Keywords
Candidiasis, invasive, pediatric, sinusitis, dacryocystitis
Invasive sino-orbital fungal infection is an uncommon, yet severe condition that predominantly affects individuals with compromised immune systems.
In this study, we report the case of a 5-month-old immunocompetent infant who exhibited persistent dacryocystitis despite receiving broad-spectrum antibiotics. Subsequently, the patient developed ethmoiditis, orbital subperiosteal abscess, and ulceration of the hard palate. Mycological and histological samples were indicative of Candida infections. The patient underwent sinus surgery and surgical debridement, along with antifungal therapy. The treatment was successful, and the follow-up was uneventful for up to 6 months.
To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of invasive sino-orbital candidiasis in an immunocompetent infant with dacryocystitis as the entry point.
This study explores the clinical features, management approaches, and outcomes of this potentially fatal disease.
Candidiasis, invasive, pediatric, sinusitis, dacryocystitis
Invasive sino-orbital fungal infection (ISOFI) is a severe and potentially life-threatening condition in which fungi invade the sinus and orbital regions. Diagnosis can be challenging and often delayed because of the nonspecific nature of the signs and symptoms.
Herein, we report a case of ISOFI originating from dacryocystitis. The patient was a 5-month-old, immunocompetent infant.
To the best of our knowledge, ISOFI has only been reported in immunocompromised patients, and no study has reported it in an immunocompetent pediatric population. This case is unusual because the entry point for the infection was dacryocystitis.
This study investigated the clinical features, management approaches, and outcomes of this potentially fatal disease.
A 5-month-old female with no previous medical history was admitted to our pediatric department with fever, medial canthal purulent discharge, tenderness, and swelling of the left eye (Figure 1). Blood tests showed an elevated white blood cell count and high C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. Initial CT revealed the presence of dacryocystitis. The patient was treated with amoxicillin–clavulanate.
