Keywords
referential brain, repulsive shifts, attractive shifts, plasticity, visual cortex
referential brain, repulsive shifts, attractive shifts, plasticity, visual cortex
As suggested by the reviewers,we have added an explanation on the role of refractory and repulsive neurons. Moreover, text related to the role of inhibitory neurons in maintaining this recalibration of orientation columns has also been added.
See the authors' detailed response to the review by Jose Fernanado Maya-Vetencourt
See the authors' detailed response to the review by Stanislaw Glazewski
In daily life we use reference points to evaluate and analyse options around. Brain exhibits phenomenal plasticity during youth and even adulthood that helps animals adapt to different experiences (Bachatene et al., 2015b; Dragoi et al., 2001; Hensch, 2005; Kohn, 2007; Turrigiano & Nelson, 2004).
In general, neurons in the brain are selective to certain features. For example, a primary visual neuron (V1) is selective to a range of orientations (Hubel & Wiesel, 1962; Hubel & Wiesel, 1968; Swindale, 1998). Neuronal plasticity can be studied by employing several techniques and protocols (Kohn, 2007; Turrigiano & Nelson, 2004) such as visual deprivation and adaptation. Adaptation refers to the imposition of a non-optimal stimulus (adapter) within neuronal receptive fields for specific periods of time (usually several minutes) to alter their response behaviour (Kohn, 2007). Indeed, using various techniques in different brain areas, the effects of adaptation have been investigated on various neuronal properties such as orientation selectivity (Bachatene et al., 2015b; Dragoi et al., 2000; Gutnisky & Dragoi, 2008; Ghisovan et al., 2009), motion (Kohn & Movshon, 2003), spatial frequency (Bouchard et al., 2008; Marshansky et al., 2011), and contrast (Baccus & Meister, 2002). After adaptation protocol, neurons typically show two types of behavioural shift patterns: attraction and repulsion. An attractive shift is the displacement of a tuning curve toward the adapter following adaptation, whereas a repulsive shift corresponds to the movement of the tuning curve away from the adapter. Some neurons refract the adapter and do not change their selectivity (Jeyabalaratnam et al., 2013).
Interestingly, contingent upon the duration of stimulus, neurons may predominantly shift in one characteristic fashion. For example, a 3-min adaptation (Dragoi et al., 2000) of visual neurons leads to a majority of repulsive shifts, whereas, a prolonged adaptation (> 6 min) potentiates attractive shifts (Bachatene et al., 2015b; Cattan et al., 2014; Ghisovan et al., 2009). Why do some neurons learn and some do not, even though challenged by the same adapter? Does this apply to all the brain regions?
Here we put forth a concept through our recent results on the functional reprogramming of orientation columns in the visual cortex (Bachatene et al., 2015b). In that report, we showed that neurons at the adapted and non-adapted cortical sites exhibited similar pattern of shifts. It is particularly interesting that the non-adapted neurons (not challenged by the adapter) also displayed changes in their orientation selectivity (they exhibited both types of shifts). This is illustrated as an example in Figure 1. The upper row displays a hypothetical layout of orientation columns in control conditions. The activities of nine neurons under observation were recorded simultaneously that were tuned distinctly at each location (neurons at each location are linked by a black triangle; all three sites had non-overlapping receptive fields). After the adaptation procedure, neurons at each site changed their selectivity irrespective of the fact that only neurons tuned to 90° (pre-adaptation, red-columned neurons, middle triangle) were challenged with an adapter (157.5° degree orientation, purple bar). Notably, post-adaptation, two neurons (middle triangle, purple neurons) at the adapted site exhibited an attractive shift whereas one neuron displayed repulsion. In other words, only two neurons learnt the adapter whereas the third neuron swayed away from this behaviour. Interestingly, non-adapted neurons in other columns (left and right triangles) also displayed orientation selectivity shifts following adaptation.
