Keywords
bioinformatics, r, bioconductor, software, reproducible research
This article is included in the Bioconductor gateway.
This article is included in the RPackage gateway.
This article is included in the Bioinformatics gateway.
bioinformatics, r, bioconductor, software, reproducible research
Bioconductor is a open source software project (comprising 1741 individual analysis packages) and community for the analysis and comprehension of large-scale biological data. Newly submitted software packages undergo a technical review to ensure that best practices and Bioconductor coding conventions are followed. The project maintains an automated build system that ensures that packages in the Bioconductor project are compiled and built successfully and pass basic checks. Package downloads are tracked and aggregated by package and month, longitudinally. Finally, package details such as title, description, version, author, and dependencies on other R packages are compiled based on package metadata.
The current size and growth of the Bioconductor project suggests that there is merit in exposing computable forms of the metadata describing the Bioconductor package ecosystem. To that end, we developed a small suite of tools, BiocPkgTools, to provide easy access to project details such as download statistics, bulk package metadata, and package build status. Developers, project leaders, open source software researchers, and Bioconductor end users can build on the availability of these data for applications such as custom reporting, dependency graph analytics, package filtering, and text mining.
The core functionality of BiocPkgTools is to expose Bioconductor project and package metadata as tidy data1 objects (Figure 1). The data presented by the package are accessed directly from online resources available from Bioconductor. As such, the package relies on web connectivity and collects the most recent data. Installation instructions are detailed on the package website.
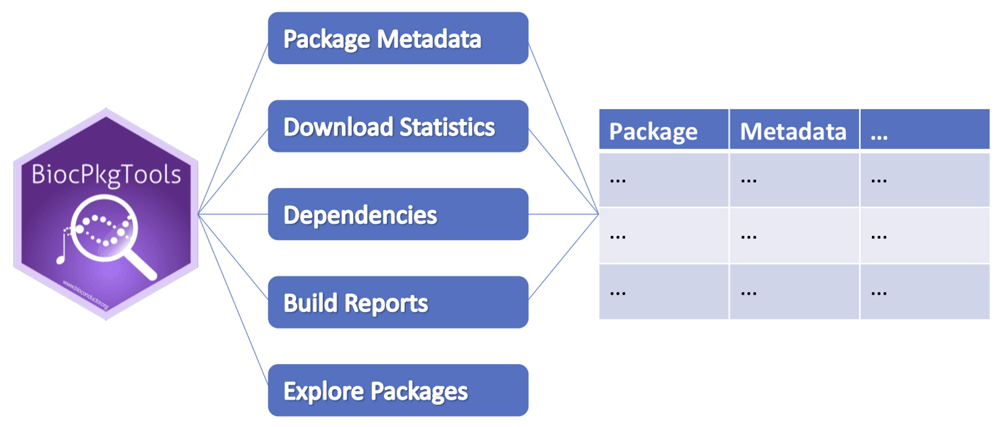
BiocPkgTools can access and transform web-accessible resources including package metadata, download statistics, dependencies between packages, and updated Bioconductor build report status to "tidy data" reports that can be manipulated using standard R tools. Interactive package exploration is also available.
Package functionality can be roughly divided into data access, data presentation, and graph/network functionality. See Table 1 for an overview.
After installing BiocPkgTools, the biocDownloadStats function can generate a tidy data structure summarizing monthly download statistics (both total and unique IP addresses) for all Bioconductor packages.