The condition progressed with ongoing fever and, after five days, the emergence of a necrotic ulceration on the palate (Figure 2). A repeat CT scan revealed ethmoiditis and an orbital subperiosteal abscess measuring 16 × 7 mm, with no evidence of bone lysis (Figure 3).
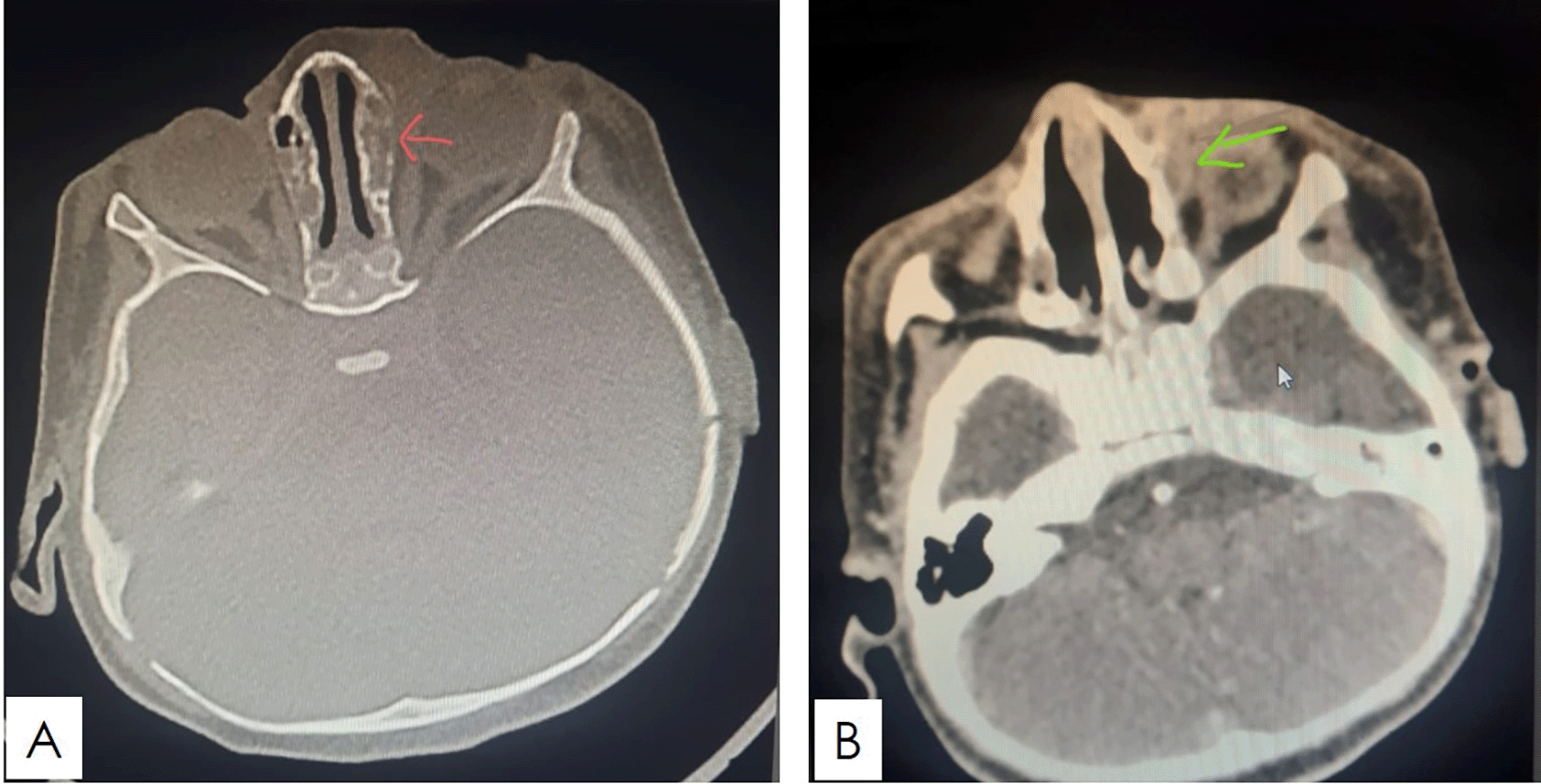
(A) Axial CT scan image demonstrating left ethmoidal sinus opacification. (B) Axial CT scan image showing subperiostal abscess in the medial wall of the left orbit.
A swab of the nasal cavity, palate, and eye discharge was obtained, followed by bacteriological and mycological examinations. Biopsies of the nasal and palatine mucosae were also performed. A biopsy of the palate identified yeast with angioinvasion. Mycological examination of the biopsy samples and eye discharge revealed Candida Tropicalis, which was found to be sensitive to Amphotericin B, Voriconazole, Caspofungin, and Fluconazole. Bacterial analysis of eye discharge revealed Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which was susceptible to high doses of ceftazidime.
In response to these findings, fluconazole was promptly initiated and amoxicillin-clavulanate was replaced with high-dose ceftazidime. The patient underwent urgent surgery, which included drainage of the subperiosteal abscess through external orbitotomy, left ethmoidectomy, and surgical debridement of the ulceronecrotic palatine lesion.
Immunological tests, including complete blood count, HIV serology, nitroblue tetrazolium test, HLA-DR typing, quantitative immunoglobulins (IgG, IgA, IgM), total complement activity, and lymphocyte phenotyping (CD3, CD4, CD45, CD8, B cells, and natural killer cells CD16/CD56) were normal, indicating no underlying immunosuppression.
The patient responded well to the treatment. Fever and inflammatory marker levels resolved within 5 days. The canthal discharge was cleared, and the palatine tissue defect healed after six weeks. A follow-up CT scan three weeks after completing the treatment showed complete resolution of the infection.
Six months after treatment, the patient remained symptom-free.
