Introduction
The current Ebola virus outbreak is one of the largest outbreaks of its kind in history and the first in West Africa. By January 14, 2015, a total of 21296 probable and confirmed cases, including 8429 deaths from Ebola virus disease (EVD), had been reported from five countries in West Africa - Guinea, Liberia, Nigeria, Senegal, and Sierra Leone (http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/148237/2/roadmapsitrep_14Jan2015_eng.pdf?ua=1). EVD with a high case-fatality rate of 40% and with currently no approved vaccine or therapy, represents a major public health threat.
In response to the current Ebola virus outbreak, the international community has urged for accelerated development of drugs against EVD but also has endorsed the clinical use of unregistered treatments for Ebola1. Conventional time and the money consuming approach of drug development (> 10 years; > 2 billions $) does not meet the current urgent need for anti-Ebola drugs. Repurposing or repositioning of existing drugs could overcome some of these obstacles and help in the rapid discovery and development of therapeutics for EVD, although this approach does not negate the need for some preclinical studies and clinical trials for validation of the proposed indications. Recently, results of two large repurposing screenings of Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drugs have been reported. In the first study, Madrid and co-workers performed in vitro and in vivo (in mice) screening of 1012 FDA-approved drugs and selected 24 candidate entry inhibitors for Ebola virus2. In the second study, 53 inhibitors of Ebola virus infection with IC50 < 10 µM and selectivity index SI > 10-fold have been identified by in vitro screening of 2816 FDA-approved drugs3. In the same study, an additional 95 drugs which are active against Ebola virus infection with IC50 > 10 µM and SI <10-fold were also reported.
Although in vitro and in vivo screening for repurposing/repositioning of existing drugs could significantly accelerate discovery of new drugs these approaches are time-consuming and costly for screening of large drug libraries. Recently, we proposed a novel approach for in silico screening of molecular libraries for drug candidates4–8. This approach, which uses the average quasi valence number (AQVN) and the electron-ion interaction potential (EIIP), parameters determining long-range interaction between biological molecules, might hold a key to overcoming some of these obstacles in experimental screening by significantly reducing the number of compounds which should be in vitro and in vivo tested9.
Herein, 267 approved and 382 experimental drugs, selected by the EIIP/AQVN-based virtual screening of DrugBank (http://www.drugbank.ca), have been proposed as candidate drugs for treatment of EVD. An open access portal allowing screening of molecular libraries for candidate drugs for treatment of EVD was established.
Material and methods
Molecular libraries
For screening of drugs for repurposing to select candidates for Ebola virus entry inhibitors, 1463 approved and 4975 experimental drugs from DrugBank (http://www.drugbank.ca) were screened. For development of the predictive criterion used in this analysis, the learning set (Dataset 1) encompassing 152 drugs which are selected as inhibitors of Ebola virus infection by in vitro and in vivo screening of 3828 FDA-approved drugs2,3, was established. As control data sets 45,010,644 compounds from PubChem (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pccompound) and 49 Ebola virus entry inhibitors collected by data mining of literature and patents, were used. For screening of literature data the NCBI literature database PubMed (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed) was used. For search of patents and patent applications we used the Free Patent Online browser (http://www.freepatentsonline.com).
Drug repurposing screen to identify active compounds that block Ebola entry
Specific recognition and targeting between interacting biological molecules at distances > 5Å are determined by the average AQVN and the EIIP10, which are derived from the general model pseudopotential11,12. These parameters for organic molecules are determined by the following simple equations10:
Where Z* is the average quasi-valence number (AQVN) determined by
where Zi is the valence number of the i-th atomic component, ni is the number of atoms of the i-th component, m is the number of atomic components in the molecule, and N is the total number of atoms. EIIP values calculated according to equation 1 and equation 2 are expressed in Rydberg units (Ry).
Among 3300 currently used molecular descriptors, AQVN and EIIP represent the unique physical properties which characterize the long-range interactions between biological molecules10. Small molecules with similar AQVN and EIIP values interact with the common therapeutic target, which allow establish criterions for virtual screening of molecular libraries for compounds with similar therapeutic properties4–9. Here we develop the EIIP/AQVN-based criterion for virtual screening of molecular libraries for candidate drugs against Ebola virus infection.
