Keywords
behavior therapy, software, tic disorders, Tourette syndrome, reward
This article is included in the Tics collection.
behavior therapy, software, tic disorders, Tourette syndrome, reward
Recent years have seen increasing evidence for and acceptance of behavior therapies for tic disorders such as Tourette syndrome (Capriotti et al., 2014). Tic suppression plays a key role in these therapies (Specht et al., 2014). One of these is exposure and response prevention (ERP), a first-line treatment for obsessive-compulsive disorder. ERP also showed similar tic reduction efficacy to the most extensively studied behavior therapy for tics in a randomized, controlled trial (Verdellen et al., 2004). However, tic suppression, an essential component of ERP, is difficult or frustrating for some tic patients. Fortunately, we showed that even children with recent-onset tic disorders could suppress tics when brief tic-free periods were rewarded immediately by small tokens (Greene et al., 2015). Our experience with that study, and in an unrelated project, suggested to us that automating the process of immediate rewards for tic-free intervals might facilitate ERP, even in those who at first could suppress tics only for a few seconds at a time (Black et al., 2017; Miller et al., 2015).
Here we present a simple, web-based tool to facilitate training intended to allow increasing periods of tic suppression. Design goals included using this program to record tics, to provide rewards for tic suppression in a video-game-like format that many children would be familiar with, to gradually increase rewards for increasing periods of tic suppression, to respect confidentiality, to gather anonymous information that can be used to assess use patterns and initial information about efficacy and safety, and to provide features that facilitate research use, i.e. creation of research subject accounts that can be assigned to different reward schedules at different points in time.
The system is designed to ensure security of users’ personally identifying information. Instead of recording a name, each user is assigned a simple account ID used to log on. To track the collective age of users and to allow potential individualized training dependent on age, the user is asked his or her birth month and year. However, the system saves only a randomly chosen birthdate within 45 days of the 15th day of the month supplied.
Administrative accounts also can be created. Admins can flag certain users as research participants and assign them to receive rewards differently from regular users. They can also view system and session log files, or create another admin account.
Each user and trainer account has its own text-based account data file on the server. This is a simple way to store modest amounts of data without using a database, at the possible expense of keeping numerous files open simultaneously if traffic to a single site becomes very heavy. System design may need to change if the number of users increases very substantially.
A user’s ID, password, and other account information are sent back and forth as needed between client and server. When a user types his ID and password into the “Manage Account” sign in page, for example, the server sends back a unique web page that includes the credentials, as he/she provided them, and some information loaded from his/her account data. If he/she edits something in his/her account, those same credentials are sent back to the server for authentication along with the new data.
Any page on the website that has information specific to a signed-in user is created dynamically by the server. These dynamic web pages are stored as .dynh files on the server. (“.dynh” is a custom extension which stands for DYNamic Html.) These files have designated locations for the server to inject the required unique fields (usually these include the user’s ID and password) before sending the edited page back to the client. Almost every page involved in a training session is stored and generated this way by the server, so as to preserve the user’s credentials as he/she typed them at the beginning of the session.
During a session, the server mediates between the user and trainer via a session log file. When the trainer records a user’s tic, the trainer’s page sends an XMLHttpRequest asking the server to write a line to the log file. On the other side, the user’s page continually checks the session log file on the server for changes, so it can reset the rewards when the user tics and end the session when the trainer leaves. At the end of a session, the log file is archived with the end time in the filename.
TicTrainer runs on a node.js server. Users need a web browser that supports javascript. The program may not function properly on browsers that do not support HTML5, and currently does not work with Microsoft browsers.
A visitor to TicTrainer first registers an account. User and trainer accounts are created separately. Either one next goes to the “Manage Account” page and links to another account. Specifically, trainers specify the users they train, and users specify the trainers that can train them.
During a session, the trainer is presented with two buttons: “Tic Detected,” and “End Session.” When “Tic Detected” is pressed, the server logs a tic. Trainers also see a 1-minute timer progressing continuously next to an “I’m Here” button, which restarts that timer (as does the “Tic Detected” button). If the trainer presses “End Session,” closes the page, or lets the “I’m Here” timer elapse, the session ends. The timer helps ensure that the trainer stays engaged in watching and recording the user’s tics.
The user’s session page displays a large counter for their current point total, followed by a superscript number indicating the current point accrual rate. Each time the user refrains from ticcing for a number of seconds equal to his/her level, their point total increases by the current rate, and the rate then increases by the square of the current level (rate is capped at 10 × levels2). Finally, a user “levels up” when his/her points exceed 1000 × levels2. He/she then also receives “coins” equal to the square of the previous level. The coins can be traded in for digital medals at an online store. Parents or clinicians may choose to provide tangible rewards for the digital coins or medals. The medals are displayed during training sessions and on the user’s “Manage Account” page. In total, this reward strategy is intended to provide users increasing incentives to suppress their tics for increasingly long intervals.
