Keywords
Catalan Initiative for the Earth Biogenome Project, Birds, Phasianidae, Genome assembly, Reference Genome, Aves
This article is included in the Genomics and Genetics gateway.
This article is included in the Nanopore Analysis gateway.
The red-legged partridge (Alectoris rufa) is a socio-economically important game bird in southern Europe. Despite previous efforts, achieving a high-quality, chromosome-level genome assembly has remained challenging. Here, we present a de novo phased, gapless reference genome of A. rufa, combining Nanopore long-read sequencing and Hi-C data from both sexes. The assembly resolves 40 nuclear chromosomes (38 autosomes and the 2 sex chromosomes, Z and W) and the mitochondrial genome, achieving chromosome-scale resolution and 99.1% completeness based on the Aves BUSCO dataset. This high-quality genome provides a critical resource for studying genetic diversity, sex-linked traits, and evolutionary adaptations.
Catalan Initiative for the Earth Biogenome Project, Birds, Phasianidae, Genome assembly, Reference Genome, Aves
The red-legged partridge (Alectoris rufa) is a species of significant ecological and economic importance, particularly in southwestern Europe,1 where it is a key game bird for hunting and rural economies. Despite its prominence, wild populations are declining due to habitat degradation and hunting pressure, leading to increased reliance on farm-reared partridges to meet hunting demands.
Limited insights into the bird’s evolution were obtained from the analysis of previous efforts that created assemblies with high to moderate genome fragmentation.1–4 That fragmentation limits our ability to fully explore the genomic basis of traits relevant to both wild and farmed populations, such as behavior, physiology, and adaptation.
Here, we present a de novo high-quality, chromosome-level genome assembly of A. rufa, incorporating both macro- and micro chromosomes, sex chromosomes, and the mitochondrial chromosome. We created this assembly through a hybrid approach combining long-read sequencing technologies (Oxford Nanopore) with Hi-C Illumina data, significantly improving contiguity, accuracy, and completeness over previous efforts. The inclusion of sex chromosomes provides a critical resource for understanding sex-linked traits and genetic diversity, which are essential for both conservation and breeding programs.
This chromosome-level assembly provides a foundation for identifying genetic markers associated with desirable traits, facilitating the development of genomic tools to ensure the genetic purity of wild partridges and enhancing the sustainability and productivity of farmed partridges.
Table 1 provides the details on all software tools used for the assembly of the A. rufa genome.
| Tool | Version | Parameters | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poreshop | 0.2.4 | Default | https://github.com/rrwick/Porechop |
| Fastp | 0.23.4 | Default | 8 |
| NextDenovo | 2.5.21 | Default | 21 |
| NextPolish | 1.4.0 | Default | 6 |
| purge_haplotigs | 1.1.3 | -wind_min 10000 | 7 |
| Gfastats | 1.3.6 | Default | 15 |
| BUSCO | 5.7.1 | -l aves_odb10 | 16 |
| HapHiC | 1.0.6 | --correct_nrounds 2 max_inflation 10 --bin_size 200 | 9 |
| Juicebox | 1.6 | Default | 22 |
| Ragtag | v2.1.0 | Default | 11 |
| BlobToolKit | 2.6.2 | Default | 17 |
We randomly selected a wild female from Ciudad Real (central Iberian Peninsula) and a farm-raised male from Lleida (northeastern Iberian Peninsula). They were both anesthetized by inhaling isoflurane, before blood samples (0.25 ml) were drawn from the brachial vein of the wing using a sterile syringe with a 20G needle. After the procedure, the birds were allowed to recover and closely monitored for any signs of distress. The protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee on Animal Experimentation of the University of Lleida in 2016 (Ref. CEEA 09-06/16).
High molecular weight (HMW) DNA was extracted from that blood for library preparation with the genomic DNA sequencing kit of Oxford Nanopore technology (ONT) as described in2 and then sequenced the libraries using a GridION platform.
