Keywords
online system, virtual platform, management, sales, UNDC, Cañete
In today’s business environment, information security and availability are critical to the success of SMEs. This article presents research that addresses the challenges of security and availability of information in sales registration faced by SMEs worldwide. The main objective was to implement a virtual platform for the sales process in SMEs in San Vicente de Cañete, taking into consideration information security standards to preserve user data.
The development of the system was divided into five phases: Initiation, Planning, Implementation, Review and Launch. After implementation, an efficient sales process was achieved, guaranteeing the security and availability of information, and optimising management in an agile and secure manner.
In addition, the virtual platform improves the purchasing experience by allowing the generation of reports and revenue management through a dashboard, promoting the use of information and communication technologies (ICT) in SMEs.
In conclusion, the research implemented a virtual platform for sales in SMEs, ensuring the security and availability of information. It improved management with reports and a control panel, encouraging the use of ICTs in these companies.
online system, virtual platform, management, sales, UNDC, Cañete
In the current context, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are facing an increasingly digitalised landscape, which presents them with challenges in the use and adoption of technology (Ma et al., 2023). Sales management through virtual platforms is becoming imperative for their survival and growth (Pandey et al., 2022). However, this transition brings with it concerns about the security and availability of information, as the proper safeguarding of customer and transaction data is crucial to build trust and avoid vulnerabilities to potential cyber threats in a global environment (Ma & Hu, 2022; Onyekwere et al., 2023; Díaz, 2020a,b). SMEs can use virtual platforms to improve their sales process and provide excellent customer service, reduce sales times and manage revenue and orders through a dashboard (Sanchez, 2019). According to definitions from (Castro et al., 2018; Freire & Rojas, 2018), the sales process is a set of phases from product advertising to final sale. For distribution, hypermarkets offer a basket of goods and services to consumers and at the purchase stage, the consumer chooses a product.
In countries in Asia, America, the Middle East and Europe 74% of companies use online platforms to sell products and services (Olalere & Olanrewaju, 2022; Ore et al., 2020). The most implemented platforms were: Magento, Woocommerce, Shopify, Opencart, Prestashop and Vtex (Huang & Huang, 2020). According to reports from the Lima Chamber of Commerce, 12.3% of 3,000 Peruvians buy products through a virtual platform using credit and debit cards (Fadhil et al., 2020). Studies certify that the implementation of a virtual platform reduces time in the sales process, and (Sanchez, 2019) generates a technological advantage over competitors (Malca, 2021; Hasan et al., 2023). On the other hand, (Freire & Rojas, 2018) believe that the unstable internet connection is a disadvantage of the virtual platform, since, if the web is down, it will cause difficulty in making the sale. In this regard (Cañazaka, 2018; Malca, 2021; Castilla et al., 2023), argues that one of the characteristics of a virtual sales platform is to give the user information about the sale in a classified and organised manner, having a user-friendly interface. The administration of sales revenue should not be complicated, on the contrary, it should be very easy and quick to generate a good impact as an SME.
In this section, research on the same topic is presented in order to make some points of comparison. In Siuna - Nicaragua (Valiente et al., 2022), a sales system was implemented that improved the flow of sales by facilitating and streamlining business tasks. Likewise, in Guayaquil - Ecuador (You et al., 2018), in their research on the use of e-commerce and its profitability in SMEs (Small and Micro Enterprises) obtained as a result, the growth of sales, 67% of companies using e-commerce have been able to exceed their annual sales revenue, demonstrating that virtual platforms offer a benefit to adapt to technological changes. In Balzar - Ecuador (Aguadero, 2022), in his research on a mobile application identified that businesses do not have the capacity to implement new strategies that help to increase sales. On the other hand, in Mexico (Galán & Venegas, 2016) implemented an online platform to evaluate the demand for buying and selling in financial institutions, offering the customer security, efficiency and flexibility. The implementation of these systems brings as positive consequences, ease and convenience to users. To calculate customer satisfaction in a payment process, the CSAT (Customer Satisfaction Score) measurement is used, which consists of a survey that divides the sum of scores and total ratings by 100 units (Zhou, 2022). Coming to a national context, in the department of Tumbes (López, 2018), in his research he showed that a web-based system improves sales and optimises the process of inventory and information control.
