Keywords
Retroviruses, Mimiviruses, Giant Viruses, anti-FeLV gag, human T cell Leukaemia, Retro-Giant Virus
Retroviruses, Mimiviruses, Giant Viruses, anti-FeLV gag, human T cell Leukaemia, Retro-Giant Virus
This new version of the manuscript contains the Whole Genome Shotgun sequences of a human oncogenic Retro-Giant Virus isolated from human T cell leukaemia (Datasets 4 and 5).
This complete sequence confirms my preliminary findings.
See the authors' detailed response to the review by Didier Raoult
Our previous paper described the presence of unusual Mimiviruses-like structures in human tissues1. Like Mimiviruses (~450 nm giant viruses found in the amoebas), these human structures had the ability to retain Gram staining, and mass spectrometry revealed the presence of histone peptides that had the same footprints as giant viruses2–9. However, the human giant virus-like structures displayed a distinct and unique mammalian retroviral antigenicity.
Our initial discovery in human tissues presented the conundrum of whether the structures were giant viruses with a retroviral nature or cellular components having a viral footprint. The distinction between the virus and the cells was blurred. The most difficult part to explain arose from the unique mammalian retroviral antigenicity associated with the human Mimivirus-like structures.
There was only one possibility to solve the dilemma: isolate the viruses (if really present) and verify if they contain genetic material. Consequently, in the present study we chose the traditional way of isolating virus using a sucrose gradient, following the same protocols and steps described by Prof Robert Gallo in his discovery of the first human retrovirus, human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV)10.
The gigantic dimension of our viral particle excluded it from the orthodox understanding of retroviruses but simultaneously presented the antipodean challenge to establish if this giant virus’s retroviral properties signified the discovery of the first human Retro-Giant virus.
In this manuscript, we report the isolation of a human giant virus, mimivirus-like, with a retroviral core from human T cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, and the various experiments on the purified giant virus, including immunogold electron microscopy, nucleic acid extraction, reverse transcriptase assay, whole genome sequencing and phylogenetic analyses.
The experiments, validated by independent operators kept blind, determined the retroviral nature of a human giant virus with associated viral factory that is ancestral to archetypal retroviruses.
108 human T cell leukaemia (HPB-ALL, DSMZ, Germany), grown at 37°C in RPMI-1640, 10% fetal bovine serum and 2 mM L-glutamine, were centrifuged at 1,500 rpm g for 5 minutes at 4°C. The cell pellet was washed with 1x PBS. The cells were lysed (vortexed) with 2.5 ml PBS in the presence of 25μl of protease inhibitor cocktail (Abmgood, Richmond BC, Canada). Cell suspension was vortexed and incubated a 4°C for 30 minutes. Cell lysis was monitored using a phase contrast light microscope. The resulting crude extract was centrifuged at 3,000 rpm for 5 minutes. The pellet containing the cellular nuclei was discharged.
The resulting supernatant was collected and slowly dripped over 9 ml of a 35-30-25% sucrose gradient (Sigma, Milan, Italy) and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 5 h in a 15 ml Corex glass centrifuge tubes (Fisher Scientific, Dublin, Ireland). Once a visible white disk, corresponding to 25% sucrose fraction, was observed, the viral pellet was collected after centrifugation at 14,000 rpm for 30 min, at 4°C.
The viral pellet was lysed with 1ml of RNA-XPress Reagent (Himedia, Mumbai, India), a monophasic solution of phenol-guanidine thiocyanate, and incubated at room temperature (RT) for 5 minutes. This was followed by the addition of 200 µL chloroform, vortexing for 15 sec and incubation at RT for 10 min. The organic and aqueous phases were separated by centrifuging the sample at 11,000 rpm for 15 minutes at 4°C. The aqueous phase, containing RNA, was harvested and precipitated with 600 μl of isopropyl alcohol and glycogen. After incubation for 1h at 20°C, RNA was pelleted by centrifugation at 11,000 rpm for 10 minutes. The RNA pellet was washed with 75% of ethanol, air dried and resuspended in RNase free H2O (Himedia). One aliquot was utilized for concentration determination in a MaestroNano Spectrophotometer (Maestrogen Inc, Hsinchu City, Taiwan).
1 μg of total RNA was utilized for cDNA synthesis using EasyScript cDNA Synthesis Kit (Abmgood) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, 20 μl of reaction contained 200 units of reverse transcriptase, 0.5 μM of random primers, 20 units of ribonuclease inhibitors, 500 μM dNTP. The reaction was carried out at 25°C for 10 min, then at 42°C for 50 min.
We performed a Pan-retrovirus PCR from the RNA extracted from the giant viruses. To amplify a segment of the Pol gene, we used degenerate primers targeting a conserved region, of approximately 140bp, between the most conserved domain VLPQG and YMDD in the Pol gene of retroviruses. The oligonucleotide primers and conditions were derived from those described by Tuke et al.11. The first PCR mixture was performed by amplifying 1 μl of the double-stranded cDNA reaction with the following reagents: 1 μM primer PAN-UO (5’-CTT GGATCCTGGAAAGTGCTAAGCCCAC-3’) and 1μΜ primer PAN-D1 (5’-CTCAAGCTTCAG CGATGGTCATCCATCGTA-3’) with 1.25 unit of thermostable DNA polymerase (Precision DNA Polymerase, Abmgood). The above mixture was brought to a final volume of 25μl with a PCR mix (Abmgood, Richmond, BC, Canada) containing 0.2 mM dNTPs/2.0mM MgCl2 in 1X PCR reaction buffer. The PCR was performed in a Thermal Cycler (GET3X Triple Block Thermal Cycler, Bio-Gener, China) using the following conditions: 1 cycle of 95°C for 10 minutes; 35 cycles of 95°C for 1 minute, 34°C for 1 minute, 72°C for 1 minute; 1 cycle of 72°C for 10 minutes.
In total, 1 μl of this reaction was re-amplified in a semi-nested reaction using the PAN-UI (5’ CTTGGATCCAGTGTCTAGCCCACAAGGG-3’) primer in combination with PAN-D1. Conditions for the semi-nested PCR were: 1 cycle of 10 minutes at 95°C; 40 cycles of 95°C for 1 minute, 45°C for 30 seconds, 72°C for 1 minute; 1 cycle of 72°C for 10 minutes.
A 10-μl aliquot of the resulting PCR product was analyzed after electrophoresis on a 2.5% MS8 agarose gel (Laboratorios Conda, Madrid, Spain). The amplified bands were recovered from the gel with UltraPrep Agarose Gel Extraction Kit (AHN Biotechnologie GmbH, Nordhausen, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, the DNA was excised from the agarose gel and weighted. Three volumes of buffer (volume: weight of the excised gel band size) was added and the mixture was incubated at 50°C for 10 minutes. The DNA was bound to a column and centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 1 minute. After awash with 700 µl of washing buffer, the DNA was recovered from the column with 50 µl of elution buffer.
DNA sequencing was performed on an ABI 3500 Automatic Sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) using Big Dye Terminator v3.1 (Applied Biosystems).
Molecular phylogenetic analyses were made at BMR Genomics Institute (Padua, Italy). Our sequences were aligned against other retroviral viral sequences. Sequence accession numbers used in the alignment between 150 bp segment from retro- giant viruses with equivalent VPLP—YMDD Polregion (RT) of different retroviruses, amplified with the same Pan Retrovirus-PCR, are reported in Dataset 112. For the phylogenetic analysis of the 400 bp amplicon, retroviral sequences and accession numbers are displayed in Dataset 213.
Phylogenetic tree for the 150bp VLPQ-YMDD interval was made using Phylogeny.fr (A La Carte Mode). T-Coffee was used for multiple alignment, Gblocks v 0.91b for alignment curation, PhyML 3.1 for phylogeny and TreeDyn 198.3 for tree drawing. A non-parametric, Shimodaira-Hasegawa-like approximate Likelihood-Ratio branch test (SH-like aLTR) was used as a statistical test.