Chromatin conformation capture sequencing (Hi-C) libraries were prepared using the Hi-C High-Coverage kit (Arima Genomics) in the Metazoa Phylogenomics Lab (Institute of Evolutionary Biology [CSIC-UPF]). Sample concentration was assessed by Qubit DNA HS Assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and library preparation was carried out using the ACCEL-NGS 2S PLUS DNA LIBRARY KIT (Swift Bioscience) and using the 2S Set A single indexes (Swift Bioscience). We carried out library amplification with the KAPA HiFi DNA polymerase (Roche). The amplified libraries were sequenced on the NovaSeq 6000 (Illumina) with a read length of 2x151bp and a ~60Gb coverage, resulting in ~400M reads per library.
Nuclear genome assembly was performed using Nanopore raw data from one female and one male, as described in our previous work.2 We implemented and used the Dorado base caller5 to improve per-base quality of the original noisy ONT raw reads.
Assembly was carried out with NextDenovo pipeline.6 The yielded contig-level assembly was polished using the NextPolish v1.4.06 based on the ONT data. Haplotypic duplications were identified and removed using purge_haplotigs.7 The purge_haplotigs contigs were used to filter out mitochondrial genome form the nuclear contig, as described below.
Fastp8 was used to process the Hi-C removing low quality and duplication raw reads and HapHiC9 was used on the Hi-C data to scaffolds the purged contigs. HapHiC is an allele-aware tool that enables scaffolding the haplotype-phased genome assembly into chromosome-scale pseudomolecules without the need for a preexistent reference genome. Chromosome assignment results were validated based on their synteny with respect to the Gallus gallus reference genome GCA_024206055.2,10 using Ragtag v2.1.0.11 Note that RagTag orders, orients, and joins sequences with gaps without altering the input query. We performed a final round of gap filling with Medaka12 using the ONT raw reads. This was sufficient to generate the final gapless genome and capture the chromatin signal of both sex chromosomes of A. rufa. We independently assembled the male and female autosomes using sex-specific Hi-C data. We choose the autosome with the highest quality as the reference. However, due to the lower quality of the male Hi-C data, we used only female Hi-C data to assemble the sex chromosomes.
The mitogenome was extracted from the polished and purged nuclear contigs using a combined approach. First, the get_organelle_from_assembly.py script from GetOrganelle13 was applied to the nuclear contigs, producing an uncircularized, gapped sequence. Next, Illumina short reads were used to circularize the mitogenome assembly. For annotation, MitoZ v3.614 was employed. The genome assembly metrics were estimated using the Gfastats tool.15 The BUSCO completeness score16 was calculated within the BlobtoolKit2.17
We sequenced the genome of two A. rufa individuals, one male and one female. We summarize the statistics and deposition data in Table 2. We generated a total of 60-fold coverage data in Nanopore Ultra-long reads (N50 20 kb). We also generated 60-fold coverage data in Illumina NovaSeq6000 Hi-C sequencing. We scaffolded the primary assembly contigs from nanopore sequences with chromosome conformation HiC data. We also performed a final quality control step for the HiC scaffolds by validating them through synteny comparison to the Gallus gallus reference genome. The final assembly has a total length of 1.38Gb in 46 sequence scaffolds with scaffold/contig N50 of 92 Mb. 99.91% of the assembly sequence was assigned to 40 chromosomal-level scaffolds representing 38 autosomes plus the W and Z sex chromosomes ( Figures 1, 2, 3, and 4 and Table 2). The mitochondrial genome was 16.694 kbp long and contained 38 genes, including 22 tRNAs and 14 protein coding genes, with a GC percentage of 45.27 % ( Figure 5). The genome has a BUSCO completeness of 99.1% using the aves_odb10 reference dataset of orthologue single copy genes. The statistics for each chromosome, together with their ENA accession numbers are given in Table 3.