Results and discussion
Previously, analyses of the EIIP/AQVN distribution of 45,010,644 compounds from the PubChem database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pccompound) revealed that 92.5% of presented compounds are homogenously distributed within EIIP and AQVN intervals (0.00 – 0.11 Ry) and (2.4 – 3.3), respectively). This domain of the EIIP/AQVN space, encompassing the majority of known chemical compounds, is referred to as the “basic EIIP/AQVN chemical space” (BCS)6. Analysis of the molecular training set (Dataset 1), encompassing 152 small molecule inhibitors of Ebola virus infection selected by in vitro screening of 3828 FDA approved drugs2,3, show that 79% of these compounds are placed within AQVN and EIIP region (2.3 – 2.7) and (0.0829 – 0.0954 Ry), respectively (“Ebola Virus Infection Inhibitors Space”, EVIIS). The AQVN region (2.36 – 2.54) and the EIIP region (0.0912 – 0.0924 Ry) form the part of EVIIS which encompasses 55.5% of all drugs from the learning set (core EVIIS, cEVIS). Literature data mining reveals 49 compounds with experimentally proved activity against Ebola virus infection (Table 1)13–29. Most of these compounds 47 (95.9%) are placed within EVIIS (Table 1). Of note is that EVIIS and cEVIIS domains contain only 14.6% and 6.5% of compounds from PubChem, respectively. This confirms high specificity of clustering of Ebola virus infection inhibitors within the EIIP/AQVN space. Comparison of distributions of Ebola virus infection inhibitors and compounds from PubMed is given in Figure 1.
Table 1. Small-molecule entry inhibitors for Ebola virus.
| Compound | Formula | AQVN | EIIP [Ry] | Reference |
|---|
| Chloroquine | C18H26ClN3 | 2.375 | 0.0941 | 16 |
| Bafilomycin A1 | C35H58O9 | 2.471 | 0.0960 | 17 |
| Cytochalasin B | C29H37NO5 | 2.611 | 0.0810 | 17 |
| Cytochalasin D | C30H37NO6 | 2.676 | 0.0672 | 17 |
| Latruculion A | C22H31NO5S | 2.667 | 0.0693 | 17 |
| Jasplakinolide | C36H45BrN4O6 | 2.674 | 0.0676 | 18 |
| Clomiphene | C26H28ClNO | 2.526 | 0.0926 | 18 |
| Toremifene | C26H28ClNO | 2.526 | 0.0926 | 18 |
| Chlorpromazine | C17H19ClN2S | 2.600 | 0.0829 | 19 |
| Amiodarone | C25H29I2NO3 | 2.567 | 0.0880 | 20 |
| Dronedarone | C31H44N2O5S | 2.578 | 0.0864 | 20 |
| Verapamil | C27H38N2O4 | 2.535 | 0.0917 | 20 |
| Clomiphene | C26H28ClNO | 2.526 | 0.0926 | 21 |
| AY-9944 | C22H28Cl2N2 | 2.370 | 0.0938 | 21 |