Only 1.2% of all dacryocystitis cases are caused by fungal agents.1 Aspergillus Niger and Trichosporon, and other fungi have been reported.2,3 However, Candida rarely affects the lacrimal drainage system.2 Most cases occur in immunocompromised patients.4 Cases have also been reported in patients with nasolacrimal stents,1 dacryoliths, and ophthalmic surgery.2 To our knowledge, only two cases of fungal dacryocystitis in the pediatric population have been reported in the literature, both of which are associated with infections caused by Aspergillus Fumigatus and Aspergillus Niger.5 Our case appears to be the first instance of fungal dacryocystitis related to Candida infection in a child. In our case, dacryocystitis was the initial site of invasive fungal infection. Davies et al.5 reported two cases of ISOFI occurring after dacryocystitis. In both cases, the patients were children aged 9–11 years with a history of leukemia under chemotherapy.5 In contrast, our patient was significantly younger (5 months), and investigations did not reveal any immunodeficiencies.
Although rare, ISOFI is most frequently observed in immunocompromised patients.6 However, it is important to consider this diagnosis, especially if there is no improvement with antibiotic treatment even in immunocompetent patients. The diagnosis of ISOFI presents significant challenges because there are no specific clinical or imaging signs. Common symptoms include fever, nasal congestion, crusting, rhinorrhea, and lateral or retro-orbital pain.7,8
Computed tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are crucial for assessing the full extent of the infection and for surgical planning, with some data suggesting that MRI may be more sensitive than CT for diagnosis. CT can reveal bony erosion, sinus opacification, calcifications, mucosal thickening, and orbital cellulitis. MRI outlines the spread of infection through soft tissues, detects abscesses and necrosis, and assesses the impact on surrounding structures while also identifying complications.7,9
Traditional microbiological techniques, light microscopy, and culture methods are generally effective for identifying Candida spp. In some cases, combining different techniques and additional specific tests, such as antigen detection and PCR, can be useful. Sometimes, the simultaneous presence of bacteria in clinical samples might be misleading,8 as in our case, in which we noted the presence of Pseudomonas in the ocular samples. Therefore, biopsies should be repeated as needed to increase the chances of isolating fungi.7,10
A treatment protocol for invasive candidiasis was established by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) in 201611 and the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) in 2012,12 involving initial echinocandin administration followed by a transition to azoles.8,10
The duration of treatment varies across different studies and typically depends on the severity of the disease and presence of underlying comorbidities. In ISOFI, even with timely surgical debridement and adjunct systemic antifungal therapy, the mortality rate remains high, ranging from 50% to 80% (19). Rapid diagnosis, treatment, and better control of the predisposing factors for immunosuppression are essential to improve the mortality rate.10,13
In conclusion, invasive sino-orbital fungal infection is a rare and poorly documented condition, especially in children. There are no specific signs of this pathology, making it essential to consider a fungal origin in severe cases, particularly if there is no improvement with antibiotic treatment. This consideration should also be applied to immunocompetent patients, even though the condition can occur in those with normal immune status. In addition, this case highlights that dacryocystitis can serve as an entry point for this infection.
Early and prolonged treatment, along with surgical intervention, is necessary. Currently, there are no specific treatment guidelines, especially when the fungal agent is Candida, as the available data primarily consists of case reports. Despite treatment, the mortality rate remains high, mainly because of underlying medical comorbidities and delayed diagnosis.
The authors declare that signed consent to publish was obtained from the legal guardian (parent) of the patient regarding the publication of data and findings related to this study.
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Is the background of the case’s history and progression described in sufficient detail?
Yes
Are enough details provided of any physical examination and diagnostic tests, treatment given and outcomes?
Partly
Is sufficient discussion included of the importance of the findings and their relevance to future understanding of disease processes, diagnosis or treatment?
Yes
Is the case presented with sufficient detail to be useful for other practitioners?
Yes
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: mycologist, molecular identification of human pathogenic fungi, antifungal susceptibility testing
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|
Version 2 (revision) 06 Jan 25 |
read | read | read |
|
Version 1 15 Oct 24 |
read | ||
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Comments on this article Comments (0)