| Project accession data | |
|---|---|
| Assembly identifier | A_rufa_assembly2 |
| Species | Alectoris rufa |
| Specimen | Arufa2401F |
| NCBI taxonomy ID | 9079 |
| BioProject | PRJNA1164475 |
| Biosample ID | SAMEA114518447 |
| Isolate information | Blood tissue (female & male) |
| Raw data accessions | |
| Nanopore raw data | ERR12165669, ERR12165668, ERR12165667, ERR12165666, ERR12165665, ERR14375934 |
| Hi-C Illumina | ERR14648049, ERR14648048 |
| Genome assembly | |
| Assembly accession | GCA_963854145 |
| Span (Mb) | 1,233 |
| Number of contigs | 46 |
| Contig N50 length (Mb) | 92 |
| Number of scaffolds | 46 |
| Scaffold N50 length (Mb) | 92 |
| Longest scaffold (Mb) | 198 |
| BUSCO* genome score | C:99.1%[S:99.0%,D:0.1%], F:0.1%,M:0.8%,n:8338 |

The distribution of chromosome lengths is shown in dark grey with the plot radius scaled to the longest chromosome present in the assembly shown in red.
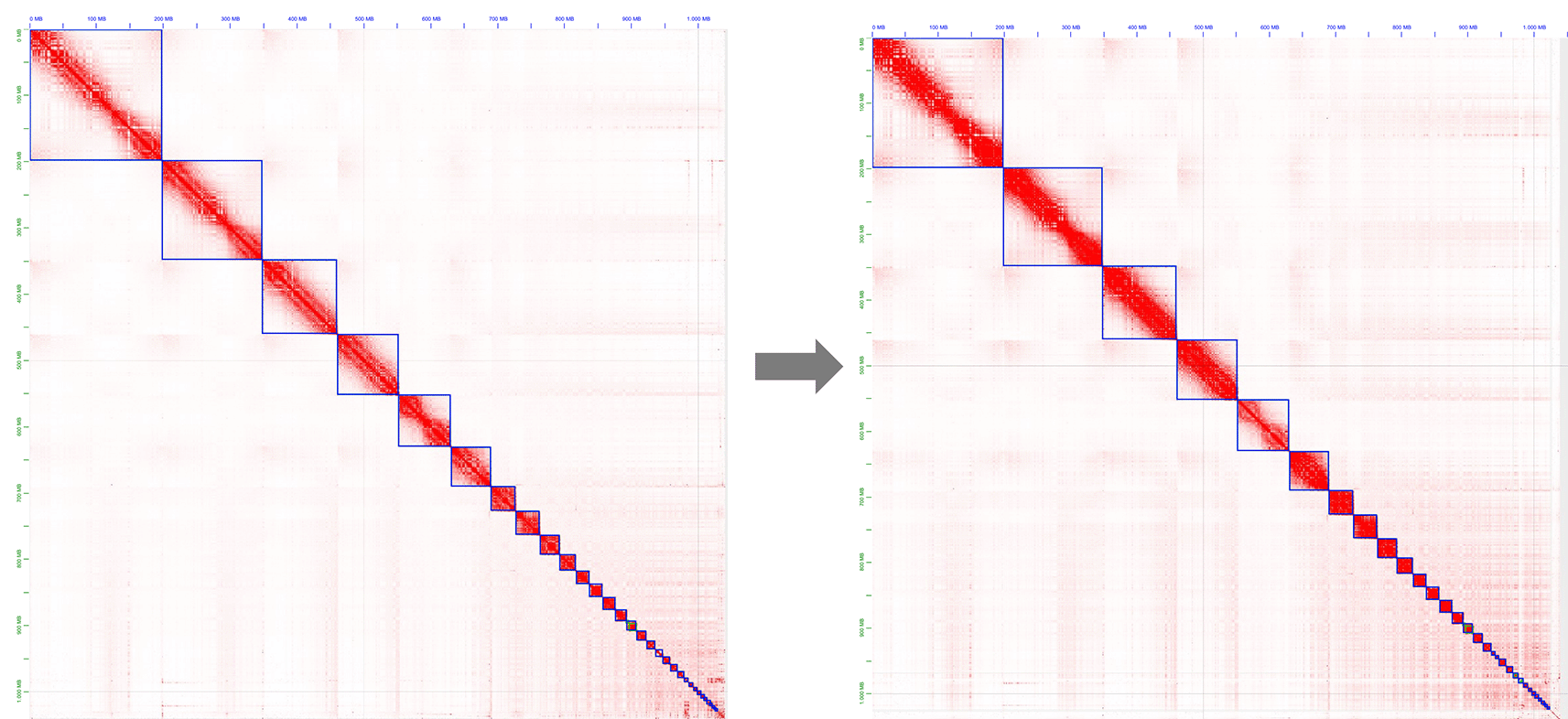
Left-hand side: Original mapping. Right-hand side: Contact map after manual curation.