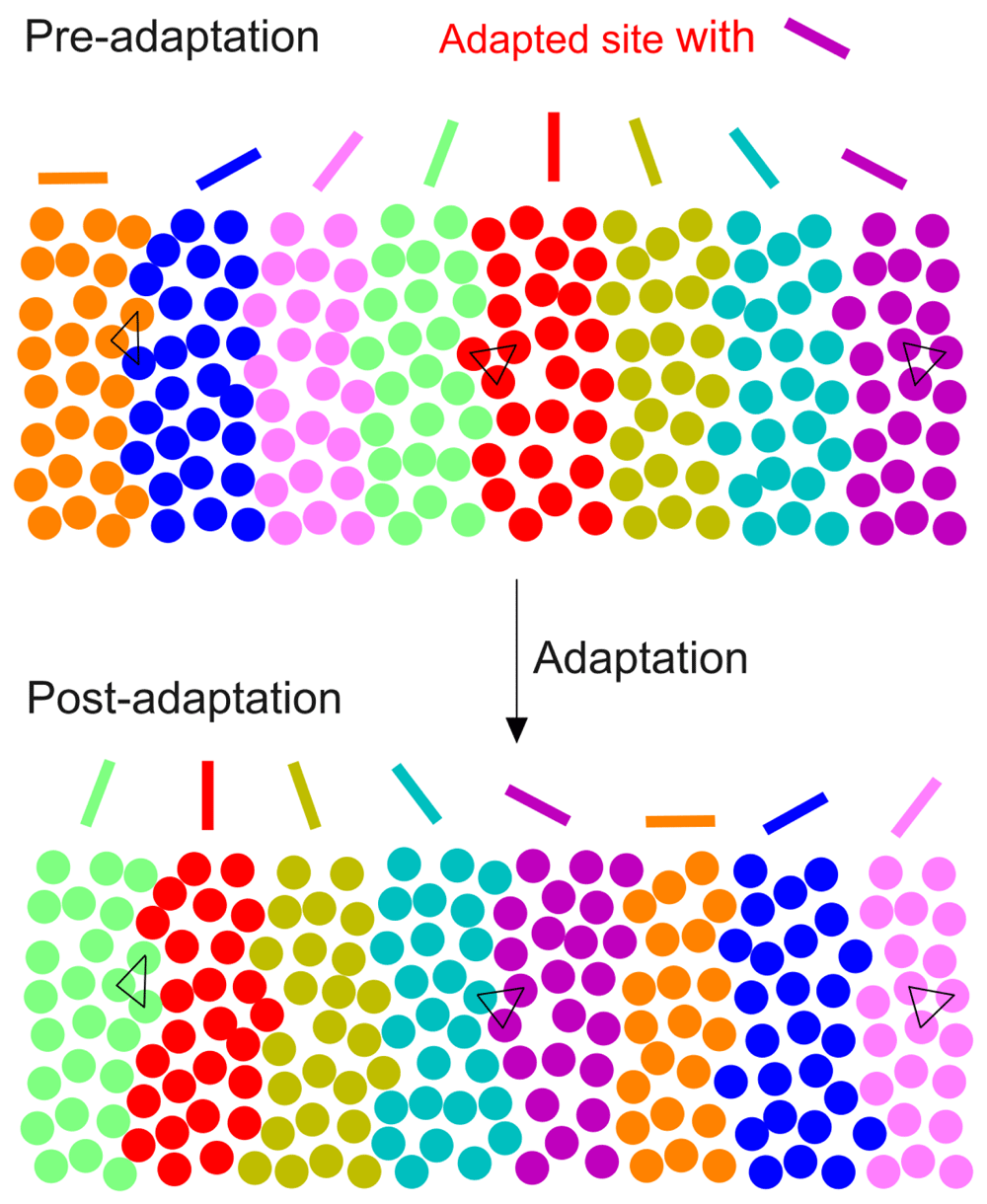
The upper row corresponds to the orientation layout of columns in the control (pre-adaptation) condition. The triangles show three distinct groups of neurons (with non-overlapping receptive fields) under observation within different columns. After an adaptation procedure (neurons in the red column, 90°, are adapted to 157.5°), the orientation layout of the columns is reconfigured (lower row). It is to be underlined that, although only neurons corresponding to 90° column were challenged by an adapter, neurons in other columns (non-adapted) also changed their selectivity. Two out of three neurons at the adapted site changed their selectivity toward the adapter, whereas one neuron shifted its selectivity away from the adapter. The repulsive neurons may have an important role to play in maintaining the functional dogma of orientation processing in the visual cortex. Note: Each colored sphere represents a neuron.