| Ro 48-8071 | C23H27BrFNO2 | 2.505 | 0.0940 | 21 |
| U18666A | C25H41NO2 | 2.290 | 0.0849 | 21 |
| Terconazole | C26H31Cl2N5O3 | 2.687 | 0.0644 | 21 |
| Triparanol | C27H32ClNO2 | 2.508 | 0.0941 | 21 |
| Impramine | C19H24N2 | 2.444 | 0.0964 | 22 |
| 3.47 | C34H43N3O5 | 2.635 | 0.0763 | 23 |
| Cytochalasin B | C29H37NO5 | 2.611 | 0.0810 | 24 |
| Cytochalasin D | C30H37NO6 | 2.676 | 0.0672 | 24 |
| Latrunculin A | C22H31NO5S | 2.667 | 0.0693 | 24 |
| Jasplakinolide | C36H45BrN4O6 | 2.674 | 0.0676 | 24 |
| NSC62914 | C31H40O3 | 2.460 | 0.0962 | 25 |
| Compound 1 | C30H38N6O2 | 2.632 | 0.0770 | 26 |
| Compound 2 | C32H46N6 | 2.429 | 0.0963 | 26 |
| Compound 3 | C28H34N6O2 | 2.686 | 0.0635 | 26 |
| Compound 5 | C42H58N10O6 | 2.690 | 0.0635 | 27 |
| Compound 8a | C17H23N3O3 | 2.695 | 0.0621 | 27 |
| Compound 8b | C17H23N3O3 | 2.695 | 0.0621 | 27 |
| Compound 8y | C16H20BrNO2 | 2.610 | 0.0812 | 27 |
| Compound 15h | C15H20JN5O | 2.667 | 0.0693 | 27 |
| Compound 15k | C15H128Br3N5O | 2.667 | 0.0693 | 27 |
| Retinazone | C38H56Na3N5S2 | 2.385 | 0.0947 | 28 |
| Compound 7 | C17H12F4N2 | 2.467 | 0.0647 | 29 |
| Brincidofovir* | C27H52N3O7P | 2.467 | 0.0961 | 30 |
| Hit compound 3 | C25H35N3O2 | 2.494 | 0.0950 | 31 |
| Hit compound 3.1 | C21H24ClN3O2 | 2.667 | 0.0693 | 31 |
| Hit compound 3.2 | C20H29N3O2 | 2.518 | 0.0933 | 31 |
| Hit compound 3.3 | C30H35N3O2 | 2.556 | 0.0894 | 31 |
| Hit compound 3.4 | C25H32N4O3 | 2.656 | 0.0717 | 31 |
| Hit compound 3.5 | C20H23N3O2 | 2.708 | 0.0587 | 31 |
| Hit compound 3.6 | C25H33N3O2 | 2.540 | 0.09913 | 31 |
| Hit compound 3.7 | C22H27N3O3 | 2.691 | 0.0633 | 31 |
| Hit compound 3.18 | C26H37N3O2 | 2.471 | 0.0471 | 31 |
| Hit compound 3.48 | C34H43N3O5 | 2.635 | 0.0763 | 31 |
| Hit compound 3.105 | C34H40N6O2 | 2.658 | 0.0712 | 31 |
| NSC 62914 | C31H39O3 | 2.480 | 0.0957 | 32 |
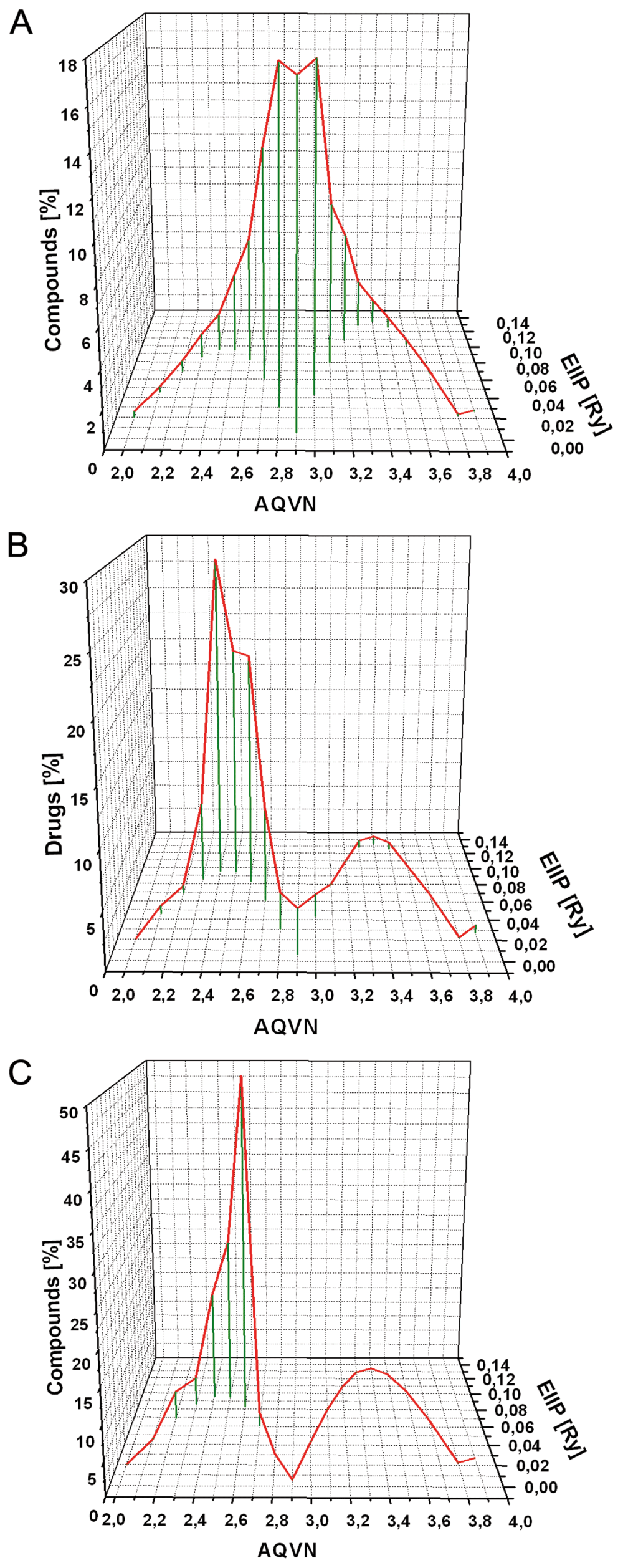
Figure 1. Distribution of compounds according to their average quasivalence number (AQVN) and electron-ion interaction potential (EIIP) values.
(A) 45010644 compounds from the PubChem database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pccompound); (B) FDA-approved drugs which are active against Ebola virus infection (Dataset 1)2,3; (C) Entry inhibitors of Ebola virus (Table 1).
| Drug Name | Formula | AQVN | EIIP [Ry] | Approved Indication |
|---|
| Perhexiline | C19H35N | 2.109 | 0.0479 | Antianginal |