For potential use in controlled trials, research participant accounts can also be assigned to an alternative (control) reward strategy, noncontingent reward (Greene et al., 2015; Himle et al., 2008). In this case the admin user can set the initial mean frequency of rewards. This frequency may be set based on the participant’s previously recorded tic frequency, to better mask the treatment allocation. Thereafter the frequency of rewards increases automatically based on the subject’s achieved “level,” with the intention of approximately matching reward frequency with the two methods.
Figure 1 shows a “user” window (for the person with tics) and a “trainer” window as they might appear during a session. Normally the two windows would appear on separate devices. This user is currently on level one, with 958 points, and is accruing 5 points for every second during which no tics are detected. This user has not yet earned any coins.
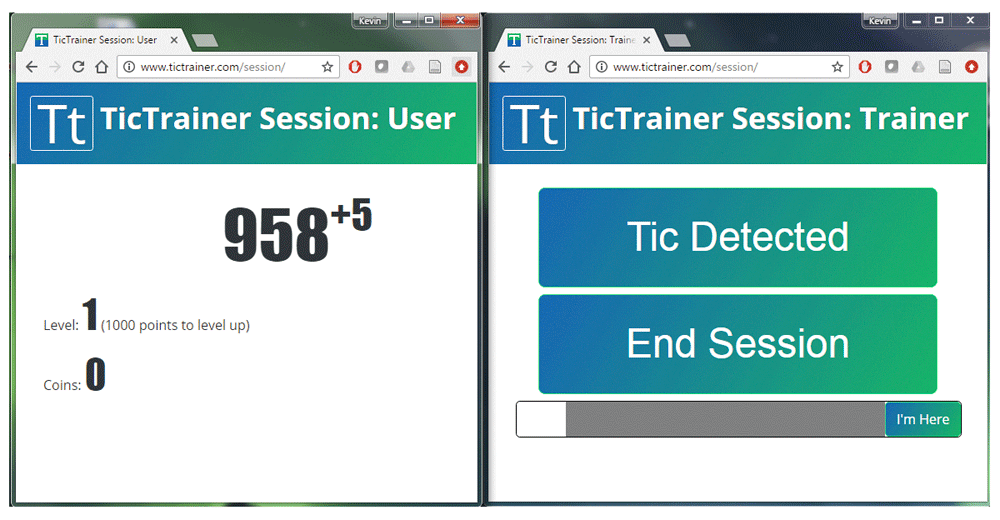
Left: the “user” window (person with tics). Right: the “trainer” window (clinician or other trained observer). Typically the two windows would appear on separate devices.
Supplementary File 1 is a session log file for a test session (no human subjects were observed). Admin users can view or download these session log files, from which they can compute for each session any of the following:
measures of tic frequency and tic suppression, e.g.
number of rewards
other metrics, e.g.
◦ tests of whether inter-tic intervals fit a fractal pattern (Peterson & Leckman, 1998)
◦ tests of the timing of tics vis-à-vis timing of rewards
This simple web-based platform is available at TicTrainer.com, and provides features that allow prospective trials including with different reward schedules. Features that could yet be implemented include adding self-report (and/or trainer-report) measures of inter-session tic severity or of other symptoms, or measures of premonitory sensations/urge intensity before, during or after sessions (Himle et al., 2007; Specht et al., 2014; Verdellen et al., 2008).
TicTrainer available from: https://tictrainer.com/
Source code available from https://github.com/jonkb/TicTrainer-node
Archived source code as at time of publication: http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1098270 (Black, 2017).
License: MIT
Supplementary File 1: Sample regular log file. The log file from a sample training session. This test user account was not flagged for research, so this log file demonstrates the typical reward strategy (differential reinforcement of other behavior, or DRO).
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Is the rationale for developing the new software tool clearly explained?
Yes
Is the description of the software tool technically sound?
Partly
Are sufficient details of the code, methods and analysis (if applicable) provided to allow replication of the software development and its use by others?
Partly
Is sufficient information provided to allow interpretation of the expected output datasets and any results generated using the tool?
Partly
Are the conclusions about the tool and its performance adequately supported by the findings presented in the article?
Partly
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Is the rationale for developing the new software tool clearly explained?
Partly
Is the description of the software tool technically sound?
Partly
Are sufficient details of the code, methods and analysis (if applicable) provided to allow replication of the software development and its use by others?
Partly
Is sufficient information provided to allow interpretation of the expected output datasets and any results generated using the tool?
Partly
Are the conclusions about the tool and its performance adequately supported by the findings presented in the article?
Partly
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Is the rationale for developing the new software tool clearly explained?
Yes
Is the description of the software tool technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of the code, methods and analysis (if applicable) provided to allow replication of the software development and its use by others?
Yes
Is sufficient information provided to allow interpretation of the expected output datasets and any results generated using the tool?
Partly
Are the conclusions about the tool and its performance adequately supported by the findings presented in the article?
Partly
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Tic disorders, behavioral paradigms
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|
Version 2 (revision) 06 Aug 18 |
read | read | read |
|
Version 1 19 Dec 17 |
read | read | read |
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Comments on this article Comments (0)