For the 400 bp amplicon, phylogenetic tree was made using Phylogeny.fr. Muscle v3.8.31 was used for multiple alignment, Gblocks v 0.91b for alignment curation, PhyML 3.1 for phylogeny and TreeDyn 198.3 for tree drawing. A non-parametric, Shimodaira-Hasegawa-like approximate Likelihood-Ratio branch test (SH-like aLTR), default HKY85, was used as a statistical test.
25 μl of the 25% sucrose isolated viral pellet was placed on Holey Carbon film on Nickel 400 mesh. The grids were treated for 30 minutes at room temperature with the primary monoclonal antibody (moAb) anti-Feline Laeukemia Virus p27gag (catalog number, PF12J-10A; Custom Monoclonals International, West Sacramento, CA, USA) and subsequently with a secondary anti-mouse gold conjugated antibody (BB international anti-mouse IgG 15 nm gold conjugate; catalog number, EM.GMHL15, Batch 4838). After staining with 1% uranyl acetate, the sample was observed with a Tecnai G2 (FEI) (Thermo Fisher) transmission electron microscope, operating at 100 kV. Images were captured with a Veleta (Olympus Soft Imaging System) digital camera.
After sucrose gradient isolation, the viral pellet was lysed in 20 μl of 20 mM Tris-HCL pH7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM EDTA, 1mM DTT, 50% (v/v) glicerol, 0.25% Triton X-100 (Sigma). To test the ability of the human giant viruses to retro-transcribe, 10 μl of the viral lysate, instead of a reverse transcriptase enzyme, were used to retro-transcribe 1 μg of total RNA from Human Liver Total RNA (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The reverse transcriptase reaction for the viral pellet was carried out with random primers using a commercial kit (EasyScript cDNA Synthesis kit; Abmgood), deprived of the supplied reverse transcriptase enzyme. The reverse transcriptase reaction was carried at 25°C for 10 minutes, then at 42°C for 50 minutes. The reaction was stopped by heating at 85°C for 5 minutes. The viral reverse transcriptase activity was compared to positive controls where a commercial RT enzyme was included (EasyScript RTase; Amgood).
After the reverse transcription, 2 μl of the obtained single stranded cDNA was further amplified in presence of 10 pmol of primers for GAPDH, 1.25 units of thermostable DNA polymerase (Precision DNA Polymerase; Abmgood), 0.2 mM dNTPs/2.0 mM MgCl2 in 1X PCR buffer in a final volume of 25μl. PCR conditions were: 1 cycle of 95°C for 5 minutes; 40 cycles of 94°C for 1 minute, 58°C for 1 minute, 72°C for 1 minute; 1 cycle of 72°C for 5 minutes. 20 μl of the PCR reaction was loaded on a 1% agarose gel for electrophoresis.
Sequencing and bioinformatics analysis were performed by Genomix4Life (University of Salerno). In detail, the libraries were prepared using DNA as starting material, with Nextera flex Kit (Illumina Inc). Libraries were sequenced (paired-end, 2 × 75 cycles) on NextSeq platform (Illumina Inc.) Fastq underwent Quality Control using FastQC tool. De novo assembly was performed using Geneious (version 11.1) software. The assembler was used with standard parameters. Blast2Go was used to perform the blast alignment sequences. Annotation with respect to the NCBI Viruses database (taxa 10239) was made through Gene Ontology. The algorithm used was blastx-fast and the statistical significance threshold for reporting matches against a sequence viruses database was set 1.0E-3. The number of sequence alignments to retrieve was set to 20. The other parameters was set as default. All statistical values regarding assembled contigs were computed using QUAST (QUAlity Assessment Tool).
Giant viral particles, isolated from human T cell leukemia (HPB-ALL) cells, formed a white ring on 25% of sucrose gradient. Only the 25% fraction was collected. This fraction was pure and did not contain any contamination such as cellular nuclei; the nuclear fraction was discharged in the first step of differential centrifugation, before layering onto the sucrose gradient.
EM immunogold of the viral pellet depicted giant viral particles (~400nm) that were specifically marked by an anti-Feline Leukaemia virus core p27 gag moAb (Figure 1A). The purified human giant viruses retained the Gram stain, like Mimiviruses in amoebas (Figure 1B). In some micrographs, the predominant 400 nm viral particles are ‘budding’ around a much larger giant particle that also displays the retroviral antigens. This suggests a possible reproduction of the Retro-Giant viruses that strongly recalls the archaea features.
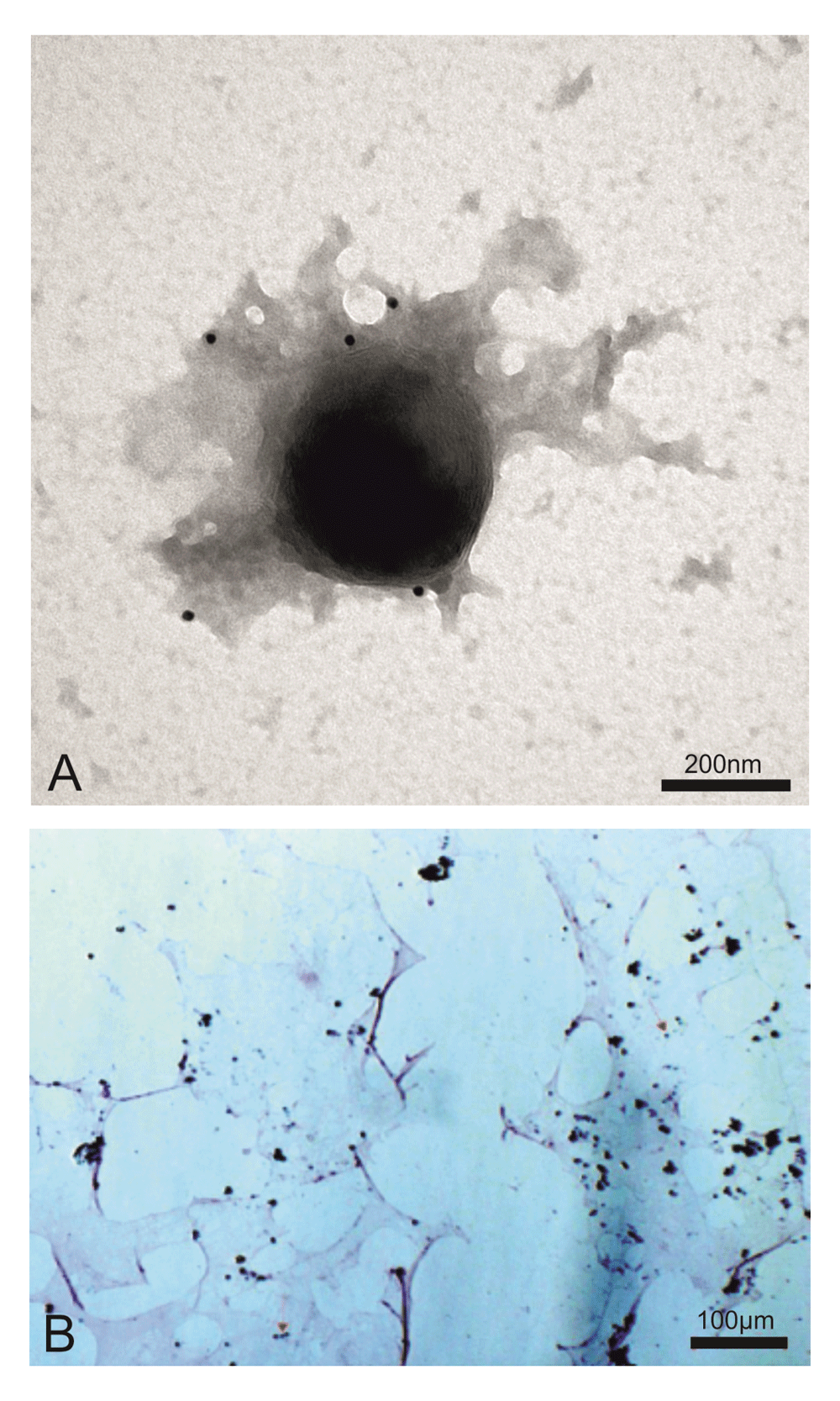
(A) Electron microscopy immunogold shows a ~400 nm giant virus isolated from human T cell leukemia marked with anti-FeLV p27gag moAb (picture representative of 100 repeats). (B) The same viral pellet during Gram staining shows blue granules that diagnose giant viruses (red arrows indicate some of these, but blue granules can be seen all over the slide). Mimiviruses (giant viruses) were first discovered in the amoebas. The amoebas had Gram positive granules that proved to not be bacteria but giant viruses, mimicking microbes. In the previous manuscript1, we showed the presence in human cells of Gram positive giant viral particles associated with viral factories, both sharing the retroviral antigenicity. The viral factories are located inside the cells. What we are presenting here are giant viral particles isolated from human T cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by sucrose gradient. This human giant virus differs from amoebas’s giant viruses in that it displays the properties of classical retroviruses.
