Keywords
anti-hypercholesterolemic, Zingiber montanum
This article is included in the ICTROPS 2018 collection.
anti-hypercholesterolemic, Zingiber montanum
Hypercholesterolemia is a condition characterized by very high levels of cholesterol in the blood1. Excess cholesterol in the bloodstream can be deposited into the walls of blood vessels. Hypercholesterolemia certainly predicts coronary heart disease risk2. Numerous agents can be used for hypercholesterolemia patients, one of them is HMG CoA reductase inhibitors or statins (i.e. Simvastatin)3. Side effects of statins are usually very well tolerated but can cause hepatitis-like symptoms and myopathy4.
Many plants have been used in traditional medicine in Indonesia. Zingiber montanum (J.Koenig) Link ex A.Dietr. (in Indonesian is called Bangle) are potent as antihypercholesterolemic5. Among the synonyms, Zingiber cassumunar Roxb. and Zingiber purpureum Roscoe are commonly used for Z. montanum6. In Southeast Asian countries, Z. montanum is well-known for its anti-inflammatory properties7. Z. montanum is used as a traditional medicine in East Kalimantan for health problems caused by high cholesterol level8. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the anti-hypercholesterolaemic effect of Z. montanum in rat models of hypercholesterolemia.
The sampling of medicinal plants was conducted in the Kutai Kartanegara District, East Kalimantan (0°24’18.4”S 117°4’24.7”E).
The rhizomes of Z. montanum were sliced and dried at room temperature for 3 days, crushed and transferred into a glass container. Crushed rhizomes was soaked in absolute ethanol (9401-03 Alcohol, Anhydrous, Reagent, J.T. Baker) for 5 days. The mixture was shaken occasionally with a shaker (3525 Incubator Orbital Shaker, Lab-Line, US). After 5 days, the materials were filtered (Whatman Filter Paper 11µm, Sigma-Aldrich) and evaporated using a rotary evaporator (RV06-ML Rotary Evaporator, IKA, Germany). The dried extracts were obtained and stored at 4°C in a dark bottle until use.
Based on Federer’s rule, with six group of induction, 30 male Wistar rats (Rattus norvegicus), weighing 250–350g, aged 12–13 months, were obtained from Animal House Faculty of Medicine (Mulawarman University) and randomly divided into 6 groups: control, high fat diet, high fat diet with simvastatin and high fat diet with 3 different doses of Z. montanum extract (100, 200, and 400 mg/kg). They were acclimatized for 1 week in a controlled room temperature of 25°C, with a 12-hour light/dark cycle, and access to food pellets and filtered water ad libitum to adapt to the new environment. They were housed in wire cages (30×30×30 cm), one animal in each cage. All the treatment rats were given high fat diet for 4 weeks with 10% chicken egg yolk and reused cooking oil to their standard pellet diet (Japfa, Comfeed, Indonesia) with tap water ad libitum.
After 4 weeks of treatment, blood was collected from all groups after an overnight fasting. All animals were anesthetized intraperitoneally with a ketamine injection (Hameln, Germany) at a dose of 60 mg/kg before blood was taken. After anesthetized, animals were euthanized by cervical dislocation. Blood was aspirated through the left ventricle of each animals’ heart. Two mililiters of blood was aspirated using a 3 ml disposable syringe and then inserted in a vaccutainer tube with an anticoagulant. Plasma concentrations of triglycerides, total cholesterol, high density lipoproteins (HDLs), and low density lipoproteins (LDLs) were measured with an automatic analyzer system (BiOLis 24i; Boeki, Tokyo, Japan).
All statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 16.0 for Windows. Data normality was examined using Shapiro-Wilk normality test. Then data were analyzed using ANOVA and post hoc with Tukey test. A p value of ≤ 0.05 was considered to be significant.
All protocols used in this experiment received approval from the Ethical Animal Care from the Medical and Health Research Ethics Commission, Faculty of Medicine, Mulawarman University with approval number 81/KEPK-FK/V/2018. All efforts were made to ameliorate any suffering of animals used in this research.
The results showed that significant differences between total cholesterol (p=0.000), LDL (p=0.000) and triglycerides (p=0.001) (Figure 1) levels achieved between high fat diet group and Z. montanum extracts. Meanwhile, there were no significant differences in the HDL (p=0.830) level between the high fat diet group and other groups. Tukey post hoc test showed significant differences between total cholesterol (p=0.000) and LDL (p=0.000) levels with the high fat diet group. The results of Z. montanum 400 mg/kg also showed a significant reduction, not only for total cholesterol, but also for triglyceride (p=0.030) levels (Table 1).
