Keywords
Kidney, biphasic squamoid alveolar renal cell carcinoma, papillary renal cell carcinoma, immunohistochemistry
Kidney, biphasic squamoid alveolar renal cell carcinoma, papillary renal cell carcinoma, immunohistochemistry
The so-called biphasic squamoid alveolar renal cell carcinoma (BSARCC) was described for the first time in 2012 by Petersson et al.1 and has been very recently revisited and fully characterized by Hes et al.2. Histological, immunohistochemical, comparative genomic hybridization and fluorescence in situ hybridization analyses have revealed that BSARCC is a renal neoplasm closely related to papillary renal cell carcinoma (PRCC)2.
The present paper describes a new BSARCC with multifocal presentation that was associated with a conventional clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC). To note, multifocality has not been reported in BSARCC so far.
A 68-year-old man presented with transient hematuria. CT scan revealed multiple tumors on his right kidney, four of them being located at the periphery (Figure 1). Radical nephrectomy was performed. The post-surgery period did not show any clinical complications. The patient was asymptomatic and free of disease at the last contact, 6 months after diagnosis.
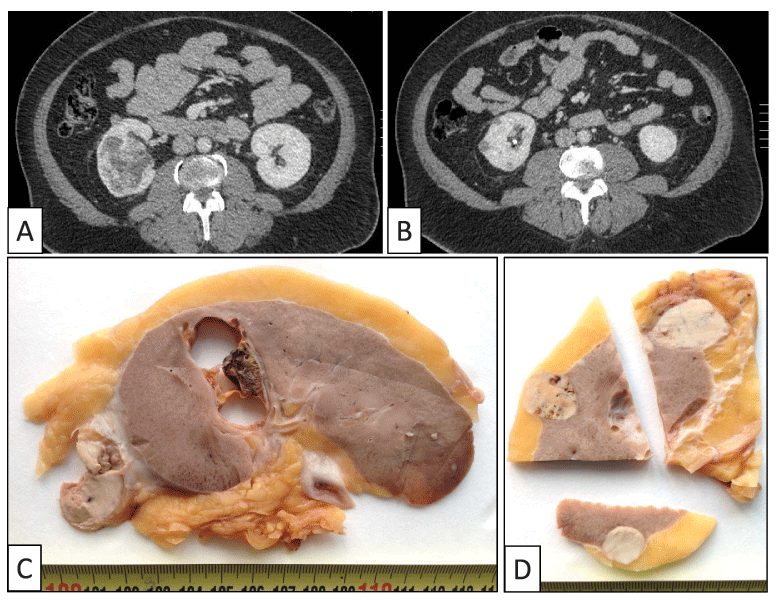
CT scans show multiple tumors in the right kidney (A and B). Gross examination displays a yellowish central tumor with solid-cystic areas corresponding to a clear cell renal cell carcinoma (C) and four peripheral whitish tumors and several intrarenal micronodules corresponding to biphasic squamoid alveolar renal cell carcinomas (C and D).
On gross examination up to five tumors and several small intrarenal micronodules were discovered (Figure 1). Four tumors were subcapsular and showed a whitish homogeneous cut surface, measuring between 1 and 3 cm in diameter. The fifth tumor was centrally located, presented mixed solid and cystic areas with a yellowish cut surface and measured 4.5 cm in diameter.
Histologically, the yellowish central tumor was a conventional organ-confined CCRCC grade 1 (ISUP 2013)3. On low-power view, all the whitish peripheral tumors and the micronodules displayed a similar histology consisting in areas reminiscent to glomerular-like structures (Figure 2 and Figure 3) alternating with others typical of type 1 PRCC. On high magnification, these structures were composed of a single row of small cells with scant cytoplasm displaying an alveolar disposition. The alveoli were filled with cell groups with large cytoplasm and squamoid appearance. True squamous cell differentiation, however, was not observed. Mitosis and necrosis were not seen.
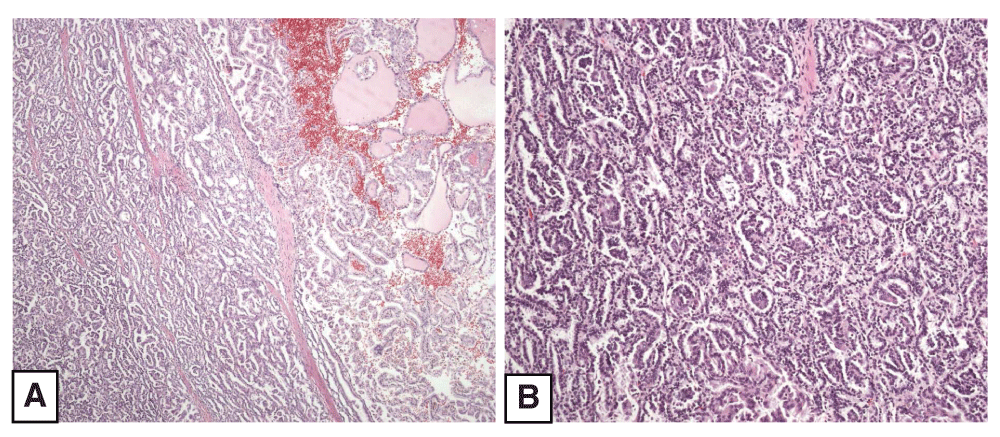
Panoramic view of one of the biphasic squamoid alveolar renal cell carcinomas displaying a conventional type 1 papillary renal cell carcinoma component (A). Alveolar structures filled with large cells are typical of biphasic squamoid alveolar renal cell carcinoma (B).