The human giant particles contained retroviral RNA. Identification of the retroviral sequences, extracted from the isolated giant viral particles, was accomplished by PCR with degenerate primers targeting a mostly highly conserved sequence in the reverse transcriptase gene of retroviruses, between two conserved domains VLPQG and YMDD. This amplification approach with degenerate primers was initially described by Tuke et al. and it is called Pan-retrovirus PCR11. This PCR system has the ability to detect a ~140 bp amplicon of the Pol gene across many different retroviruses. HIV-1, HTLV-1, Simian D type virus Mason Pfizer monkey virus, Moloney murine leukaemia virus, HERV-W, ERV9 and unknown lymphoma associated retroviruses have been successfully detected with this approach14–16. The principles of the technique and the primers are illustrated in Figure 2. We performed the Pan–retrovirus -PCR experiments exclusively on sucrose gradient purified giant viruses that were first examined using EM immunogold.
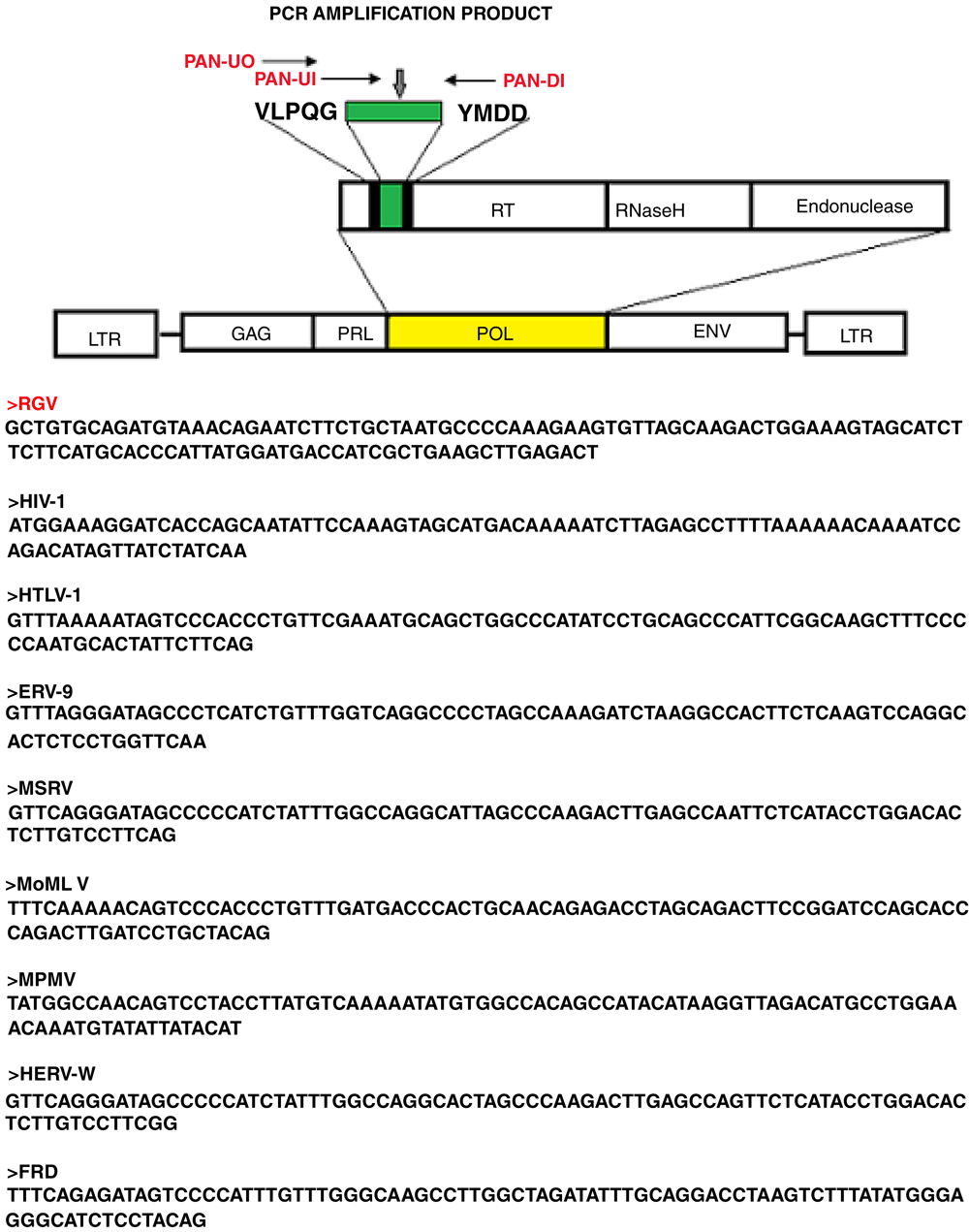
The technique uses degenerate primers capable of amplifying a region in Reverse Transcriptase, between two conserved motifs VLPQ and YMDD in the Pol gene across different retroviruses. The Pol sequence amplified from the human giant viruses is indicated as RGV (bold red). Corresponding same size region of different retroviruses, amplified with the same technique11,14, are reported.
A predominant band of the expected size of >150 bp was amplified from RNA extracted from the human giant viruses (Figure 3, lane 1). Multiple alignments with equivalent and already established Pol region of retroviruses, amplified by the same technique, confirm that our 150 bp amplicon is a Pol-like gene. A molecular phylogenetic analysis based on this region suggests that this amplicon (indicated as RGV) belongs to a distinct evolutionary branch among the whole retroviral families (Figure 4).

A ~400 bp band and a >150bp band were amplified, lane 1 on the agarose gel. Lane 2 is the marker (100-200-300-400-500-600-700-800-900-1000-1500bp). Multiple alignments of our 150bp band (RGV bold red) with equivalent and already established Pol region of retroviruses, amplified by the same technique, confirm that our 150 bp amplicon is a Pol-like gene.