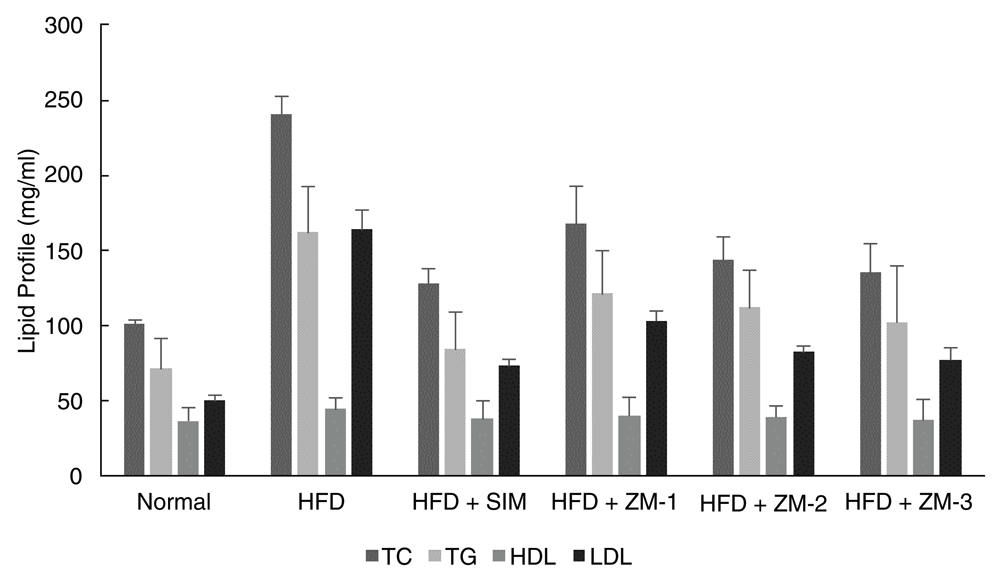
| Group | Total Cholesterol (mg/ml) | HDL (mg/ml) | LDL (mg/ml) | Triglycerides (mg/ml) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFD control | 241.0 ± 11.6 | 44.8 ± 6.7 | 163.8 ± 13.1 | 161.8 ± 30.6 |
| HFD + SIM | 128.2 ± 9.4* | 38.2 ± 11.8 | 73.2 ± 4.7* | 84.2 ± 24.6* |
| HFD + ZM-1 | 168.0 ± 25.4* | 40.6 ± 11.2 | 103.1 ± 6.9* | 121.4 ± 28.4 |
| HFD + ZM-2 | 144.2 ± 14.9* | 39.2 ± 6.7 | 82.6 ± 3.4* | 112.0 ± 25.0 |
| HFD + ZM-3 | 135.2 ± 19.0* | 37.2 ± 14.1 | 77.5 ± 7.7* | 102.6 ± 37.1* |
| Normal control | 101.4 ± 2.2* | 36.8 ± 8.4 | 50.3 ± 3.3* | 71.4 ± 19.7* |
Note: HFD = high-fat diet, SIM = simvastatin; ZM-1 = Z. montanum 100 mg/kg;
ZM-2 = Z. montanum 200 mg/kg; ZM-3 = Z. montanum 400 mg/kg
*Tukey post hoc test significant p<0.05 compared to HFD control
Z. montanum (Supplementary File 1) is used medicinally in Asia, primarily as a carminative and stimulant for the stomach, and to treat diarrhea and colic9. Pharmacological properties of Z. montanum include antimicrobial activity, anti-oxidant activity, insecticidal-activity, anti-cancer, anticholinesterase activity, and anti-inflammatory10. The main constituents, terpinen-4-ol and DMPBD, has been found to be effective against bacteria and also have anti-inflammatory activity11.
The rhizome extracts of Z. montanum showed the highest total curcuminoid content compared to other species of Zingiber7,12. Curcuminoid isolated from Z. montanum may possess a potent protective action against oxidative stress13. The major target for anti-atherosclerotic activity is a modification of lipoprotein levels or LDL oxidation14. Curcumin as antioxidants could efficiently prevent LDL oxidation15. The decrease in the total cholesterol and triglycerides levels may be attributed to hypolipidemic agents in Z. montanum. The significant changes in LDL levels suggest that Z. montanum is having an effect on lipid metabolism16. It is suggested that curcumin with other chemical compounds from Z. montanum could show anti-hypercholesterolemic effects.
It could be concluded that Z. montanum extracts have the potenial to reduce lipid profile level, which could be further developed as a natural source of the anti-hypercholesterolemic agents.
F1000Research: Dataset 1. Effect of ethanol extract of Zingiber montanum and simvastatin in total cholesterol, triglycerides, high density lipoproteins (HDL), and low density lipoproteins (LDL) levels after 4 weeks of treatment in a high fat diet rat model., http://dx.doi.org/10.5256/f1000research.16417.d22166817
This work was supported with funding from the Project Implementation Unit IsDB Universitas Mulawarman for financing this research, as part of the implementation of IsDB Grant Research Year of 2018 [448/UN17.45/DL/2018].
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Supplementary File 1: Picture of rhizome of Zingiber montanum (J.Koenig) Link ex A.Dietr.
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Is the work clearly and accurately presented and does it cite the current literature?
Yes
Is the study design appropriate and is the work technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of methods and analysis provided to allow replication by others?
Yes
If applicable, is the statistical analysis and its interpretation appropriate?
Yes
Are all the source data underlying the results available to ensure full reproducibility?
Yes
Are the conclusions drawn adequately supported by the results?
Yes
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Natural Product Chemistry, Bioactivity study
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |
|
Version 2 (revision) 14 Aug 19 |
read | read |
|
Version 1 15 Nov 18 |
read | |
Click here to access the data.
Spreadsheet data files may not format correctly if your computer is using different default delimiters (symbols used to separate values into separate cells) - a spreadsheet created in one region is sometimes misinterpreted by computers in other regions. You can change the regional settings on your computer so that the spreadsheet can be interpreted correctly.
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Comments on this article Comments (0)