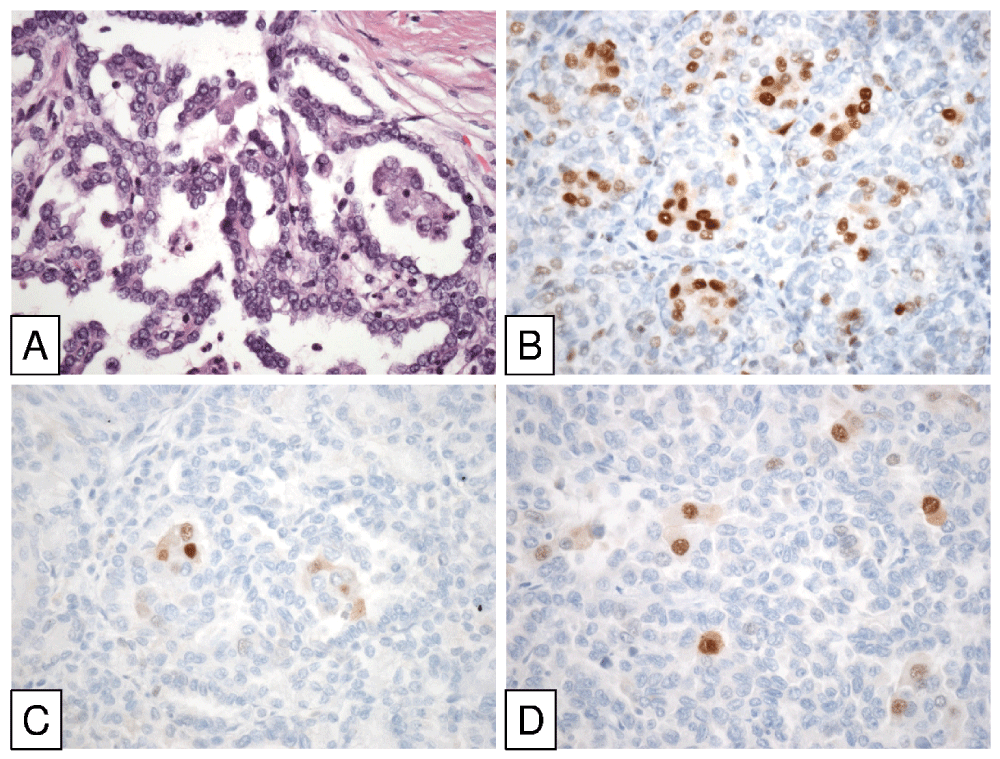
By immunohistochemistry, the tumor was positive with CK7, vimentin, PAX-8, racemase, RCC marker, AE1/AE3, 34βE12, carbonic anhydrase IX, CD10, and cyclin D1. Immunostaining pattern was distinct depending on the cell type. For instance, cyclin D1 and 34βE12 immunostained selectively the squamoid cells whilst RCC marker and carbonic anhydrase IX did it only in small alveoli-forming cells. The rest of the antibodies immunostained both cell types. The tumor was negative with p63 and CK20.
BSARCC is a recently recognized variant of renal carcinoma1,2. Its pathological diagnosis can be suggested on hematoxylin-eosin slides and is based on the recognition of two different cell types arranged in a distinct architecture. Small groups of large cells with abundant cytoplasm and squamoid appearance are surrounded by small cells with scant cytoplasm forming alveolar-like structures. This distinct growth pattern can be more or less evident in different tumor areas and, same as happens in the case here presented, can be combined with areas of conventional PRCC2. The combination of BSARCC and PRCC histologies in almost half of the previously published cases favors the inclusion of this tumor within the broad spectrum of PRCC2. No association of BSARCC with CCRCC, as in the case here presented, has been reported so far.
Morphological diagnostic features of BSARCC can be supported by immunohistochemistry and, if necessary, by genetics. All BSARCC reported to date are positive with cytokeratin 7, epithelial membrane antigen, vimentin and, interestingly, cyclin D1. Cyclin D1 immunostaining is specific of this tumor and helps in its recognition in daily practice. Interestingly, Cyclin D1 immunostaining is restricted to the centrally located squamoid cells. Molecular-genetic data show gains of chromosomes 7 and 17, thus linking BSARCC to PRCC.
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images and/or other details that could potentially reveal the patient’s identity.
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|
Version 2 (revision) 24 May 16 |
read | read | |
|
Version 1 08 Apr 16 |
read | read | read |
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Comments on this article Comments (0)