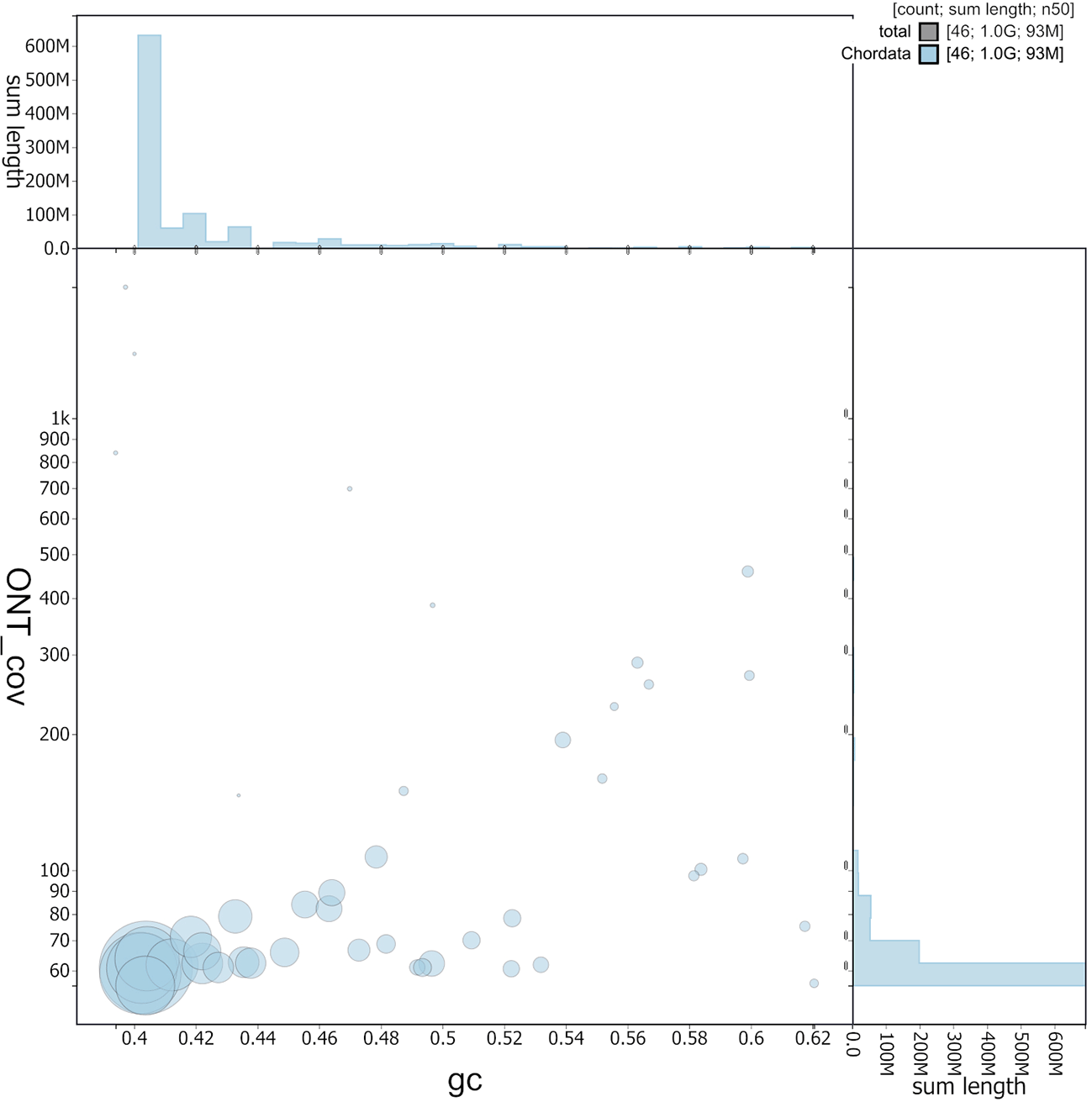
Circles are sized in proportion to scaffold length. Histograms show the distribution of scaffold length sum along each axis. Y-axis ontogene covariance (Chordata).

The grey line shows cumulative length for all sequences.
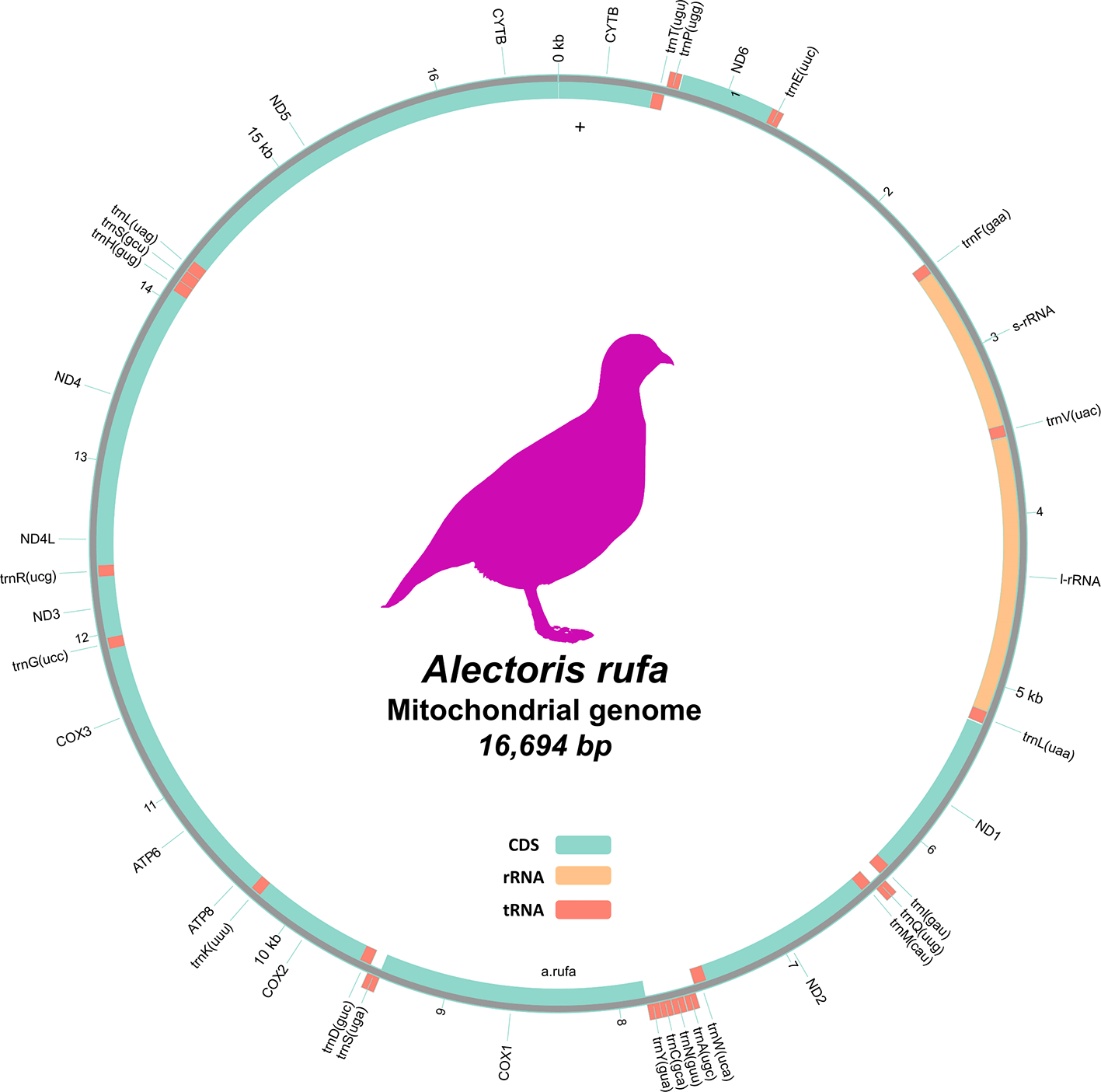
The outermost track displays the annotated genes features. The middle track shows the coverage depth from ONT sequencing in 100 bp windows. The innermost track illustrates the GC content across the mitogenome, also in 100 bp windows.
Figshare: ARRIVE Checklist for the Genome Note “The genome sequence of the red-legged partridge, Alectoris rufa Linnaeus 1758”, https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.29501561.v123
This project contains the following data:
ARRIVE Author Checklist - E10 only.pdf
Data are available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license (CC-BY 4.0).
ENA Chromosome Sequences: All sequence data is deposited at the ENA, under accession numbers