In Oman (Ramachandran & Mohammed, 2019) in its article on the challenges of SMEs, it mentions that small and medium enterprises are the main source of income generation, but it has difficulties such as low use of technology, so it does not allow it to keep up with the course of globalisation and lack of knowledge. Similarly in Turkey (Sevinç et al., 2018) in their article on the difficulties during the implementation of Industry 4.0 pointed out that the advancement of technology in SMEs is of great importance because it allows them to be more competitive. Likewise, in Indonesia (Indrawati et al., 2020) in their article on difficulties in the face of technological developments they mentioned that SMEs need technological innovation to perform in front of their competitors. In Ecuador, in their research on online sales, it was found that the pandemic generated by covid-19 caused the cessation of some economic activities, so SMEs were forced to adopt the use of digital media in order to survive in the market (Almendares & Ramos, 2021). In the Piura region (Malpica, 2015), a large percentage of small businesses or SMEs do not have any type of information system to help them in their operational tasks and in monitoring the information they produce. In Lima, cases have been seen in certain enterprises where their activities are carried out in a traditional way, such as registering the sale of products (Redkoborodiy, 2018). In San Vicente, a district in the province of Cañete, the commercial processes of the SMEs are carried out manually, they do not have a product catalogue, they do not register sales, payments and order control. This leads to a loss of customers and therefore to business failure.
It is important to mention that not all SMEs have an optimised sales process, so they resort to complex and slow processes. It was reported that 40.3% of Cañete inhabitants still go to points of sale and only 0.7% make their payments via the web (Shao & Liu, 2020). SMEs do not have a virtual platform to receive the income from the sales of their products, so users have to go in person, queue, follow the precautionary measures by covid-19 or place orders through a delivery service by application. Therefore, this research aims to implement a virtual platform for the sales process in SMEs in San Vicente de Cañete, taking into consideration information security standards to preserve user data. In this way, the virtual platform optimises the sales process to generate a good buying experience for users, and also allows for the generation of reports and the management of income through the dashboard, promoting the use of ICT (Information and Communication Technologies) in SMEs.
Thus, previous studies have found that SMEs worldwide face significant challenges in terms of security and availability of sales record information (Gobin-Rahimbux et al., 2023; Neelakantan & Yadav, 2023; Castilla et al., 2020). However, the technology sector literature lacks solid, correct and up-to-date evidence on specific approaches to address these problems. In this sense, some case studies have shown some progress in the implementation of virtual platforms to improve the sales process in SMEs, but more in-depth and detailed research is required to assess their impact and effectiveness. This paper aims to fill this gap by analysing the development and implementation of a virtual platform for the sales process in SMEs in San Vicente de Cañete, taking into account information security standards. Through a clear methodological approach divided into different phases, it was possible to optimise the sales process, guaranteeing the security and availability of information, and improving the user’s shopping experience. On that, this work demonstrates that the implementation of a secure and efficient virtual platform in the sales process of SMEs can solve the problems identified in the research, allowing an accurate registration of customer data, sales reporting and revenue management in an agile and secure way. Furthermore, it highlights the recommendation to implement additional technologies such as artificial intelligence, ethereum and fingerprint detection, which can bring additional improvements to the sales process. Therefore, the objective of this study is to implement a virtual platform for the sales process in SMEs in San Vicente de Cañete, taking into consideration information security standards to preserve user data. This research contributes to the literature in the technology sector by filling the existing gap and providing valuable information for future studies and practices in the field of virtual platforms and the sales process in SMEs.
The current research is based on the type of applied research, quantitative approach, the design is experimental and its modality is pre-experimental. The population of study is constituted by a set of sales of inputs of two SMEs located in the district of San Vicente de Cañete within a period of 30 days. The technique to be used is observation through a data collection instrument, which will be the observation guide. For the data analysis, the pre-test and post-test will be carried out in the SPSS programme. It is important to note that we have a copyright license that fully authorizes us to use this tool. For the development of the virtual platform, the scrum agile development framework was used, which includes 5 phases: initiation, planning, implementation, review and launch (Triputra & Atqiya, 2021; Sánchez, 2024a,b).
In the Inception phase, the research question was established: How can SMEs improve the sales process through a web platform? This question stems from the context of the pandemic, where users had to go face-to-face to shop, queue, comply with covid-19 and monkeypox protocols or place orders via app-delivery services, which demonstrated the growing need to implement the use of ICTs in people’s daily lives. Subsequently, the development team was established: Product Owner, Scrum Master, Front-End Developers, Back-End Developers and Systems Analyst. Next, the project vision, tasks, dates and backlog were built.