| Methylbenzethonium | C28H44ClNO2 | 2.29 | 0.0848 | Anti-Ulcerogenic |
| Trihexyphenidyl | C20H31NO | 2.302 | 0.0866 | Antiparkinsonian |
| Trihexyphenidyl | C20H31NO | 2.302 | 0.0866 | Antiparkinsonian |
| Drofenine | C20H32ClNO2 | 2.321 | 0.089 | NA |
| Alverine | C20H27N | 2.333 | 0.0904 | antispasmoic |
| Penbutolol | C18H29NO2 | 2.36 | 0.0929 | beta blocker |
| Butriptyline | C21H27N | 2.367 | 0.0935 | Antidepressant |
| Aprindine | C22H30N2 | 2.37 | 0.0938 | antiarrhythmic |
| Halofantrine | C26H30Cl2F3NO | 2.381 | 0.0945 | Antimalaria |
| Biperiden | C21H29NO | 2.385 | 0.0947 | anti-cholinergic anti-parkinsonian |
| Bepridil | C24H34N2O | 2.393 | 0.0952 | Anti-Anginal |
| Ipenoxazone | C22H34N2O2 | 2.4 | 0.0955 | NA |
| Vanoxeamine | C28H34Cl2F2N2O | 2.406 | 0.0957 | Cardiac Arrhythmias |
| Proadifen | C23H32ClNO2 | 2.407 | 0.0958 | Inhibitor Of Cytochrome P450 Enzymes |
| Trimipramine | C20H26N2 | 2.417 | 0.0961 | Antidepressant |
| Carbetapentane | C20H31NO3 | 2.436 | 0.0964 | Antitussive |
| Thenalidine | C17H22N2 | 2.439 | 0.0964 | Antihistamine |
| Clemastine | C21H26ClNO | 2.44 | 0.0964 | antiallergic |
| Methadone | C21H27NO | 2.44 | 0.0964 | Anti-Addictive |
| Diphenidol | C21H27NO | 2.44 | 0.0964 | Antiemetic |
| Cyclomethycaine | C22H33NO3 | 2.441 | 0.0964 | anestethic |
| Clomipramine | C19H23ClN2 | 2.444 | 0.0964 | antidepressant |
| Homochlorcyclizine | C19H23ClN2 | 2.444 | 0.0964 | Antihistamine |
| Bamipine | C19H24N2 | 2.444 | 0.09964 | Antihistamine |
| Dopexamine | C22H32N2O2 | 2.448 | 0.0964 | Adrenergic Beta-Agonists |
| Amitriptyline | C20H23N | 2.454 | 0.0963 | Antidepressant |
| Estradiol | C18H24O2 | 2.455 | 0.0963 | estrogen |
| Maprotiline | C20H23N | 2.455 | 0.0963 | antidepressant |
| Dimethisoquin | C17H24N2O | 2.455 | 0.0963 | Antipruritic |
| Octylonium | C29H43N2O4Br | 2.456 | 0.0963 | Antimuscarinic |
| Cinacalcet | C22H22F3N | 2.458 | 0.0927 | Hyperparathyroidism |
| Bifemelane | C18H23NO | 2.465 | 0.0961 | antidepressant |
| Orphenadrine | C18H23NO | 2.465 | 0.0961 | Parkinsonism |
| Zanapezil | C25H32N2O | 2.467 | 0.09961 | NA |
| Azithromycin | C38H72N2O12 | 2.468 | 0.0961 | antimicrobial |
| Rimcazole | C21H27N3 | 2.471 | 0.096 | Antipsychotic |
| Dexbrompheniramine | C16H19BrN2 | 2.474 | 0.0959 | antihistaminic |
| Salmeterol | C25H37NO4 | 2.478 | 0.0957 | antiasthma |