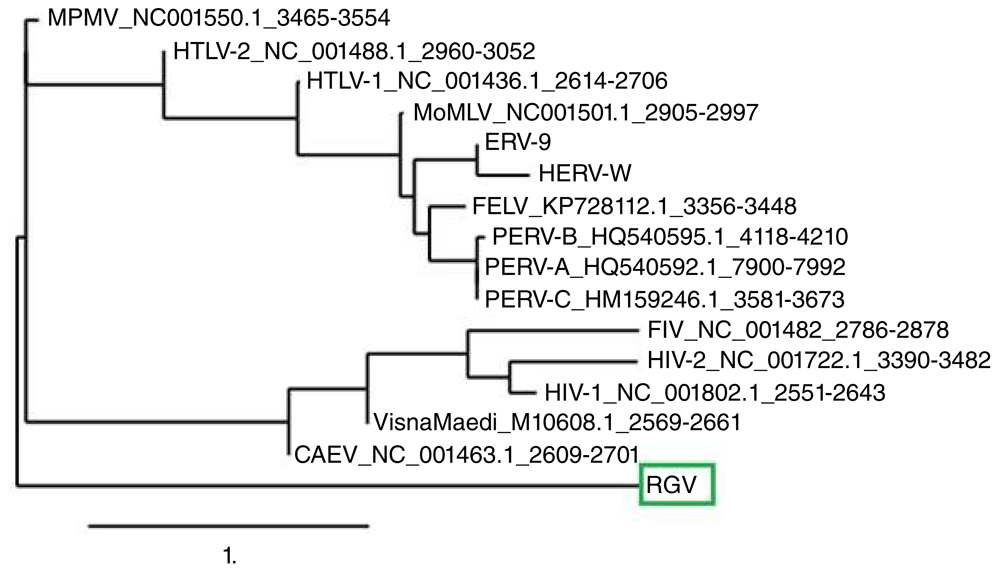
The Retro-Giant Virus (RGV) >150 amplicon (red circle) was analyzed and compared with the same conserved region of other retroviruses. See the Methods section for information on phylogenetic analysis. The RGV amplicon (green box) appears as a new, distinct, ancestral branch.
Along with the 150 bp band, a ~400bp amplicon was also detected (Figure 3, lane 1). Multiple alignment and phylogenetic analysis showed that the 400 bp band aligns entirely on the human chromosome 7 and clusters with human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs) genes (Figure 5). This finding replicates consolidated reports of almost intact human endogenous retrovirus genomes in chromosome 717–24. Additional information is in Dataset 1–Dataset 3.
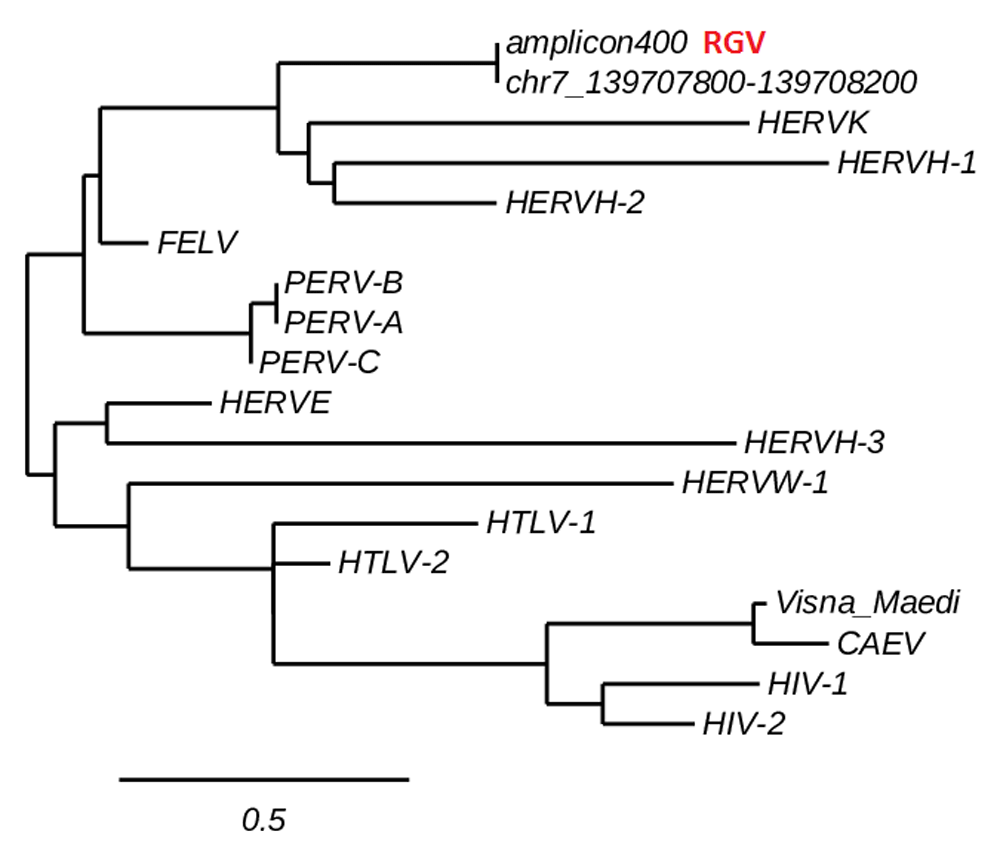
The ~400bp amplicon aligns entirely on a fragment of the human chromosome 7 and clusters with HERVs. This finding replicates established data of HERVs mapping in the human chromosome 7. See the Methods section and Dataset 2 for information on phylogenetic analysis.
Phylogenetic tree was made with webserver http://www.phylogeny.fr. Musclev3.8.31 was used for multiple alignment, Gblocks for alignment curation, PhyML for phylogeny and TreeDyn for treedrawing. A non-parametric, Shimodaira-Hasegawa-like approximate Likelihood-Ratio branch test (SH-like aLTR) was used as statistic test.
The retro-giant viruses has reverse transcriptase activity. 10 μl the lysated viral pellet produced cDNA from an RNA template (Figure 6).
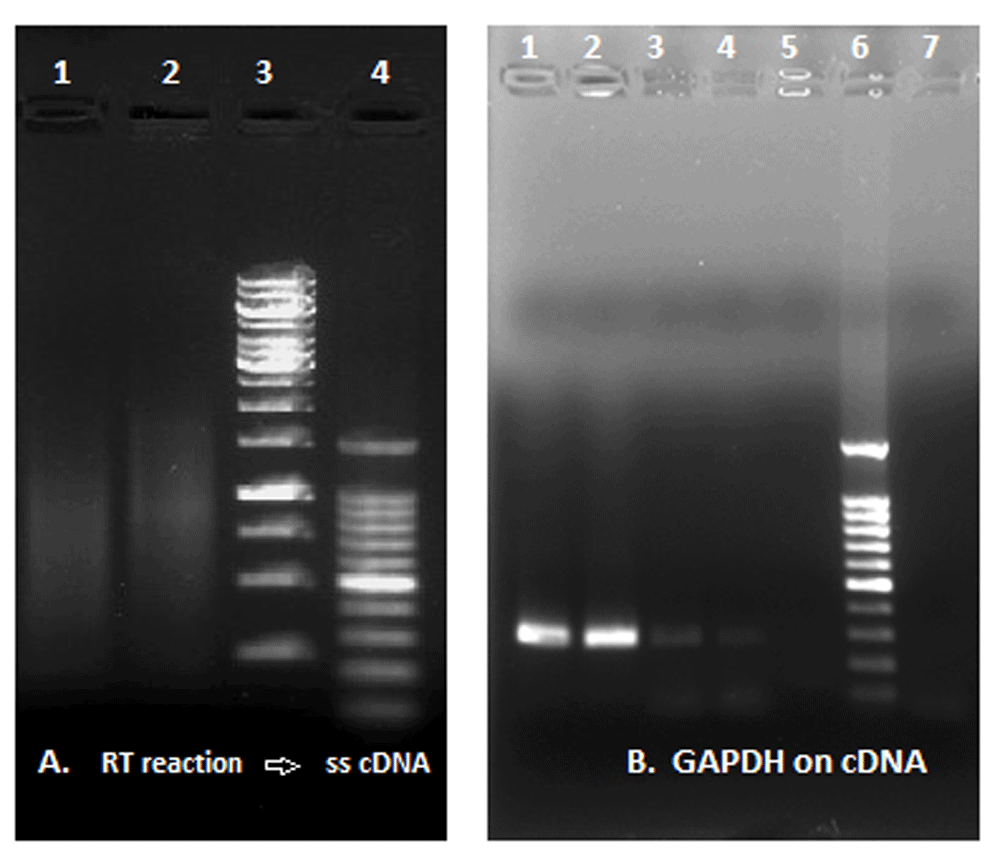
(A) RT reaction and synthesis of ss c-DNA: Lane 1, reaction with a commercial RT enzyme; Lane 2, reaction with viral pellet (reaction without RT enzyme); Lane 3, GeneRuler 1Kb DNA ladder; Lane 4, 100bp DNA ladder. (B) GAPDH amplification from ss-cDNA template: Lanes 1 and 2, reaction with commercial RT enzyme; Lanes 3 and 4, reaction with the lysated viral pellet; Lane 5, negative control; Lane 6, DNA ladder; Lane 7, additional negative control.
