Keywords
Lipoma, Orbit, Histopathology, MRI, Surgery.
Introduction
Orbital lipoma is an extremely rare tumor, representing less than 1% of all orbital tumors. We review the literature and describe the presentation, the differential diagnosis and the management of this tumor.
Case report
We report the case of a 63-year-old patient who was referred for a diplopia with recent hemi-cranial headache. Physical examination showed no exophthalmos nor decrease in visual acuity. The patient complained of diplopia on elevation and oculomotricity examination showed limited elevation of the right eye. The Hess Lancaster test was in favor of a limited course of the right inferior rectus muscle. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed a fusiform tissue process in the right inferior rectus muscle with a fatty signal. A complete excision of the tumor was performed by a trasncunjonctival approach. Cytopathological examination was consistent with a pleomorphic lipoma. The postoperative period was uneventful. The definitive histopathologic diagnosis was a lipoma. The postoperative Magnetic resonance imaging showed the complete disappearance of the lesion. With 3 years of follow up, there is no sign of recurrence or ocular motility trouble.
Conclusion: Lipomas are rare tumors in the orbit. The clinic is variable depending on the size and the site. The clinical diagnosis is difficult to make. Only histology allows the final diagnosis.
Lipoma, Orbit, Histopathology, MRI, Surgery.
The appearance of pleomorphic lipoma in imaging studies is variable and not pathognomonic for diagnosis, as variation in the ratio of adipose to non-adipose components results in a wide spectrum of imaging features. MRI features such as the hyper-vascularized tissue process and the hypointense T1 and hyperintense T2 character are explained by the presence of a high proportion of non-adipose elements pleomorphic lipoma. The small size of the tumor and its early diagnosis explain the absence of exophthalmos.