| Clocapramine | C28H37ClN4O | 2.479 | 0.0957 | Antipsychotic |
| (S)-(+)-Dimethindene | C20H24N2 | 2.479 | 0.0957 | Antihistamine / Anticholinergic |
| Oxethazaine | C28H41N3O3 | 2.48 | 0.0956 | Anesthetic |
| Buprenorphine | C29H41NO4 | 2.48 | 0.0956 | Anti-Addictive |
| Mycophenolate mofetil | C22H29NO2 | 2.481 | 0.0956 | immunosuppressant |
| Levopropoxyphene | C22H29NO2 | 2.482 | 0.0956 | antitussive |
| Fluoperazine | C21H25ClF3N3S | 2.482 | 0.0956 | Antipsychotic |
| L-Alpha-Acetyl-N-Normethadol | C22H29NO2 | 2.482 | 0.0956 | NA |
| Ebastine | C32H39NO2 | 2.486 | 0.0954 | Antihistamine |
| Protriptyline | C19H21N | 2.488 | 0.0953 | antidepressant |
| Fendiline | C23H25N | 2.49 | 0.0952 | Calcium Channel Blocker |
| Protryptyline | C19H21N | 2.488 | 0.0953 | Antidepressant |
| Amindocate | C19H29N3O2 | 2.491 | 0.0951 | NA |
| Diphenylpyraline | C19H23NO | 2.5 | 0.0946 | antihistaminic |
| Dirithromycin | C42H78N2O14 | 2.5 | 0.0946 | antibacterial |
| Fluoxetine | C17H18F3NO | 2.5 | 0.0946 | antidepressant |
| Benztropine | C21H25NO | 2.5 | 0.0946 | anticholinergic |
| Tomoxetine | C17H21NO | 2.5 | 0.0946 | Attention Deficit-Hyperactivity Disorder |
| Lidoflazine | C30H35F2N3O | 2.507 | 0.0941 | Antiarrhythmic |
| Triparanol | C27H32ClNO2 | 2.508 | 0.0941 | Antilipemic |
| Malachite Green | C23H25ClN2 | 2.51 | 0.0939 | Antiinfective Agent |
| Clarithromycin | C38H69NO13 | 2.512 | 0.0937 | antimicrobiall |
| Premethadone | C19H22N2 | 2.512 | 0.0938 | NA |
| Propiverine | C23H30ClNO3 | 2.517 | 0.0934 | Anticholinergic |
| Dibucaine | C20H29N3O2 | 2.518 | 0.0933 | local anesthetic |
| Mosapramine | C28H35ClN4O | 2.522 | 0.03 | Antipsychotic |
| Mefloquine | C17H16F6N2O | 2.524 | 0.0928 | antimalarial |
| Erythromycin | C37H67NO13 | 2.525 | 0.0927 | antibacterial |
| Tamoxifen | C26H29NO | 2.526 | 0.0926 | anticancer |
| Tilorone | C25H34N2O3 | 2.531 | 0.0921 | antiviral |
| Metixene | C20H23NS | 2.533 | 0.0919 | Anticholinergic |
| Trifluoperazine | C21H24F3N3S | 2.538 | 0.0914 | antipsychotic |
| Mibefradil | C29H38FN3O3 | 2.54 | 0.0912 | antihypertensive |
| Spiramycin | C43H74N2O14 | 2.556 | 0.0893 | antimicrobial |
| Triflupromazine | C18H19F3N2S | 2.558 | 0.0891 | Antipsychotic |
| Cyproheptadine | C21H21N | 2.558 | 0.0891 | Antihistamine |
| Difeterol | C25H29NO2 | 2.561 | 0.0887 | NA |
| Oxyphencyclimine | C20H28N2O3 | 2.566 | 0.0881 | anti-cholinergic |