During the planning phase, functional requirements were identified: recording sales with product details, selecting payment method, type of receipt, and non-functional requirements: scalability, integrity, confidentiality and availability. Subsequently, the technologies to be used were defined: JSX (JavaScript XML), JavaScript syntax extensions; SASS (Syntactically Awesome Stylesheets), Cascading Style Language (Sugiantoro et al., 2020); JavaScript and Mysql, and the Izipay payment gateway (www.izipay.pe) was chosen, implementing the BackOffice credentials, which generated a SSL Let’s Encrypt analysing a 3% commission on each sale. The hardware used was a laptop with an AMD Ryzen 5, 11th generation 7-8700 processor, 16GB of RAM with a frequency of 2600 MHz and 520GB of disk storage.
In the implementation phase, a prototype of the system was developed, then the project repository was created on GitHub (https://n9.cl/codespace), then the frontend was coded using JSX 16.8, SASS 1.35.1 and the database architecture using MySQL 8.0.25. The payment gateway BackOffice was then added and linked to the system.
In the review phase, A/B tests were carried out to examine two versions of the product and observe its performance (Li et al., 2020), obtaining feedback from users on the optimisation of the system. Finally, the material was annexed (https://n9.cl/documentation).
In the last phase, called launch, the project was uploaded to hosting (www.bluehosting.pe) with unlimited SSD (Solid State Drive) storage space with x64 architecture database and SSL Let’s Encrypt and SUCURI (www.sucuri.net) was used with WAF (Web Application Firewall) protection and incident response services to determine the security of the system which resulted in low risk, as shown in Figure 1. Figure 2 below shows the flowchart of the system development.
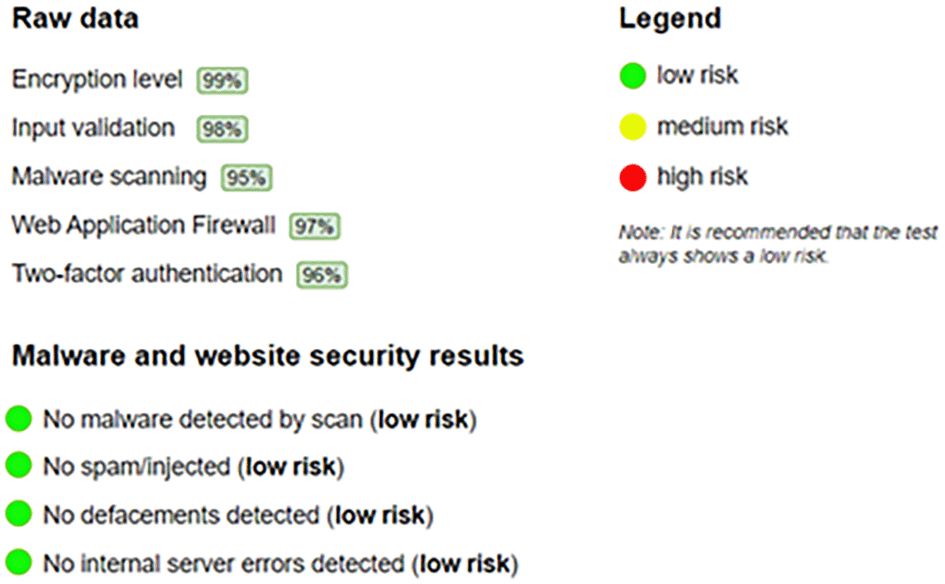
These figures have been reproduced with permission of Sucuri (n.d.).
Figure 3 shows the ’Register Sale’ interface for the shop administrator. In this section, the administrator can register the customer details, products sold, receipt type and payment method to generate the sales receipt. It also provides the ability to identify customers by their ID (Identity Card) number. If an invoice is required, the RUC (Single Taxpayers Register) number can be entered to automatically fill in the company details, reducing customer service time. In addition, if the customer has a seasonal discount code, this can be entered to reduce the total amount payable.
Figure 4 shows the Sales History interface, which allows the administrator to view a summary of sales and details of the products sold. This interface also provides the ability to download the sales receipt in PDF format, email the receipt to the customer, and print the receipt.
Figure 5 shows the ’Sales Report’ interface, which allows the administrator to select a range of dates to search for sales in that period and export them in Excel format. This tool is very useful for making decisions and purchasing according to the monthly demand of the products sold.