Summary of results (Figure 7 and Figure 8)
1. The fraction extracted from human T cell leukaemia cells and purified through 25% sucrose gradient are human giant viruses with a retroviral core.
2. The anti FeLV p27 gag antibody labelled the giant viral particles at EM immunogold
3. The Retro-Giant viruses have reverse transcriptase activity.
4. Pan-retrovirus PCR (Tuke protocol) suggested the presence inside the giant particles of retroviral amplicons.
5. The whole genome shotgun sequencing confirmed the presence of oncogenic retroviral core genes.
6. Like giant mimiviruses in the amoebas, these human giant viruses retain the Gram stain and they are associated with viral factories, but the substantial difference is their T tropism and the retroviral core: they are human Retro-Giant viruses (RGV), missing from the current retroviral classification.
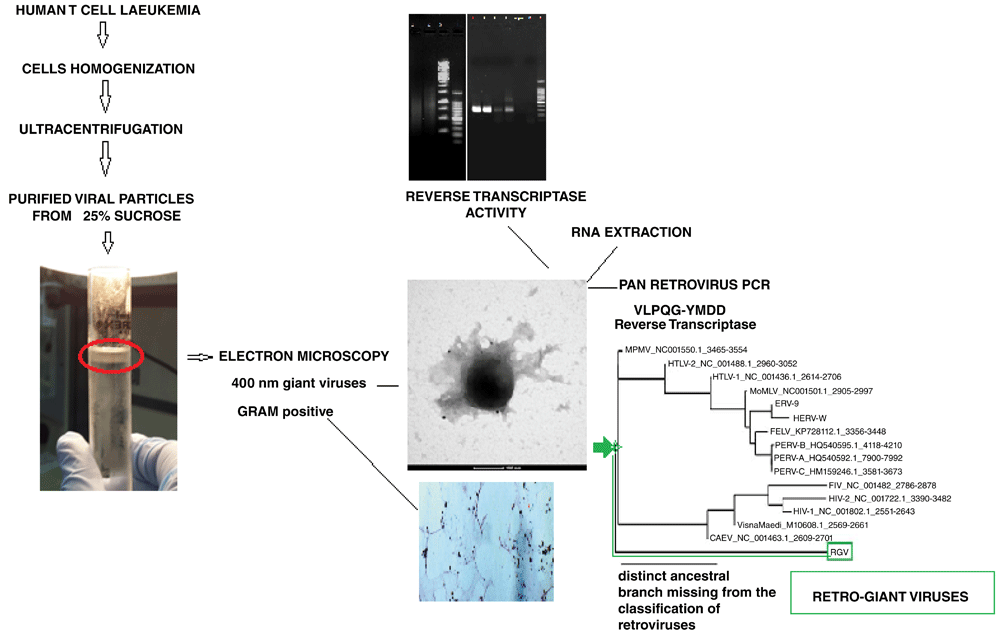
Giant viruses were isolated from human leukaemia T cells on 25% sucrose gradient (sedimentation fraction of giant viruses in general). Cell nuclei was discharged before layering onto the sucrose. The isolated viral pellet was examined using EM immunogold, which confirmed the presence of ~400 nm giant viruses with retroviral antigens (anti-FeLV gag). The viral pellet was also stained with the Gram stain. The viral lysate had reverse transcriptase activity. A Pan retroviral PCR of the RNA extracted from the giant viral particles and whole genome sequencing showed the presence in the giant viruses of retroviral core genes.
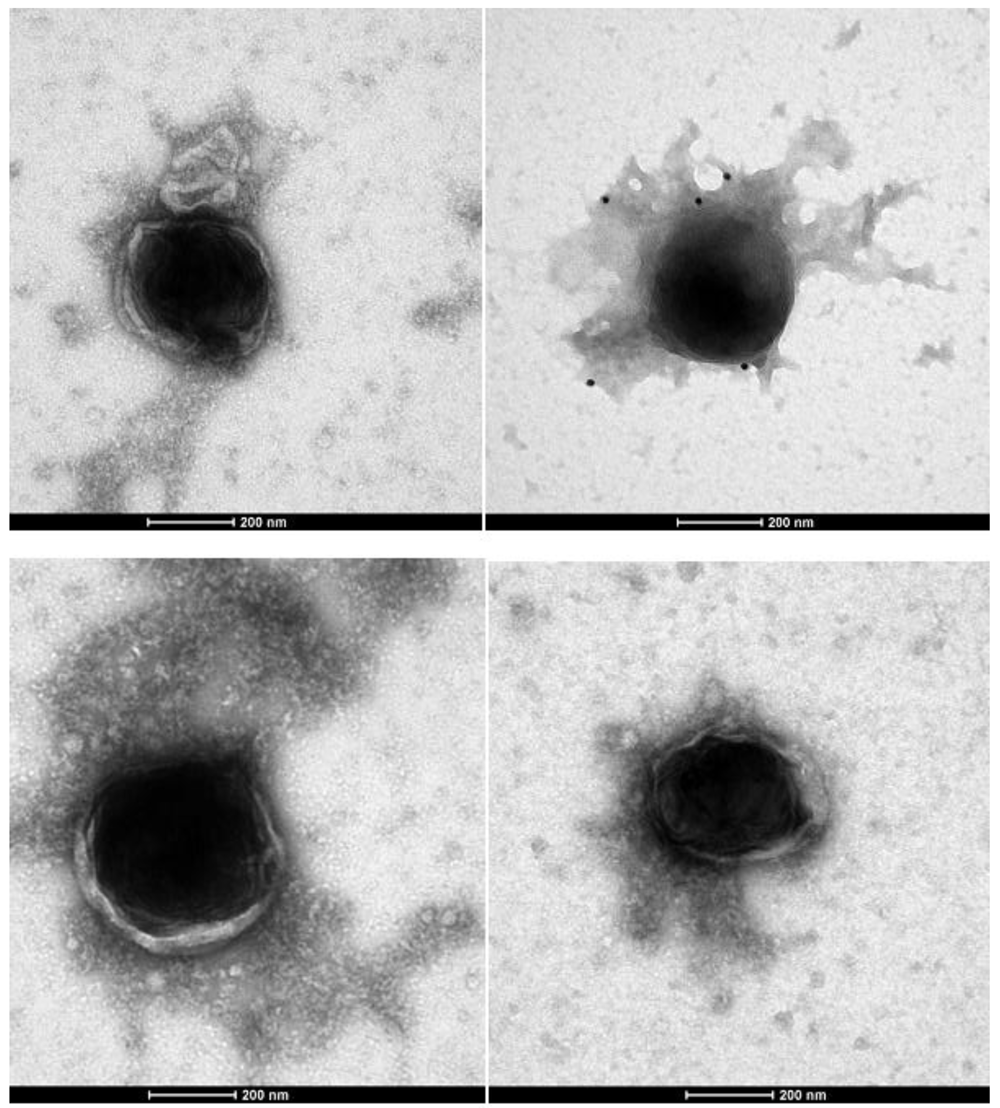
These pictures are representative of 100 micrographs. Contact the corresponding author to inspect the entire collection. These human giant viruses have a retroviral antigenicity (positive immunogold with moAbs anti-FeLV retroviral antigens, black dots in the picture), reverse transcriptase activity and retroviral core genes. The human Retro-Giant viruses retain the Gram stain and inside the cells they are associated to their viral factories, also displaying the retroviral antigenicity1.
