Keywords
Systems Biology, Metabolic Maps, Pathways, SVG, Metabolism, Data Visualization, Omics Data
Systems Biology, Metabolic Maps, Pathways, SVG, Metabolism, Data Visualization, Omics Data
The field of systems biology is based on the integration of data from different biological fields, e.g. transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, modelling, to gain a detailed understanding of an organism. However, the data integration is still challenging to date. In particular, correlating transcriptome or proteome data to metabolome data requires careful revision based on expert knowledge of metabolic pathways and intensive manual work (Cavill et al., 2016). Therefore, easily accessible tools are needed to help during analysis and interpretation of multi-omics data. When one tries to understand metabolic changes, pathway maps are often used for guidance (Cavill et al., 2016). However, the number of pathway maps in scientific publications is large, as is the diversity. Solely the TCA cycle was drawn hundreds of times, being one of the most conserved pathways among all domains of life. However, even such conserved pathways exhibit differences among species: the gut pathogen Clostridioides difficile uses an incomplete TCA cycle (Dannheim et al., 2017) and some Cyanobacteria use a TCA cycle with an additional GABA shunt and a variety of anaplerotic reactions (Will et al., 2019). Conclusively, there are pathway maps that can be used for a broad range of different organisms while others are exclusive for a few species. For this reason, single comprehensive pathway maps, e.g. the KEGG maps, the BRENDA pathway maps, or printed pathway maps (Michal & Schomburg, 2013), have their limitations: the maps cannot provide organism- or group-specific modifications. Moreover, a general map will not contain pathways that are exclusive for small groups of organisms or are currently incompletely understood. For visualization of multi-omics data, a specific map is required both, regarding the organism and the underlying scientific question. Here we present MetaboMAPS (Helmecke, 2020), a novel web-based tool that on one hand, serves as a platform to share metabolic pathway maps in an organism-dependent manner. On the other hand, MetaboMAPS assists during interpretation of metabolism-associated data by visualizing experimental data sets on pathway maps.
PHP is used to access an internal SQL database and to handle file and user management. In addition, a user-friendly web interface is integrated to handle pathway exploration and user interactions. The pathways can be uploaded, stored and downloaded in SVG format. SVG manipulation, including zoom, editing, and plotting of data, is done with the JavaScript Library D3. Hosting, infrastructure maintenance, and issue tracking is provided by the enzyme database BRENDA.
MetaboMAPS (Helmecke, 2020) can be accessed with every modern browser. Log-in is required for upload, editing, and sharing of pathways, but not for exploring pathways, data visualization and downloads.
MetaboMAPS (Helmecke, 2020) is a platform where users can upload individual metabolic pathways and release them for the scientific community. In this process, the pathway gets a unique accession number for reference in publications. Furthermore, the user can link pathways to publications. If the pathway map includes unpublished information, it can be uploaded in confidential mode. In this way, the pathway can be shared with specified colleagues and used for data visualization, but is not available for the general public. Pathways can be found by searching category, name, assigned identifier (e.g. EC number, locus tag), or accession. A unique feature of MetaboMAPS is that uploaded maps must not follow strict conventions as other tools require. The style, detail level and content of the maps is according to the scientist’s needs, and since the maps can be downloaded and modified, they can also be adjusted by other users. Pathway rating and the possibility to add comments increase the quality of uploaded pathways via community contributions. In this way, MetaboMAPS does not compete with but complements curated, comprehensive maps that are already well established. It offers a niche for tentative, novel or incomplete pathways to support ongoing research beyond common knowledge. Since MetaboMAPS creates reproducible, customizable visualizations of high quality, it is suitable to generate publication-ready figures with little effort.
Each pathway is associated with one or more organisms. In fact, it is possible to add the same pathway to hundreds of different organisms. An organism overview shows all pathway maps that are associated to a selected organism. On the other hand, the pathway overview page displays all background information, such as a list of authors, the pathway description, links to publications, and all organisms that are associated to this pathway. The pathways and information are also easily accessible on mobile devices.
Users can upload their own metabolic pathways in SVG format. We chose this particular format because it can be displayed in every modern browser, can be easily manipulated, is completely scalable, and of small file size. Additionally, SVG-files can be exported from every program that users eventually use to draw a metabolic pathway (e.g. Inkscape, Adobe Illustrator, Microsoft Powerpoint, LibreOffice Impress) and users can continue to work with their preferred software.