| Maduramicin | C47H80O17 | 2.569 | 0.0876 | antimicrobial |
| Prochlorperazine | C20H24ClN3S | 2.571 | 0.0874 | antiemetic |
| Bromperidol | C21H23BrFNO2 | 2.571 | 0.0874 | Antipsychotic |
| Fluspirilene | C29H31F2N3O | 2.576 | 0.0867 | Antipsychotic |
| Propafenone | C21H27NO3 | 2.577 | 0.0866 | antiarrhythmic |
| Sertraline | C17H17Cl2N | 2.577 | 0.0866 | antidepressant |
| Roxindole | C23H26N2O | 2.577 | 0.0866 | Schizophrenia |
| Desloratadine | C19H19ClN2 | 2.585 | 0.0853 | Allergies |
| Thioridazine | C21H26N2S2 | 2.588 | 0.0848 | Antipsychotic |
| Octoclothepin | C19H21ClN2S | 2.591 | 0.0844 | NA |
| Dipivefrin | C19H29NO5 | 2.592 | 0.0842 | glaucoma |
| Promazine | C17H20N2S | 2.6 | 0.0829 | Antipsychotic |
| Pimozide | C28H29F2N3O | 2.603 | 0.0824 | Antipsychotic |
| Perphenazine | C21H26ClN3OS | 2.604 | 0.0823 | Antipsychotic |
| Carfilzomib | C40H57N5O7 | 2.605 | 0.082 | anticancer |
| Benzydamine | C19H23N3O | 2.609 | 0.0814 | Anti-Inflammatory |
| Piperacetazine | C24H30N2O2S | 2.61 | 0.0811 | antipsychotic |
| Indocate | C22H26N2O2 | 2.615 | 0.0802 | NA |
| Astemizole | C28H31FN4O | 2.615 | 0.0802 | Antihistamine |
| Chlorprothixene | C18H18ClNS | 2.615 | 0.0802 | Antipsychotic |
| Digoxin | C41H64O14 | 2.622 | 0.079 | antiarrhythmic |
| Mequitazine | C20H22N2S | 2.622 | 0.0789 | Antihistamine / Anticholinergic |
| Methiothepin | C20H24N2S2 | 2.625 | 0.0784 | Antipsychotic |
| Proscillaridin A | C30H42O8 | 2.625 | 0.0784 | Cardiac Arrhythmia |
| Ami-193 | C22H26FN3O2 | 2.63 | 0.0774 | 5-Ht2A 5-Ht1A and D2 Receptor Antagonist |
| Sertindole | C24H26ClFN4O | 2.632 | 0.077 | Antipsychotic |
| Diphenoxylate | C30H32N2O2 | 2.636 | 0.0761 | anti-peristaltic |
| Amodiaquine | C20H22ClN3O | 2.638 | 0.0756 | anti-malarial |
| Bazedoxifene | C30H34N2O3 | 2.638 | 0.0758 | postmenopausal osteoporosis |
| Amodiaquine | C20H22ClN3O | 2.638 | 0.0756 | antimalarial |
| Sunitinib | C22H27FN4O2 | 2.643 | 0.0747 | anticancer |
| Metergoline | C25H29N3O2 | 2.644 | 0.0744 | Antipsychoactive |
| Pimethixene | C19H19NS | 2.65 | 0.0731 | Antihistamine / Anticholinergic |
| Tandutinib | C31H42N6O4 | 2.651 | 0.073 | Anticancer (Experimental) |
| Sarpogrelate | C24H32ClNO6 | 2.656 | 0.0717 | Diabetes Mellitus |
| Monatepil | C28H30FN3OS | 2.656 | 0.0717 | Antihypertensive |
| Ftormetazine | C21H22F3N3OS | 2.667 | 0.0693 | NA |