The sequences resulting from the whole genome shotgun sequences are reported in Dataset 5. The very large genome (~1861 ORFs) appears more complex than Mimiviruses and contains retroviral core genes. Sequences indicated in yellow are the retroviral core genes (see Dataset 5: Shotgun annotations).
In particular, the oncogenic Gag-AKT fusion gene, related to FeLV (Dataset 5: Gag-AKT fusion protein analogy; E-value 2.00E-33; >95.04% identity), confirms our proteomics results and the documented retroviral antigenicity at the EM immunogold.
Mimiviruses and Archaea genes are also present. The Archaea features are very dominant (thermosome, operons, histone-like proteins, plasmids and anaerobic metabolism). The viral transcription apparatus is also well represented. Viral Notch and other viral oncogenes involved in retroviral induced leukaemia are also present. Some sequences also suggest that this giant microbial entity has its own metabolic apparatus and its own immune system.
In conclusion, this complex human giant is the summary of giant viruses, mimiviruses and archaea. The presence of reverse transcriptase and mammalian core retroviral gene establish the presence in acute human T cells Leukaemia of oncogenic Retro-Giant Viruses with archaea features.
Robert Gallo reported the first human retrovirus HLTV in 1980. What we report here is the discovery of the first Mimivirus-sized human giant virus with a retroviral core.
In our previous work, conducted initially on human tissues with anti-FeLV gag p27 moAb, EM depicted previously unreported ~400 nm gigantic particles associated with large aggregates, resembling viroplasms, recognized by anti-FeLVp27 gag Ab1. The particle diameters were more than four times the 100 nm size expected in retroviruses. These large particles and associated structures discovered in human cells appeared to morphologically parallel previously reported amoebas Mimiviruses (giant viruses and their viral factories)7.
Gram positive blue granules that disclosed the existence of giant viruses in the amoeba, similarly detected this newly giant virus in human cells both in our previous study1 and current study.
Proteomic analyses suggested the presence of histone H4 variants common to environmental giant DNA viruses, but the striking difference was the unique mammalian retroviral nature of the human giant particles.
However, working on human tissues was confusing and the distinction between the virus and the cells was blurred. How to prove if we were really facing ancestral giant viruses with a retroviral core?
In order to distinguish the giant agent from the human cells, in the present study we isolated the viruses, examined their morphology using EM, extracted their nucleic acid performed a Pan-retrovirus PCR and a whole genome sequencing.
The presence of human Retro-Giant viruses was confirmed step by step. A white ring sedimented on a 25% of sucrose gradient - the same sedimentation fraction of the giant DNA viruses isolated from the amoebas7. EM depicted ~400nm giant viral particles that showed the ability to retain the Gram stain, but the striking difference was their unique mammalian retroviral nature. Distinct from the amoebas’ Mimiviruses, the viral particles were immuno-labelled with anti FeLV p27gag moAb, they contained retroviral RNA and showed reverse transcriptase activity.
RNA extracted exclusively from the viral particles, isolated on a sucrose gradient, was initially amplified with a Pan-retrovirus PCR, able to detect a conserved fragment in the Reverse transcriptase across different retroviral genera, and subsequently a shotgun whole genome sequencing was performed. To avoid any other source of contamination, we made sure that the cells’ nuclei were removed before layering on the sucrose gradient. The shotgun whole genome sequencing confirmed the presence in the giant viruses of retroviral core genes and acute transforming gag-akt fusion proteins related to feline leukaemia retrovirus lineage.
The T tropism of the Retro-Giant viruses relies on their retroviral nature, however, it is very improbable, as recently described25, to find DNA mimiviruses in human T lymphocytes. Nevertheless, the discovery of the Retro-Giant viruses was made, not only because of their ability to bind the anti-FeLV antibodies, but also for fundamental elements that we took from the discovery of the amoebas giant mimiviruses in 20032. How could we conceive the possibility of colouring the Retro-Giant viruses with the Gram staining without the previous discovery of mimiviruses in the amoeba? Our 400 nm particles would have been erroneously perceived as giant vesicles and not as gram positive giant viruses with prokaryotes-archaea features. The Retro-Giant viruses represent a unique viral entity that suggests that defective retroviruses were possibly not sufficient for replication and required the interchange of genetic information with giant viruses’ large biosynthetic assortment.
It follows by viewing our human Retro-Giant virus as a system that evolved from ancestral viruses to surround and shuttle retroviruses, providing a wider pathway for their dissemination. The `viral factories` and viral histone H4, described in our previous study1, suggests a protected system that hijacks host immunity and epigenetics to enhance viral replication.
The fact that the Retro-Giants can be detected with an anti-FeLV gag is simply an amusing co-incidence. It might be that prototypical leukaemia viruses were the first organisms to put fragments of an evolving protein machinery together to make something useful shared among ancient retroviruses, prokaryotes and giant viruses. Feline retroviruses share conserved ancestral epitopes among different mammalian retroviruses26–31. In addition, the presence of a shared 5'-leader sequence in ancestral human and mammalian retroviruses and its transduction into Feline Leukemia virus has been recently documented32. The constant presence in our giants of gag-pol leukaemogenic sequences was demonstrated by EM immunogold, genomics and proteomics.
In conclusion, we report not an archetypal human retrovirus nor even a large human retrovirus, but a human giant virus with a mammalian retroviral core. Although sharing some morphological features with mimiviruses and archaea, this human giant virus differs substantially from DNA amoebal giant viruses for its unique presence of mammalian retroviral core genes.
The whole genome shotgun sequencing confirmed the discovery of a human Retro-Giant in human acute T cells leukemia. This human giant microbial entity is the expression of a fascinating synthesis between archaea, giant viruses and retroviruses. The Retro-Giant Viruses possibly reflects the transition from the RNA to DNA world. This discovery may change our perspective in retrovirology and the way we conceive retroviruses.
With the Retro-Giants, the concept of giant virus is applied for the first time to the dogmas of retrovirology. Not the basic gag–polenv backbone and the small dimension anymore, but Gram positive giant particles with the archaeal-mimiviruses features and mammalian retroviral genes.
Temin in his 1975 Nobel address showed that a normal non carcinogenic avian virus interacts with something in human cell to create Rous Sarcoma Virus. He also suspected an ancestor for the reverse transcriptase. However, at that time the concept of Giant Viruses was missing, we had to wait till 2003, but the Retro-Giants seem to confirm Temin’s prediction about the ancestors and the mechanism of cross-speciation transition of archetypal retroviruses.
The unusual features of the Retro-Giant viruses challenge our current concepts of retrovirology and the Retro-Giants will not have an easy life. It is difficult to accept the concept of viruses being giant, but it becomes almost unbearable when the giants are Retro-Giants.
“What? A giant virus with prokaryotic features and a retroviral core? If they are so gigantic, why has nobody seen them before?” How to accept the provocative idea that the Retro-Giant viruses, could be ancestral creatures evolved earlier than archetypal retroviruses, playing a role in human leukaemia ? These kind of questions reveal how complex scientific processes shape contemporary medical discoveries and their reception.
The giant mimiviruses in the amoeba are prehistorical creatures, evolved millions of years ago, since the dawn of evolution of eukaryotic cells33,34. They are gigantic, yet nobody saw them until 20032.
For the discovery of the Retro-Giant viruses, their ability to bind a screen of antibodies anti-Feline retroviruses and some of the biochemical properties of giant viruses proved to be lucky.
The Retro-Giant viruses despite their archaea- giant viruses features should be included in the current classification of retroviruses because their oncogenic retroviral genes may be the ones responsible for some types of human leukaemia.
We could isolate constantly the Retro-Giants form acute human T cells leukaemia just with a routine sucrose gradient. Every time, in every replicate fulfilling some of Koch’s postulates.
Actions to eradicate leukaemogenic retroviruses is currently not possible, but targeting the constant presence of the ancestors may provide a new methodology.
Not archetypal retroviruses, but Gram positive ancestral creatures with leukaemogenic retroviral core genes: this is the essence of the human Retro-Giants that were missing.