A unique and highly useful feature of MetaboMAPS is the possibility to visualize experimental data on metabolic pathways. Suitable data sets include but are not limited to transcriptomic, proteomic, metabolomic studies, flux distributions, 13C-flux measurements and others. The process for sharing pathway maps and using them for visualization is shown in Figure 1. The first step is the upload of an existing metabolic pathway in SVG format (Figure 1A). Afterwards, the user can add further information and assign the pathway to a pathway category. In the second step, an intuitive online editor is used to draw plot boxes (Figure 1B), which define the positions where the experimental data should be visualized. Each plot box can be assigned to one or more identifiers, either organism-specific (e.g. locus tags, GIs) or general (e.g. EC numbers, metabolite names). Data from the BKMS (Lang et al., 2011) and BRENDA (Jeske et al., 2019) databases are used to provide auto-completion of metabolites and enzymes, synonym matching, and cross-linking identifiers to other databases, e.g. BRENDA, KEGG, and MetaCyc. The identifier connects a row in the uploaded data set to a specific plot box. In the third step, any type of numerical data can be loaded in the browser and is visualized in the respective plot box (Figure 1C). Data must be in CSV-format, containing the identifiers that connect the data to plot boxes in the first row. Different types of visualization, like colour scales, a number of plot types (e.g. bar charts, line charts, heat maps), and other visual settings offer a high degree of customization. In the end, the pathway including the data visualization as well as legends can be downloaded in SVG or PNG-format.
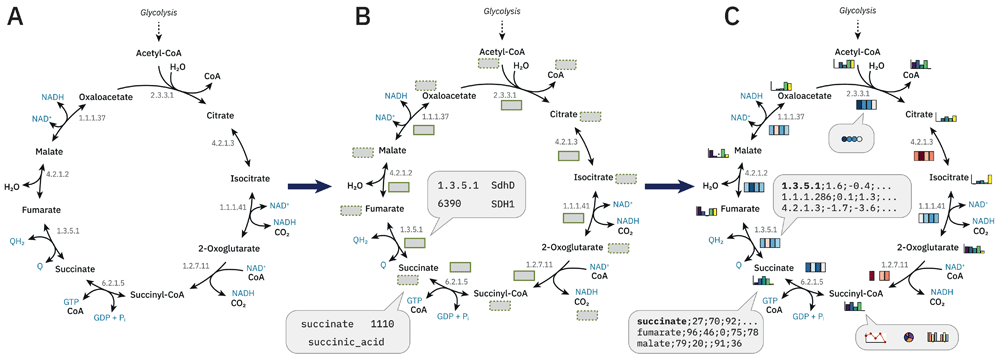
(A) Upload the metabolic pathway in SVG format. Alternatively, you can use an existing pathway. (B) Draw plot boxes for metabolite (dashed border) and reaction (solid border) associated data. Assign identifiers to each plot box (e.g. EC numbers, locus tags, GI, metabolite synonyms, database IDs). (C) Load your own data set (as CSV file) and visualize reaction and metabolite dependent data simultaneously.
In summary, MetaboMAPS (Helmecke, 2020) is a platform for sharing metabolic pathway maps and visualizing data in a metabolic context. It encourages scientists to share individual pathway maps without strict conventions and offers customizable and reproducible visualizations of experimental data. It will grow in collaboration with the community and by further development by the BRENDA team.
All data underlying the results are available as part of the article and no additional source data are required.
Software available from: https://metabomaps.brenda-enzymes.org.
Source code available from: https://github.com/JuliaHelmecke/MetaboMAPS.
Archived source code at time of publication: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3742817 (Helmecke, 2020).
License: GNU General Public License v3.0 or later.
We are grateful to Sabine Eva Will, Tobias Ludwig, Carsten Reuse, and Jacqueline Wolf for excessive beta testing and useful feedback. We thank the BRENDA team for supporting this project and for helpful discussions.
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Is the rationale for developing the new software tool clearly explained?
Yes
Is the description of the software tool technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of the code, methods and analysis (if applicable) provided to allow replication of the software development and its use by others?
Yes
Is sufficient information provided to allow interpretation of the expected output datasets and any results generated using the tool?
Yes
Are the conclusions about the tool and its performance adequately supported by the findings presented in the article?
Yes
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Computational Biology, Systems Biology, Data Integration
Is the rationale for developing the new software tool clearly explained?
Partly
Is the description of the software tool technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of the code, methods and analysis (if applicable) provided to allow replication of the software development and its use by others?
Yes
Is sufficient information provided to allow interpretation of the expected output datasets and any results generated using the tool?
Yes
Are the conclusions about the tool and its performance adequately supported by the findings presented in the article?
Yes
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: multi-omics integration, pathway analysis, omics data visualisation.
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |
|
Version 2 (revision) 17 Jul 20 |
read | |
|
Version 1 24 Apr 20 |
read | read |
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Comments on this article Comments (0)