| Nebivolol | C22H25F2NO4 | 2.667 | 0.0693 | Hypertension |
| Proglumetacin | C46H58ClN5O8 | 2.678 | 0.0666 | anti-inflammatory |
| Deslanoside | C47H74O19 | 2.686 | 0.0647 | antiarrhythmic |
| Azaclorzine | C22H24ClN3OS | 2.692 | 0.063 | antianginal |
| Odanacatib | C25H27F4N3O3S | 2.698 | 0.0614 | Osteoporosis / Bone Metastasis |
| Thioproperazine | C22H30N4O2S2 | 2.7 | 0.0609 | antipsychotic |
| Duloxetine | C18H19NOS | 2.7 | 0.0609 | Antidepressant |
| Thiothixene | C23H29N3O2S2 | 2.712 | 0.0577 | antipsychotic |
| Sulconazole | C18H15Cl3N2S | 2.718 | 0.056 | Antifungal |
| Paroxetine | C19H20FNO3 | 2.727 | 0.0534 | anti-depressant |
| Ketotifen | C19H19NOS | 2.732 | 0.0521 | anti-histaminic |
| Bosutinib | C26H29Cl2N5O3 | 2.738 | 0.0501 | anticancer |
| Bitolterol | C28H31NO5 | 2.738 | 0.0501 | bronchodilatator |
| Posaconazole | C37H42F2N8O4 | 2.753 | 0.0458 | antifungal |
| Amlodipine | C20H25ClN2O5 | 2.755 | 0.0451 | anti-hypertensive |
| Gefitinib | C22H24ClFN4O3 | 2.764 | 0.0423 | anticancer |
| (S)-(+)-Niguldipine | C36H39N3O6 | 2.786 | 0.0352 | Calcium Channel Blocker |
| Carvedilol | C24H26N2O4 | 2.786 | 0.0352 | Adrenergic Alpha-1 Receptor Antagonists |
| Amoxapine | C17H16ClN3O | 2.79 | 0.034 | Antidepressant |
| Cepharanthine | C37H38N2O6 | 2.795 | 0.032 | anti-inflammatory/antineoplastic |
| Rescimetol | C33H38N2O8 | 2.815 | 0.0253 | NA |
| Mesoridazine | C27H32N2O4S3 | 2.824 | 0.0223 | Phenothiazine |
| Dasatinib | C22H26ClN7O2S | 2.848 | 0.0137 | Anticancer |
| Raloxifene | C28H27NO4S | 2.852 | 0.0119 | anticancer |
| Tioconazole | C16H13Cl3N2OS | 2.883 | 0.0188 | Antifungal |
| Carprofen | C15H12ClNO2 | 2.903 | 0.007 | anti-inflammatory |
| Oxibendazole | C12H15N3O3 | 2.909 | 0.0092 | anthelmintic |
| Mk-2206 | C25H21N5O | 2.923 | 0.0146 | NA |
| Cantharidin | C10H12O4 | 2.923 | 0.0146 | Blister Agent |
| Lapatinib | C29H26ClFN4O4S | 2.939 | 0.0208 | Anticancer |
| Topotecan | C23H23N3O5 | 2.963 | 0.0298 | anticancer |
| Axitinib | C22H18N4OS | 3 | 0.0439 | Anticancer |
| Daunomycin | C27H29NO10 | 3.015 | 0.0495 | anticancer |
| Daunorubicin | C27H29NO10 | 3.015 | 0.0495 | antimicrobial/anticancer |
| Niclosamide | C13H8Cl2N2O4 | 3.31 | 0.1296 | antihelmintic |
| Dipyrithione | C10H8N2O2S2 | 3.417 | 0.134 | Fungicide |
| Nitrovin | C14H12N6O6 | 3.526 | 0.1214 | antimicrobial |
Dataset 1.FDA-approved drugs which are active against Ebola virus infection2,3.
