Keywords
Uniprot ID Q9H4F8, SMOC1, SMOC-1, SPARC-related modular calcium binding protein 1, antibody characterization, antibody validation, western blot, immunoprecipitation
This article is included in the YCharOS (Antibody Characterization through Open Science) gateway.
SPARC-related modular calcium-binding protein 1, otherwise known as SMOC-1, is a secreted glycoprotein involved in various cell biological processes including cell-matrix interactions, osteoblast differentiation, embryonic development, and homeostasis. SMOC-1 was found to be elevated in asymptomatic Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patient cortex as well as being enriched in amyloid plaques and in AD patientcerebrospinal fluid, arguing for SMOC-1 as a promising biomarker for AD. Having access to high-quality SMOC-1 antibodies is crucial for the scientific community. It can ensure the consistency and reliability of SMOC-1 research, and further the exploration of its potential as both a therapeutic target or diagnostic marker.. In this study, we characterized seven SMOC-1 commercial antibodies for Western blot and immunoprecipitation, using a standardized experimental protocol based on comparing read-outs in knockout cell lines and isogenic parental controls. We identified successful antibodies in the tested applications and encourage readers to use this report as a guide to select the most appropriate antibody for their specific needs.
Uniprot ID Q9H4F8, SMOC1, SMOC-1, SPARC-related modular calcium binding protein 1, antibody characterization, antibody validation, western blot, immunoprecipitation
To this revised version of the article, the authors have provided an additional description of the YCharOS antibody characterization platform as well as references to the published standardized protocols and feature article that guides readers on how to interpret the characterization data. This background information has been included to the Introduction. Additionally, the authors have indicated, in the figure legends, which secondary antibodies or detection system was used.
See the authors' detailed response to the review by Christian Tiede
The SMOC1 gene encodes the SPARC (secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine)-related calcium-binding protein 1 (SMOC-1), a secreted glycoprotein involved in numerous extracellular processes.1–3 Expressed in various tissues with localization to the basement membrane and extracellular matrix, SMOC-1 regulates cell-matrix interactions through its ability to bind cell-surface receptors, growth factors, extracellular matrix and cytokines.2,4 Through its binding to receptors on the cells surface, SMOC-1 modulates growth factor signalling involved in osteoblast differentiation.5 In addition to being a critical regulator of various biological processes, SMOC-1 plays a role in the pathophysiology of diverse diseases, including cancer development and progression.1
Proteomic studies have uncovered SMOC-1 to be highly enriched in a subpopulation of amyloid plaques, in AD patients and to be elevated in asymptomatic AD cortex.6 Recently, SMOC-1 was shown to be elevated in cerebrospinal fluid from AD patients.7 Although it remains unknown why SMOC-1 co-localizes with only some amyloid plaques, it is hypothesized that SMOC-1 may interact with amyloid-beta (Aβ) species that have been subjected to post-translational modifications.6 More comprehensive research is required to examine the mechanistic role of SMOC-1 in AD.
Mechanistic studies would be greatly facilitated with the availability of high-quality antibodies.
Here we evaluated the performance of seven commercial antibodies for SMOC-1 for use in western blot and immunoprecipitation, enabling biochemical and cellular assessment of SMOC-1 properties and function. The platform for antibody characterization used to carry out this study was endorsed by a committee of industry academic representatives. It consists of identifying human cell lines with adequate target protein expression and the development/contribution of equivalent knockout (KO) cell lines, followed by antibody characterization procedures using most commercially available antibodies against the corresponding protein. The standardized consensus antibody characterization protocols are openly available on Protocol Exchange (DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.pex-2607/v1).8
The authors do not engage in result analysis or offer explicit antibody recommendations. Our primary aim is to deliver top-tier data to the scientific community, grounded in Open Science principles. This empowers experts to interpret the characterization data independently, enabling them to make informed choices regarding the most suitable antibodies for their specific experimental needs. Guidelines on how to interpret antibody characterization data found in this study are featured on the YCharOS gateway.9
Our standard protocol involves comparing readouts from parental and knockout cells.10–14 To identify a cell line that expresses adequate levels of SMOC-1 protein to provide sufficient signal to noise, we examined public proteomics databases, namely PaxDB15 and DepMap.16 HeLa was identified as a suitable cell line and thus HeLa was modified with CRISPR/Cas9 to knockout the corresponding SMOC1 gene (Table 1).
