
read | read | ||
|
Version 1 20 Dec 22 |
read | read | ||
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
It is getting boring to read or do analysis based on these data presented here. However, the authors' effort to publish an article is highly appreciated.
It is getting boring to read or do analysis based on these data presented here. However, the authors' effort to publish an article is highly appreciated.