All slides and EM grids are available to be examined; please contact the corresponding author.
F1000Research: Dataset 1. 150 bp amplicon alignment against other VLPQG-YMDD Pol sequences of different retroviruses. DOI, 10.5256/f1000research.15118.d20807312
F1000Research: Dataset 2. 400bp amplicon sequence and its alignment against other retroviral families. DOI, 10.5256/f1000research.15118.d20807413
F1000Research: Dataset 3. Uncropped and unedited blots. DOI 10.5256/f1000research.15118.d20807535
F1000Research: Dataset 4. Illumina FastQ and FastQC raw data. 10.5256/f1000research.15118.d21855936
F1000Research: Dataset 5. Gag-AKT fusion protein analogy, Shotgun annotations, and Seq-ORF.fasta files. 10.5256/f1000research.15118.d21856037
This work was supported in part by St Vincent Health Care Group of Dublin, Ireland.
The anti-FeLV-related moAbs were kindly provided as a gift by Dr Chris Grant of Custom Monoclonals International (West Sacramento, CA 95691, USA).
We thank Microgem Laboratory Research (Napoli, Italy) for their technical assistance.
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Is the work clearly and accurately presented and does it cite the current literature?
Yes
Is the study design appropriate and is the work technically sound?
Partly
Are sufficient details of methods and analysis provided to allow replication by others?
Yes
If applicable, is the statistical analysis and its interpretation appropriate?
Partly
Are all the source data underlying the results available to ensure full reproducibility?
Yes
Are the conclusions drawn adequately supported by the results?
Partly
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
|
Version 2 (revision) 20 Sep 18 |
read |
|
Version 1 04 Jul 18 |
read |
Click here to access the data.
Spreadsheet data files may not format correctly if your computer is using different default delimiters (symbols used to separate values into separate cells) - a spreadsheet created in one region is sometimes misinterpreted by computers in other regions. You can change the regional settings on your computer so that the spreadsheet can be interpreted correctly.
Click here to access the data.
Spreadsheet data files may not format correctly if your computer is using different default delimiters (symbols used to separate values into separate cells) - a spreadsheet created in one region is sometimes misinterpreted by computers in other regions. You can change the regional settings on your computer so that the spreadsheet can be interpreted correctly.
Click here to access the data.
Spreadsheet data files may not format correctly if your computer is using different default delimiters (symbols used to separate values into separate cells) - a spreadsheet created in one region is sometimes misinterpreted by computers in other regions. You can change the regional settings on your computer so that the spreadsheet can be interpreted correctly.
Click here to access the data.
Spreadsheet data files may not format correctly if your computer is using different default delimiters (symbols used to separate values into separate cells) - a spreadsheet created in one region is sometimes misinterpreted by computers in other regions. You can change the regional settings on your computer so that the spreadsheet can be interpreted correctly.
Click here to access the data.
Spreadsheet data files may not format correctly if your computer is using different default delimiters (symbols used to separate values into separate cells) - a spreadsheet created in one region is sometimes misinterpreted by computers in other regions. You can change the regional settings on your computer so that the spreadsheet can be interpreted correctly.
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Thank you for your comment.
A version 3 of my manuscript, with updates, will be released shortly.
In this new version, I will present further experiments including the isolation of the giant particles ... Continue reading Dear Daniel Elleder
Thank you for your comment.
A version 3 of my manuscript, with updates, will be released shortly.
In this new version, I will present further experiments including the isolation of the giant particles from human cells, their purification on a sucrose gradient, whole genome sequence (this time repeated in duplicate), additional EM analyses, transformation assay on NIH 3T3 cells after giant particles infection and tumours formation in mice.
The giants induced peritoneal metastatic disease after three weeks post infection. Please, See links below.
Unfortunately, especially in the light of the new data and metastatic disease in mice, your comment is neither here nor there.
In this letter, I will anticipate some of my results to address fundamental concepts that seem to be missing.
1. The giants are not typical viruses, but microbial cell-like entities. They have genes in common with the three domains of life: eukarya, bacteria and archaea. Like bacteria, they retain the Gram stain.
2. The reported particles have been extracted and purified through a sucrose gradient, https://drive.google.com/open?id=1ai8MpZ0eat5a7LT7b43NPXNRWy0McJwo
3. These human giants infect and transform NIH-3T3 cells in vitro, https://drive.google.com/open?id=1a6ofZQNpxaZElAtCbX5SVpPdQxGAo1h2
4. The giants induce tumours formation in mice, https://drive.google.com/open?id=1Xbxtf1ximI3oTJsA3I8-1dq8CdO8I8XX
5. The tumours formation in mice is REAL and NOT a bioinformatics score.
6. Why do my Giants cause cancer? Simple : they have oncogenes INSIDE their mega-genome!
7. The giants fulfil the Koch’s postulates. I have re-extracted the giant particles from cells that became cancerous.
8.The giant have RT activity. Again this is a REALITY, a real biochemical reaction and not ONLY a bioinformatics annotation.
9.Bioinformatics are prediction and they CANNOT replace the biological reality. Metagenomics does not replace the need to cultivate and isolate microbes.
10. The function of bioinformatics is predicting, not explaining. Koch or Pasteur discovered their microbes without any software. Rous discovered RSV in 1911.
....And the databases grew, and everyone annotated their data by searching the databases, then submitted in turn. No one seems to have pointed out that this makes your database a reflection of your database, not a reflection of reality.
At this stage, with the striking evidence of tumours formation in mice, your debate on the 150 bp fragment is trivial . Honestly, I don’t base the discovery of this magnitude on a single 150 bp fragment. This was just a preliminary RT–PCR following an old protocol commonly used in retrovirology. Please refer to the new data and whole genome sequence. If the tagmentase enzyme disturb you with some background noise, just take the E. Coli sequence off . The results doesn’t change: a mega-genome is confirmed (https://mega.nz/#F!7dID0aSa!8bA-4qVdPeiY0tsSbd8G7g).
The predominant archaea features coexist with the presence of an anchoring system typical of viruses and gag-pol proteins of oncogenic retroviruses complete their chimeric essence.
The most valid bioinformatics tool was achieved through Blast2GO. This simulation went really close to the real life scenario (example of realist and desirable bioinformatics). The annotations of the many oncogenes in the mega-genome proved to be true, since the giants induced cancer in mice (please see the cancer in my mice). In addition, the predicted transforming gag-pol genes matched with the retroviral antigenicity, documented at EM immunogold and RT activity .
Note that , in my experiments, a filter supernatant DOES NOT transform.
These human giants was missing because of our definition of viruses and some people seem to struggle (new concepts , new paradigms, dynamics) .
After inspecting my data in the provided links, I would like you to answer, just with a YES/NO, my questions:
- What are the purified structures depicted at EM? Are they something human? If yes, explain why .
- Do these Giants INFECT and transform NIH 3T3 cells?
- Do they induce peritoneal metastasis in mice?
- Do they reverse transcribe in a real biochemical reaction?
- Do they retain the Gram stain?
- Do they have a mega-genome?
- Can they be isolated every single time just with a routine sucrose gradient by independent operators?
- At each extraction , do the EM reveal the same dimension and structures?
- Do they have multiple cell based oncogenes? (BISHOP)
- Do they have a capside?
- Does a filtered supernatant do the same?
- Is the anti-Felv gag antigenicity of the particles in line to the PREDICTED akt-gag and the documented RT activity?
- Does bioinformatics replace biology?
- Are you familiar with the concept of TRUC and cell like entity with genes in common to the three domain of life?
- Is it true that viruses carry also fragments of human sequences?
- Is it true that the transforming gene product, P70gag-actin-fgr, of Gardner-Rasheed feline sarcoma virus (GR-FeSV) is a single polypeptide composed of regions derived from cellular and viral genes?
- What is MPGNL?
- Did you see cancer in my mice?
- Would you like to be treated for a physiological illness by a physician who is not sure that there are human bodies, and who uses information systems that lack real referents?