library(BiocPkgTools) dlstats = biocDownloadStats() head(dlstats, 3) ## # A tibble: 3 x 6 ## <fct> <int> <fct> <int> <int> <chr> ## 1 ABarray 2018 Jan 117 150 Software ## 2 ABarray 2018 Feb 97 125 Software ## 3 ABarray 2018 Mar 102 121 Software
| Name | Functionality |
|---|---|
| biocPkgList | Package details including description, author and maintainer, dependencies, URLs, bug report mechanism |
| biocDownloadStats | Monthly download statistics for all packages |
| biocbuildReport | Bioconductor build report for all packages and systems |
| biocExplore | Interactive, browsable “bubble plot” of Bioconductor packages and details |
| problemPage | Interactive, customized build report for an individual package author |
| buildPkgDependencyDataFrame | Package dependencies as data frame |
| buildPkgDependencyIgraph | Package dependencies as a graph2 |
| inducedSubgraphByPkgs | Create a minimal subgraph of Bioconductor dependencies based on specific packages |
| subgraphByDegree | Create a subgraph of all packages within a given degree of a single package |
The biocBuildReport function gathers information from the Bioconductor build report site and can be used, for example, to summarize the “build status” for all Bioconductor pacakages.
buildrep = biocBuildReport(version = "3.9") table(buildrep$stage, buildrep$result) ## ## ERROR OK skipped TIMEOUT WARNINGS ## buildbin 2 3352 70 0 0 ## buildsrc 93 5057 0 5 0 ## checksrc 57 4181 98 8 811 ## install 39 5116 0 0 0
These data are useful to developers to track the health of their software either programmatically or via a searchable, sortable table from the problemPage function.
As an alternative to basic web browser search and the Bioconductor online software list, the biocExplore function offers interactive and graphical approach to package browsing (see Figure 2). The biocExplore widget allows browsing packages under different biocViews, Bioconductor’s software catergory tags. This interactively visualises the relative number of downloads each package has under different biocViews, allowing users to quickly determine which packages are most commonly used for different analysis tasks.

Bubbles are sized based on download statistics. Hovering over a bubble will give download number while clicking on a bubble will pop up a package details page, including a link to the package landing page.
The Bioconductor package ecosystem is, by design, highly interconnected via package dependencies. Several functions in the BiocPkgTools package provide examples of package dependency graph creation and visualization. Figure 3 displays packages within one degree of dependency relationship of the GEOquery package.
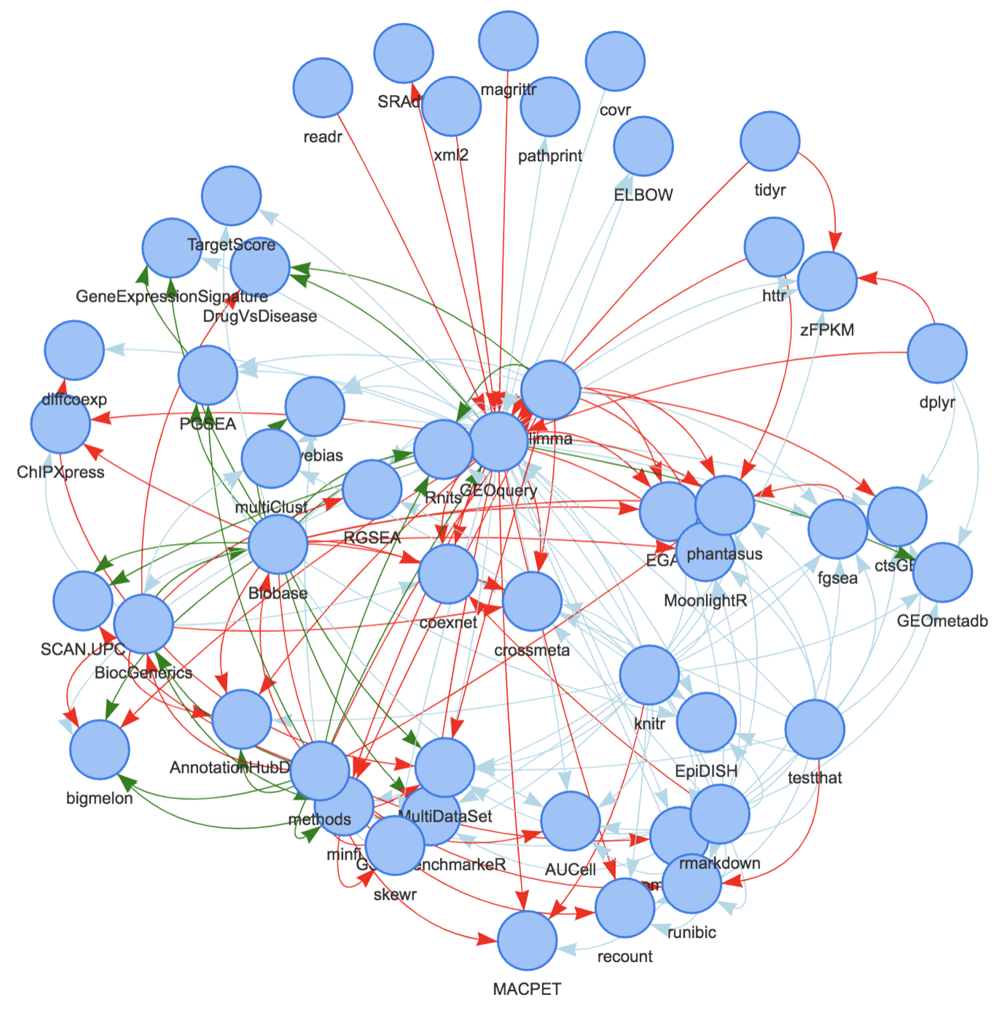
Links are colored based on type (Suggests [light blue], Depends [green], and Imports [red]) and arrows point to the “dependent” package.
The BiocPkgTools package comprises a set of functions for accessing software metadata from the growing collection of Bioconductor packages. For software developers, this metadata can be useful for tracking package build status and the health of package dependencies. Easy access to descriptive package metadata for all Bioconductor software resources can empower researchers or users interested in text mining, custom package search, or analysis of the existing software ecosystem. BiocPkgTools can provide easy access to metrics of Bioconductor sofware usage that are increasingly being incorporated into funding and promotion decisions.