In this new version, we have replied to reviewers' comments and made the following changes:
We've added a new reference (7) that also confirms our MRI findings, which show the tumor to be hypointense on T1 and hyperintense on T2.
The expression "trasncunjonctival" has been replaced by " transconjunctival".
We have replaced the expression "cytopathological" by "histopathological".
This symptom "hemi-cranial headache" has been added in the case report section.
We've added a new expression “General examination revealed no other lipoma locations”
We've added a new expression “bilateral diplopia “
See the authors' detailed response to the review by Mehdi Hasnaoui
Lipomas are benign tumors, rare in the orbit, representing less than 1% of all orbital tumors. They pose a differential diagnosis with a variety of other expansive orbital masses.1 We report a new case, review the literature and discuss the clinicopathological and radiological features, the differential diagnosis and the management of this entity.
A 63-year-old unemployed Tunisian woman, with no previous personal or family pathological history, presented with a diplopia with recent hemicranial headache evolving for two weeks. Physical examination showed no exophthalmia and no decrease in visual acuity. Furthermore, it revealed bilateral diplopia on elevation. Oculomotricity examination showed limited elevation of the right eye, which was confirmed by the Hess Lancaster test that revealed a limited course of the right inferior rectus muscle. General examination revealed no other lipoma locations. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed a fusiform and hyper-vascularized tissue process located in the right inferior rectus with fatty signal. The tumor was hyperintense on spin-echo T2-weighted images (Figure 1) and hypointense on spin-echo T1-weighted images (Figure 2).
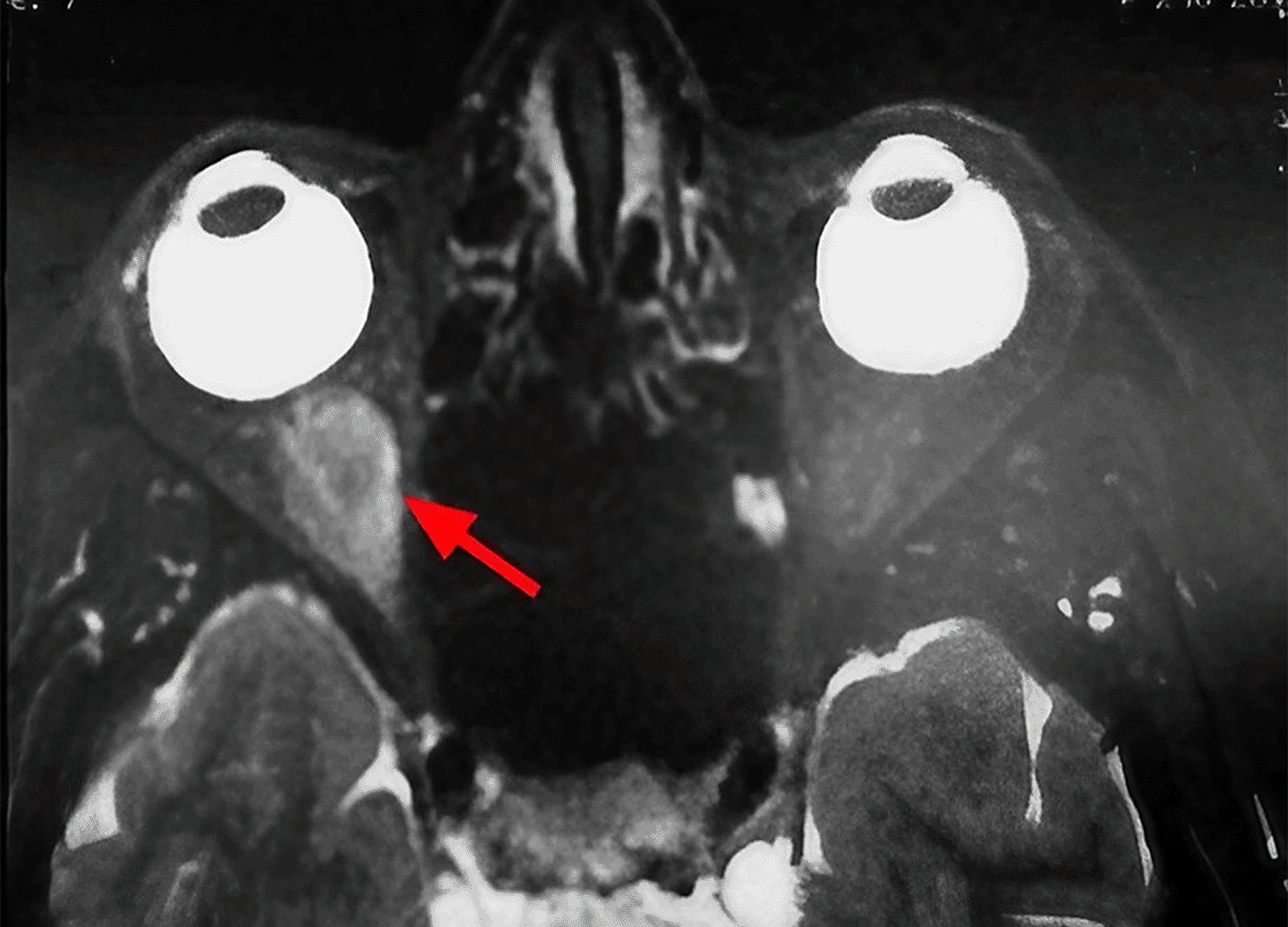
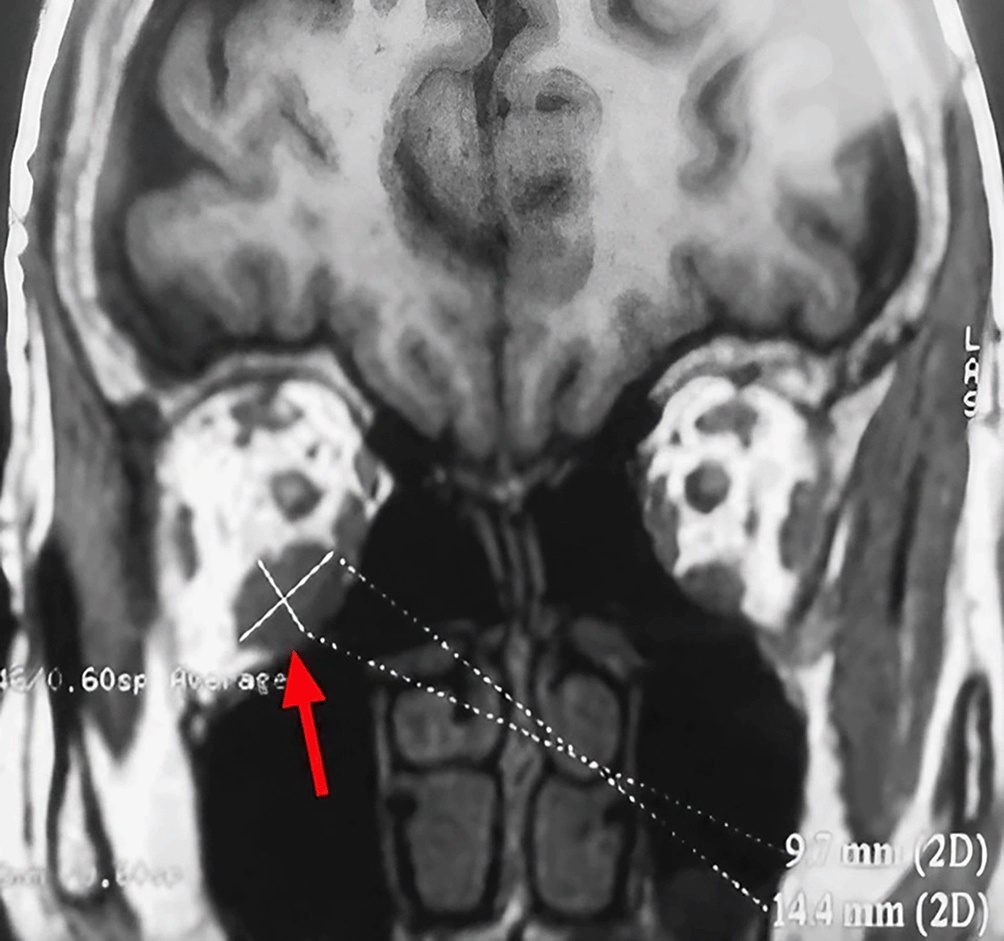
These findings suggested various diagnosis; lipoma, inflammatory process, lymphoma and malignant tumor.