| Institution | Catalog number | RRID (Cellosaurus) | Cell line | Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC | CCL-2 | CVCL_0030 | HeLa | WT |
| Montreal Neurological Institute | - | CVCL_B7DT | HeLa | SMOC1 KO |
SMOC-1 is predicted to be a secreted protein. Accordingly, we collected concentrated culture media from both parental and SMOC1 KO cells and used the conditioned media to probe the performance of the antibodies (Table 2) side-by-side by Western blot and immunoprecipitation. The profiles of the tested antibodies are shown in Figures 1 and 2.
| Company | Catalog number | Lot number | RRID (Antibody Registry) | Clonality | Clone ID | Host | Concentration (μg/μL) | Vendors recommended applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abcam | ab313569** | 3101091230 | AB_29418461 | recombinant-mono | EPR26922-29 | rabbit | 0.50 | Wb, IP, IF |
| Abcam | ab313571** | 3101065175 | AB_29418471 | recombinant-mono | EPR26922-31 | rabbit | 0.50 | WB, IP |
| Abcam | ab200219 | GR3370372-1 | AB_2833001 | polyclonal | - | rabbit | 0.50 | Wb |
| GeneTex | GTX119208 | 40331 | AB_10618293 | polyclonal | - | rabbit | 0.90 | Wb |
| Thermo Fisher Scientific | PA5-31392 | 130141931 | AB_2548866 | polyclonal | - | rabbit | 0.90 | Wb |
| Thermo Fisher Scientific | PA5-113408 | WL3463969 | AB_2868141 | polyclonal | - | rabbit | 3.50 | Wb |
| ABclonal | A20482 | 125410101 | AB_2909795 | polyclonal | - | rabbit | 2.65 | Wb |

HeLa WT and SMOC1 KO were cultured in serum free media, and 30 μg of protein from concentrated culture media were processed for Western blot with the indicated SMOC-1, antibodies. The Ponceau stained transfers of each blot are shown. Peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit was used as the secondary antibody to detect the signal produced. Antibody dilutions were chosen according to the recommendations of the antibody supplier. All antibodies were tested at 1/2000. Predicted band size: 48 kDa. **= recombinant antibody.
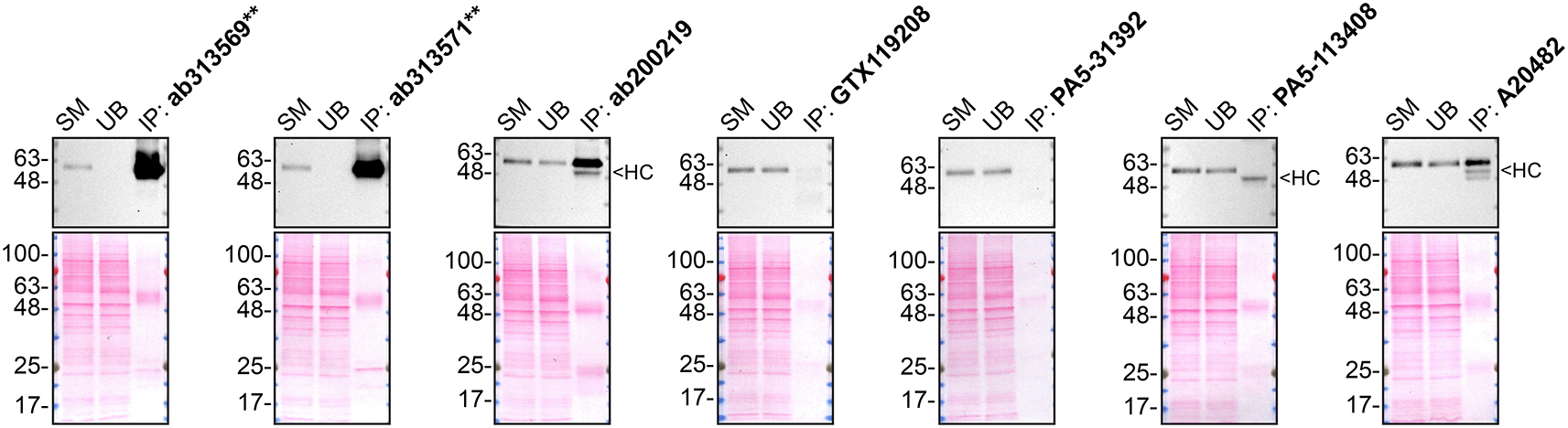
Immunoprecipitation was performed on concentrate culture media from HeLa WT, and using 2.0 μg of the indicated SMOC-1, antibodies pre-coupled to Dynabeads protein A. Samples were washed and processed for Western Blot with the indicated SMOC-1, antibody. For Western blot, ab313569** was used at 1/1000. The Ponceau stained transfers of each blot are shown for similar reasons as in Figure 1. VeriBlot for IP Detection Reagent:HRP was used as a secondary detection system. SM=8% starting material; UB=8% unbound fraction; IP=immunoprecipitated, HC= antibody heavy chain, **= recombinant antibody.