GCA_963854145.2, OZ238766.1, OZ238770.1, OZ238768.1, OZ238769.1, OZ238770.1, OZ238771.1, OZ238772.1, OZ238773.1, OZ238774.1, OZ238775.1, OZ238776.1, OZ238777.1, OZ238778.1, OZ238779.1, OZ238780.1, OZ238786.1, OZ238787.1, OZ238788.1, OZ238789.1, OZ238790.1, OZ238791.1, OZ238792.1, OZ238793.1, OZ238794.1, OZ238795.1, OZ238796.1, OZ238797.1, OZ238798.1, OZ238799.1, OZ238800.1, OZ238801.1, OZ238802.1, OZ238803.1, OZ238804.1, OZ238805.1, OZ238806.1, OZ238781.1, OZ238782.1, OZ238783.1, OZ238784.1, and OZ238785.1. NCBI raw data sequences: Nanopore raw read data are available via NCBI (Bioproject accession numbers PRJNA1050768, Biosample accession numbers: ERS16499794, ERS16499793, ERS16499792, ERS16499791, ERS16499790, SRX23440923).
Links to the data:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/105076818
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/272481228118
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Are the rationale for sequencing the genome and the species significance clearly described?
Yes
Are the protocols appropriate and is the work technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of the sequencing and extraction, software used, and materials provided to allow replication by others?
Yes
Are the datasets clearly presented in a usable and accessible format, and the assembly and annotation available in an appropriate subject-specific repository?
Yes
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Genomics, parasitology
Are the rationale for sequencing the genome and the species significance clearly described?
Yes
Are the protocols appropriate and is the work technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of the sequencing and extraction, software used, and materials provided to allow replication by others?
Partly
Are the datasets clearly presented in a usable and accessible format, and the assembly and annotation available in an appropriate subject-specific repository?
Yes
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: genomics, genome assembly, reference genomes, population genomics, conservation genomics, biodiversity genomics, bioinformatics
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |
|
Version 1 02 Sep 25 |
read | read |
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Comments on this article Comments (0)