Figure 6 shows the ’load product’ interface, which allows the administrator to add new products. To do this, he/she must enter the product search code, which is validated to avoid duplication, as well as the product name and price.
In Figure 3, through the sales register, the virtual platform allowed the administrator to register customer data and products sold, while respecting the security and availability of the information. This is in line with (Díaz, 2020), who states that an online system should provide real-time information 24 hours a day, with automatic reporting. Similarly, (Saranya & Subhashini, 2023) confirms that this system should allow information to be recorded, reducing service time by 67%.
In Figure 4, through the sales history, the virtual platform allowed the administrator to visualise the summary of sales on a monthly basis and the details of the products sold. This is in line with (Hernández et al., 2018) who state that an online platform helps to show the details of sales, reducing delays and increasing the number of customers served. On the other hand, (Chumpitaz & Pachas, 2016) points out that such a platform executes the established parameters by identifying the information recorded by the administrator, optimising the time of customer service.
In Figure 5, through the sales report, the virtual platform allowed the administrator to enter a start and end date to generate an Excel report of daily, monthly, bimonthly and annual sales. This helps top management to make decisions. This is in line with Diaz (Díaz, 2020) where he states that the online platform helps to create customer satisfaction and technological competitiveness in SMEs against competitors. On the other hand (Indrawati et al., 2020; Cañazaka, 2018), point out that such a platform helps to reduce delays in the preparation of reports and optimises the efficiency of searching for information.
In Figure 6, through the product upload, the virtual platform allowed the administrator to add new products, indicating the code, name, category and price, optimising the management of information in the sales process. This is in line with (Palacios, 2016), who points out that in order to manage a platform, it must include CRUD-type operations (create, read, update, delete). Similarly (Cañazaka, 2018), shows that platforms with CRUD-type operations speed up the insertion of new products in the database and reduce the time to assign prices and categories by 85%.
When analysing the existing literature, a similar study was found that focused on the implementation of a virtual platform for the sales process in SMEs, but without a specific focus on the challenges of security and availability of information. This previous research demonstrated improvements in sales process efficiency and customer buying experience (Ojha et al., 2023).
In previous research, a virtual platform was proposed for the sales process in SMEs, focusing mainly on improving operational efficiency and inventory management. While this proposal succeeded in optimising key aspects of the sales process, it did not delve into the security and availability of information, which can be a critical factor for SMEs today (Kim & Kim, 2022).
In contrast, our study distinguishes itself by placing special emphasis on the challenges of security and availability of information in the sales register. The implementation of a secure virtual platform not only optimises the sales process, but also ensures the protection and privacy of customer data, which is essential in a business environment increasingly concerned with information security.
The virtual platform allowed the administrator to register customers’ personal data, products sold, type of voucher, means of payment, generate sales reports, visualise monthly sales and dynamically add new products. It also ensures the availability of information and the responsible use of data, which improves the user experience and increases satisfaction with the company. This solves the problems identified in the research.
It is recommended to implement new technologies such as: artificial intelligence, to have a report of the most sold products; ethereum, to manage cryptocurrencies and create distributed applications for smart sales; fingerprint detector, to make sales automatically with a linked credit card and then send push notifications to the user’s mobile device.
This prospective study focuses on the potential future impact of a virtual platform for the sales process in SMEs. The global implementation of this solution is expected to generate significant improvements in terms of efficiency and security in sales recording, strengthening user confidence through the adoption of information security standards. In addition, it is anticipated that this tool will not only optimise sales management, but also improve the shopping experience for customers by enabling them to access customised reports and facilitate revenue management through an intuitive dashboard. This adoption of information and communication technologies (ICT) will allow SMEs to better adapt to market dynamics and foster their sustainable growth.
In a future scenario, the virtual platform is expected to become an essential tool both in San Vicente de Cañete and in other regions of the world, driving the widespread use of ICTs in the business sector. This will significantly increase the competitiveness of SMEs, enabling them to effectively address the challenges of information security and availability, and in turn contribute to strengthening the global economy through more efficient and secure sales management.
Zenodo: Virtual platform data set to improve sales security, https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10951185 (Sánchez, 2024a).
Data are available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license (CC-BY 4.0).
Sanchez, Kevin & Pacheco, Alex. A virtual platform solution for secure sales registration and management in the retail sector.
Source code available from: https://github.com/KevinSanchez-12/retailSector
Available in the Zenodo repository: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10728633 (Sánchez, 2024b).
License: MIT License
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Comments on this article Comments (0)