We performed a right inferior transconjunctival orbitotomy and excisional biopsy under general anesthesia. Peroperatively, we discovered an encapsulated mass of fatty tissue, thus complete excision was made. No adherences or involvement of adjacent structures occurred. The specimen was well circumscribed and slightly firmer than normal adipose tissue, with a yellow surface (Figure 3).
Histologic examination was consistent with a pleomorphic lipoma. The postoperative period was uneventful. Immediately after the operation, the patient reports the resolution of his diplopia. Postoperative MRI images demonstrated the complete resolution of the tumor (Figure 4). With 3 years of follow up, there is no sign of recurrence or ocular motility impairment.
Orbital lipoma is the most common mesenchymal soft tissue tumor. However, it is rarely found in the orbit despite the presence of abundant adipose tissue in the intraorbital space.2,3 A review of the largest series of orbital tumors revealed a very low incidence of lipomas.4 Shields et al. reported only two cases of lipomas in a review of 1264 cases of orbital tumors, indicating the rarity of this entity.5 On physical examination, the diagnosis is often difficult to suggest. These tumors are often asymptomatic.
However, they can cause severe morbidity by causing progressive and painless exophthalmos, which is occasionally coupled with diplopia or ocular motility defects6 such as was observed in our patient.
Orbital lipoma exceptionally leads to a compressive neuropathy responsible for a significant decrease in visual acuity, an alteration of the afferent photomotor reflex and the visual field constriction.1 Imaging based on computed tomography (CT) scanning and MRI is essentially useful in ascertaining determining the exact seat, size and relationship to the orbit content. The fatty signal is characteristic on CT sequences. Furthermore, as was found in our patient, the tumor is hypointense on spin-echo T1-weighted images and hyperintense on spin-echo T2-weighted images.7
Histology is essential for definitive diagnosis of pleomorphic lipoma. An important histologic criterion is the presence of a mixture of fat cells, pleomorphic cells and in particular floret-like multinucleated giant cells embedded in a myxoid stroma.8 That concorded with the histological result of our case. Differential diagnosis of this tumor became more important because the number of reports about some other tumors of similar morphology, are increasing. Pleomorphic lipoma may be confused with lipomatous hemangiopericytoma, myofibroblastoma or even malignant tumors such as rhabdomyosarcoma, myxoid malignant fibrous histiocytoma and liposarcoma.9,10 Surgical excision of an orbital lipoma is not only recommended for symptomatic cases such as our patient's clinical presentation but also to exclude malignancy.11 In addition, as was noted in our patient, the long-term outcome after surgery is considered excellent.12
This case highlights the importance of orbital imaging in the context of diplopia without obvious cause to rule out an intraorbital lipoma. Nevertheless, this association remains rare and requires further documentation of cases.
Lipomas are benign soft tissue tumors, rarely located in the orbit. The clinical presentation is variable depends on the size and the intraorbital site. The histology makes the definitive diagnosis and may precisely identify the variant.
Written informed consent for publication of their clinical details and/or clinical images was obtained from the patient.
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Is the background of the case’s history and progression described in sufficient detail?
Yes
Are enough details provided of any physical examination and diagnostic tests, treatment given and outcomes?
Partly
Is sufficient discussion included of the importance of the findings and their relevance to future understanding of disease processes, diagnosis or treatment?
Partly
Is the case presented with sufficient detail to be useful for other practitioners?
Yes
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Orbit and Oculoplasty
Is the background of the case’s history and progression described in sufficient detail?
Yes
Are enough details provided of any physical examination and diagnostic tests, treatment given and outcomes?
Partly
Is sufficient discussion included of the importance of the findings and their relevance to future understanding of disease processes, diagnosis or treatment?
Yes
Is the case presented with sufficient detail to be useful for other practitioners?
Yes
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Ophthamology
Is the background of the case’s history and progression described in sufficient detail?
Yes
Are enough details provided of any physical examination and diagnostic tests, treatment given and outcomes?
Yes
Is sufficient discussion included of the importance of the findings and their relevance to future understanding of disease processes, diagnosis or treatment?
Partly
Is the case presented with sufficient detail to be useful for other practitioners?
Yes
Competing Interests: This reviewer is affiliated at Tahar Sfar University Hospital, which is the same as the authors of this article. This was not declared as a conflict of interest at the time of publication of this report but this reviewer can confirm that this did not influence the impartiality of this report.
Reviewer Expertise: Oncology, sinus and nasal cavity surgery, facial bone imaging
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|
Version 2 (revision) 27 Oct 23 |
read | ||
|
Version 1 19 Jun 23 |
read | read | |
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Comments on this article Comments (0)