In conclusion, we have screened seven SMOC-1 commercial antibodies by Western blot and immunoprecipitation. Under our standardized experimental conditions, several high-quality antibodies were identified, however, the authors do not engage in result analysis or offer explicit antibody recommendations. A limitation of this study is the use of universal protocols - any conclusions remain relevant within the confines of the experimental setup and cell line used in this study. Our primary aim is to deliver top-tier data to the scientific community, grounded in Open Science principles. This empowers experts to interpret the characterization data independently, enabling them to make informed choices regarding the most suitable antibodies for their specific experimental needs.
The underlying data can be found on Zenodo, an open-access repository.17,18
All SMOC-1, antibodies are listed in Table 2, together with their corresponding Research Resource Identifiers (RRID), to ensure the antibodies are cited properly.19 Peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit is from Thermo Fisher Scientific (cat. number 65-6120).
HeLa SMOC1 KO clone was generated with low passage cells using an open-access protocol available on Zenodo.org. The guide RNA used to knockout the SMOC1 gene is CUCGUAGGACCUGCCAUCAG.
Both HeLa WT and SMOC1 KO cell lines used are listed in Table 1, together with their corresponding RRID, to ensure the cell lines are cited properly.20 Cells were cultured in DMEM high-glucose (GE Healthcare cat. number SH30081.01) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Wisent, cat. number 080450), 2 mM L-glutamate (Wisent cat. number 609065), 100 IU penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Wisent cat. number 450201). Cells were starved in DMEM high-glucose containing L-glutamate and penicillin/streptomycin.
HeLa cells WT and SMOC1 KO were washed three times with PBS 1x and starved for ~18 hrs. Culture media were collected and centrifuged for 10 min at 500 x g to eliminate cells and larger contaminants, then for 10 min at 4500 x g to eliminate smaller contaminants. Culture media were concentrated by centrifuging at 4000 x g for 30 min using Amicon Ultra-15 Centrifugal Filter Units with a membrane NMWL of 10 kDa (MilliporeSigma cat. number UFC901024). Culture media were supplemented with 1x protease inhibitor cocktail mix (MilliporeSigma, cat. number P8340).