All data accessed and used by the BiocPkgTools package are publicly available and are updated regularly at the Bioconductor project.
Software available from: https://bioconductor.org/packages/BiocPkgTools
Source code available from: https://github.com/seandavi/BiocPkgTools
Archived source code as at time of publication: https://doi.org/doi:10.18129/B9.bioc.BiocPkgTools4
License: MIT License
Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Human Genome Research Institute of the National Institutes of Health under award number U41HG004059, the National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health under award numbers U24CA180996 and U01CA214846-02, and the Center for Cancer Research, part of the Intramural Research Program at the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health. Part of this work was performed on behalf of the SOUND Consortium and funded under the EU H2020 Personalizing Health and Care Program, Action contract number 633974.
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Is the rationale for developing the new software tool clearly explained?
Partly
Is the description of the software tool technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of the code, methods and analysis (if applicable) provided to allow replication of the software development and its use by others?
Yes
Is sufficient information provided to allow interpretation of the expected output datasets and any results generated using the tool?
Partly
Are the conclusions about the tool and its performance adequately supported by the findings presented in the article?
Partly
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Statistic, Bioinformatics, Computer Science, Scientific Computations
Is the rationale for developing the new software tool clearly explained?
Partly
Is the description of the software tool technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of the code, methods and analysis (if applicable) provided to allow replication of the software development and its use by others?
Yes
Is sufficient information provided to allow interpretation of the expected output datasets and any results generated using the tool?
Partly
Are the conclusions about the tool and its performance adequately supported by the findings presented in the article?
Yes
Competing Interests: I am a co-author with VJC and MTM on https://doi.org/10.1101/590562
Reviewer Expertise: Software development, Bioinformatics
Is the rationale for developing the new software tool clearly explained?
Yes
Is the description of the software tool technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of the code, methods and analysis (if applicable) provided to allow replication of the software development and its use by others?
Partly
Is sufficient information provided to allow interpretation of the expected output datasets and any results generated using the tool?
Yes
Are the conclusions about the tool and its performance adequately supported by the findings presented in the article?
Yes
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: biostatistics, bioinformatics
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|
Version 1 29 May 19 |
read | read | read |
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Comments on this article Comments (0)