Many reports (Bachatene et al., 2013; Jia et al., 2010; Wertz et al., 2015) have shown and suggested that neuronal dendrites contain synapses corresponding to all the orientations. Within this framework, after a prolonged adaptation, the synapses representing the adapter would strengthen and become active, thus giving rise to a novel selectivity for the neuron. Therefore, new local networks are framed potentiating a changed column. Within this dynamic interplay, most local neurons may wire together and shift their responses in conjunction with each other toward the adapter whereas a minority may deflect away (repulsion) to participate in conservation of the columnar dogma. Few neurons may remain unaffected that are termed refractory neurons. Once this reference is set, other columns would systematically tilt to achieve their ultimate destiny without leaving an orientation hole. Therefore, repulsive neurons have a significantly equal role as attractive neurons to play in organizing principles of functional sensory processing. It has also been shown that putative fast-spiking neurons (inhibitory neurons) also exhibit shifts in their orientation tunings after adaptation protocols (Bachatene et al., 2012; Chanauria et al., 2016). Importantly, the inhibitory neurons which connect and regulate different brain areas (Das & Gilbert, 1995) maybe central to this robust recalibration of columnar organization. The pyramidal cells may first set the selectivity of neurons, wherein the interneurons regulate this selectivity on the local and distal (lateral) levels. Indeed, previous studies have suggested that repulsive neurons maybe implicated in improving the dissociation of different oriented gratings by reducing the response-redundancy of a population of orientation-selective neurons (Dragoi et al., 2000; Hollmann et al., 2015; Müller et al., 1999). Although, repulsive shifts induced by short duration of adaptation (< 3min) durations have been suggested to occur as a consequence of an early mechanism comprising only response depression (Ghisovan et al., 2009). Longer adaptation protocols (> 6 min) may even reverse the direction of these shifts because of a late mechanism involving the response depression followed by response enhancement to the adapter (Ghisovan et al., 2009). Biologically, this implies a homeostatic phenomenon allowing a sensory feature to conserve a basic state that will allow further plastic modifications (Bachatene et al., 2015a; Turrigiano & Nelson, 2004). Thus, the cortical column is reframed with an equal representation of each optimal stimulus.
From the above paradigm, it is suggested that the brain, especially the cortex functions on such organizing principles. In fact, similarly to the visual cortex, distinct functional maps are present in other brain regions too. For example, the auditory cortex may also be functionally reorganized in such fashion (Nahum et al., 2013). Although, neurons are arranged in a salt-and-pepper fashion in lower vertebrates, yet they exhibit selectivity to properties and may also reorganize through similar connectivity principles as higher vertebrates. Therefore, we suggest that neuronal functioning is referential in nature. This eventually facilitates the brain’s ability to modify itself easily (plasticity), to form novel networks, and most importantly, to maintain the functional homeostasis.
VB wrote the manuscript. LB helped with critical remarks and manuscript writing. Both authors agreed to the final content of the article.
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Is the topic of the opinion article discussed accurately in the context of the current literature?
Partly
Are all factual statements correct and adequately supported by citations?
Partly
Are arguments sufficiently supported by evidence from the published literature?
Partly
Are the conclusions drawn balanced and justified on the basis of the presented arguments?
Partly
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Cortical visual physiologist
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|
Version 2 (revision) 28 Feb 17 |
read | ||
|
Version 1 26 May 16 |
read | read | |
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Comments on this article Comments (0)