Western blots were performed as described in our standard operating procedure.12–14,21 Western blots were performed with precast midi 4-20% Tris-Glycine polyacrylamide gels from Thermo Fisher Scientific (cat. number WXP42012BOX) ran with Tris/Glycine/SDS buffer from Bio-Rad (cat. number 1610772), loaded in Laemmli loading sample buffer from Thermo Fisher Scientific (cat. number AAJ61337AD) and transferred on nitrocellulose membranes. BLUelf prestained protein ladder from GeneDireX (cat. number PM008-0500) was used. Proteins on the blots were visualized with Ponceau S staining (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. number BP103-10) which is scanned to show together with individual Western blot. Blots were blocked with 5% milk for 1 hr, and antibodies were incubated overnight at 4°C with 5% milk in TBS with 0,1% Tween 20 (TBST) (Cell Signalling Technology, cat. number 9997). Following three washes with TBST, the peroxidase conjugated secondary antibody was incubated at a dilution of ~0.2 μg/ml in TBST with 5% milk for 1 hr at room temperature followed by three washes with TBST. Membranes were incubated with Pierce ECL from Thermo Fisher Scientific (cat. number 32106) prior to detection with the iBright™ CL1500 Imaging System from Thermo Fisher Scientific (cat. number A44240).
Immunoprecipitation was performed as described in our standard operating procedure.12–14,22 Antibody-bead conjugates were prepared by adding 2 μg of antibody to 500 μL of Pierce IP Lysis Buffer from Thermo Fisher Scientific (cat. number 87788) in a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube, together with 30 μL of Dynabeads protein A- (for rabbit antibodies) from Thermo Fisher Scientific (cat. number 10002D). Tubes were rocked for ~1 hr at 4°C followed by two washes to remove unbound antibodies.
Starved HeLa WT culture media were concentrated as described above and supplemented with protease inhibitor. 0.3 mL aliquots at 1.6 mg/mL of protein were incubated with an antibody-bead conjugate for ~1 hr at 4°C. The unbound fractions were collected, and beads were subsequently washed three times with 1.0 mL of IP lysis buffer and processed for SDS-PAGE and Western blot on a precast midi 4-20% Tris-Glycine polyacrylamide gels. VeriBlot for IP Detection Reagent:HRP from Abcam (cat. number ab131366) was used as a secondary detection system at a concentration of 0.3 μg/mL.
Zenodo: Antibody Characterization Report for SMOC-1, https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8277962. 17
Zenodo: Dataset for the SPARC-related modular calcium-binding protein 1 (SMOC-1) antibody screening study, https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8253319. 18
Data are available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license (CC-BY 4.0).
We would like to thank the NeuroSGC/YCharOS/EDDU collaborative group for their important contributions to the creation of an open scientific ecosystem of antibody manufacturers and knockout cell line suppliers, for the development of community-agreed protocols, and for their shared ideas, resources and collaboration. Members of the group can be found below.
NeuroSGC/YCharOS/EDDU collaborative group: Riham Ayoubi, Thomas M. Durcan, Aled M. Edwards, Carl Laflamme, Peter S. McPherson, Chetan Raina and Kathleen Southern
Thank you to the Structural Genomics Consortium, a registered charity (no. 1097737), for your support on this project. The Structural Genomics Consortium receives funding from Bayer AG, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, Genome Canada through Ontario Genomics Institute (grant no. OGI-196), the EU and EFPIA through the Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking (EUbOPEN grant no. 875510), Janssen, Merck KGaA (also known as EMD in Canada and the United States), Pfizer and Takeda.
An earlier version of this article can be found on Zenodo (doi: 10.5281/zenodo.8277962).
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: antibody alternative scaffolds, phage display
Is the rationale for creating the dataset(s) clearly described?
Yes
Are the protocols appropriate and is the work technically sound?
Partly
Are sufficient details of methods and materials provided to allow replication by others?
Yes
Are the datasets clearly presented in a useable and accessible format?
Yes
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: antibody alternative scaffolds, phage display
Is the rationale for creating the dataset(s) clearly described?
Yes
Are the protocols appropriate and is the work technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of methods and materials provided to allow replication by others?
Yes
Are the datasets clearly presented in a useable and accessible format?
Yes
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: antibody characterization and validation
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |
|
Version 2 (revision) 05 Sep 24 |
read | |
|
Version 1 06 Oct 23 |
read | read |
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Comments on this article Comments (0)