BOTTOM LINE > THE HUMAN GIANT INFECT AND CAUSE CANCER> FULL STOP.The retroviral nature is peculiar, but it is just a detail. The giants are much more: an entire cancer factory that transform in few days.
Try with your bioinformatics skills to discover a new sequence. Not a variant or a subtype of something already known, but something like a TRUC that induces cancer in your chicken in three weeks. Without having your skills, I was able to achieve this in mice.
My giants might open the door to a preventive vaccine against cancer, since they give possibility to target an entire shuttling system of oncogenes and not just a solitary molecule involved in carcinogenesis.
It is like discovering HPV for the first time, or EBV for the first time, just to mention few.
This time is not a virus, but a TRUC : Not an oncogenic virus, or a slow virus, with few proteins that you can count on the fingers of one hand, but an infectious oncogenic CELL-LIKE MICROBIAL ENTITY that looks like a bacteria, with hundreds of proteins, carrying in its large mega-genome a transforming arsenal. A sort of small autonomous infectious cell, a simplified version of its eukaryotic counterparts, specialized in carcinogenesis.
The discovery of this microbial entity with an acute transformation mechanism and infecting humans suggests that the number of cancer of infectious origin would be even greater than what is supposed.
In my discovery there are no shadows, no quarrels, no misconducts and no thefts. I feel blessed and the Retro-giants is a gift.
Suggested references
"Anti-realist bioinformaticians work with data handed over to them by realist biologists. Some features of some information systems can be improved if bioinformaticians became realists as well. Still another thing makes it desirable that bioinformaticians become realists: they could then possibly provide feedback to biologists". https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S153204640500078X
Elena
Thank you for your comment.
A version 3 of my manuscript, with updates, will be released shortly.
In this new version, I will present further experiments including the isolation of the giant particles from human cells, their purification on a sucrose gradient, whole genome sequence (this time repeated in duplicate), additional EM analyses, transformation assay on NIH 3T3 cells after giant particles infection and tumours formation in mice.
The giants induced peritoneal metastatic disease after three weeks post infection. Please, See links below.
Unfortunately, especially in the light of the new data and metastatic disease in mice, your comment is neither here nor there.
In this letter, I will anticipate some of my results to address fundamental concepts that seem to be missing.
1. The giants are not typical viruses, but microbial cell-like entities. They have genes in common with the three domains of life: eukarya, bacteria and archaea. Like bacteria, they retain the Gram stain.
2. The reported particles have been extracted and purified through a sucrose gradient, https://drive.google.com/open?id=1ai8MpZ0eat5a7LT7b43NPXNRWy0McJwo
3. These human giants infect and transform NIH-3T3 cells in vitro, https://drive.google.com/open?id=1a6ofZQNpxaZElAtCbX5SVpPdQxGAo1h2
4. The giants induce tumours formation in mice, https://drive.google.com/open?id=1Xbxtf1ximI3oTJsA3I8-1dq8CdO8I8XX
5. The tumours formation in mice is REAL and NOT a bioinformatics score.
6. Why do my Giants cause cancer? Simple : they have oncogenes INSIDE their mega-genome!
7. The giants fulfil the Koch’s postulates. I have re-extracted the giant particles from cells that became cancerous.
8.The giant have RT activity. Again this is a REALITY, a real biochemical reaction and not ONLY a bioinformatics annotation.
9.Bioinformatics are prediction and they CANNOT replace the biological reality. Metagenomics does not replace the need to cultivate and isolate microbes.
10. The function of bioinformatics is predicting, not explaining. Koch or Pasteur discovered their microbes without any software. Rous discovered RSV in 1911.
....And the databases grew, and everyone annotated their data by searching the databases, then submitted in turn. No one seems to have pointed out that this makes your database a reflection of your database, not a reflection of reality.
At this stage, with the striking evidence of tumours formation in mice, your debate on the 150 bp fragment is trivial . Honestly, I don’t base the discovery of this magnitude on a single 150 bp fragment. This was just a preliminary RT–PCR following an old protocol commonly used in retrovirology. Please refer to the new data and whole genome sequence. If the tagmentase enzyme disturb you with some background noise, just take the E. Coli sequence off . The results doesn’t change: a mega-genome is confirmed (https://mega.nz/#F!7dID0aSa!8bA-4qVdPeiY0tsSbd8G7g).
The predominant archaea features coexist with the presence of an anchoring system typical of viruses and gag-pol proteins of oncogenic retroviruses complete their chimeric essence.
The most valid bioinformatics tool was achieved through Blast2GO. This simulation went really close to the real life scenario (example of realist and desirable bioinformatics). The annotations of the many oncogenes in the mega-genome proved to be true, since the giants induced cancer in mice (please see the cancer in my mice). In addition, the predicted transforming gag-pol genes matched with the retroviral antigenicity, documented at EM immunogold and RT activity .
Note that , in my experiments, a filter supernatant DOES NOT transform.
These human giants was missing because of our definition of viruses and some people seem to struggle (new concepts , new paradigms, dynamics) .
After inspecting my data in the provided links, I would like you to answer, just with a YES/NO, my questions:
- What are the purified structures depicted at EM? Are they something human? If yes, explain why .
- Do these Giants INFECT and transform NIH 3T3 cells?
- Do they induce peritoneal metastasis in mice?
- Do they reverse transcribe in a real biochemical reaction?
- Do they retain the Gram stain?
- Do they have a mega-genome?
- Can they be isolated every single time just with a routine sucrose gradient by independent operators?
- At each extraction , do the EM reveal the same dimension and structures?
- Do they have multiple cell based oncogenes? (BISHOP)
- Do they have a capside?
- Does a filtered supernatant do the same?
- Is the anti-Felv gag antigenicity of the particles in line to the PREDICTED akt-gag and the documented RT activity?
- Does bioinformatics replace biology?
- Are you familiar with the concept of TRUC and cell like entity with genes in common to the three domain of life?
- Is it true that viruses carry also fragments of human sequences?
- Is it true that the transforming gene product, P70gag-actin-fgr, of Gardner-Rasheed feline sarcoma virus (GR-FeSV) is a single polypeptide composed of regions derived from cellular and viral genes?
- What is MPGNL?
- Did you see cancer in my mice?
- Would you like to be treated for a physiological illness by a physician who is not sure that there are human bodies, and who uses information systems that lack real referents?
BOTTOM LINE > THE HUMAN GIANT INFECT AND CAUSE CANCER> FULL STOP.The retroviral nature is peculiar, but it is just a detail. The giants are much more: an entire cancer factory that transform in few days.
Try with your bioinformatics skills to discover a new sequence. Not a variant or a subtype of something already known, but something like a TRUC that induces cancer in your chicken in three weeks. Without having your skills, I was able to achieve this in mice.
My giants might open the door to a preventive vaccine against cancer, since they give possibility to target an entire shuttling system of oncogenes and not just a solitary molecule involved in carcinogenesis.
It is like discovering HPV for the first time, or EBV for the first time, just to mention few.
This time is not a virus, but a TRUC : Not an oncogenic virus, or a slow virus, with few proteins that you can count on the fingers of one hand, but an infectious oncogenic CELL-LIKE MICROBIAL ENTITY that looks like a bacteria, with hundreds of proteins, carrying in its large mega-genome a transforming arsenal. A sort of small autonomous infectious cell, a simplified version of its eukaryotic counterparts, specialized in carcinogenesis.
The discovery of this microbial entity with an acute transformation mechanism and infecting humans suggests that the number of cancer of infectious origin would be even greater than what is supposed.
In my discovery there are no shadows, no quarrels, no misconducts and no thefts. I feel blessed and the Retro-giants is a gift.
Suggested references
"Anti-realist bioinformaticians work with data handed over to them by realist biologists. Some features of some information systems can be improved if bioinformaticians became realists as well. Still another thing makes it desirable that bioinformaticians become realists: they could then possibly provide feedback to biologists". https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S153204640500078X
Elena