AQVN: average quasivalence number; EIIP: electron-ion interaction potentialIt was shown that Ebola virus glycoprotein (GP)-mediated entry and infection is subordinated with a membrane-trafficking event that translocates a GP binding partner to the cell surface, which depends on microtubules30,31. Consistently, microtubule inhibitors which block this trafficking process could decrease infection without interfering with the direct binding and translocation of the Ebola virus into cells. AQVN and EIIP values of microtubule modulators and transcription inhibitors with reported anti-Ebola virus activity are given in Table 2. As can be seen, all these compounds, which do not directly affect binding and internalization of Ebola virus, are located outside of EVIIS. This additionally confirms the specificity of the EVIS domain.
Table 2. Viral transcription inhibitors and microtubule modulators with anti-Ebola virus activity.
| Compound | Formula | AQVN | EIIP [Ry] |
|---|
|
Viral transcription inhibitors
|
| BCX4430 | C11H15N5O3 | 3.000 | 0.0439 |
| Favipiravir | C5H4FN3O2 | 3.467 | 0.1304 |
| C-c3Ado | C12H16N4O3 | 2.914 | 0.0112 |
| c3Nep | C12H14N4O3 | 3.030 | 0.0552 |
| “D-like” 1’-6’-isoneplanocin | C11H12N5O3 | 3.194 | 0.1076 |
| “L-like” 1’-6’-isoneplanocin | C11H12N5O3 | 3.194 | 0.1076 |
| CMLDBU3402 | C30H26BrN3O7 | 3.045 | 0.1343 |
|
Microtubule modulators
|
| Vinblastine | C13H8Cl2N2O4 | 3.310 | 0.0130 |
| Vinorelbine | C45H54N4O8 | 2.721 | 0.0552 |
| Vincristine | C46H56N4O10 | 2.759 | 0.0439 |
| Colchicine | C22H25NO6 | 2.852 | 0.0121 |
| Nocodazole | C14H11N3O3S | 3.312 | 0.1298 |
| Mebendazole | C16H13N3O3 | 3.143 | 0.0934 |
| Albendazole | C12H15N3O2S | 2.909 | 0.0092 |
In further analysis we used EVIIS as a filter for virtual screening for candidate Ebola virus infection inhibitors. In Dataset 2 622 approved and 1089 experimental drugs in Dataset 3 selected by EVIIS screening of 6532 drugs from DrugBank are reported. Using cEVIIS, we located 267 approved and 382 experimental drugs. This small molecular library represents a source of candidate drugs for treatment of Ebola virus disease (EVD), which can be further experimentally tested.
| Database ID | Generic Name | Formula | AQVN | EIIP [Ry] |
|---|
| DB00376 | Trihexyphenidyl | C20H31NO | 2.301887 | 0.086554 |
| DB01022 | Phylloquinone | C31H46O2 | 2.303797 | 0.086811 |
| DB00191 | Phentermine | C10H15N | 2.307692 | 0.087326 |
| DB00313 | Valproic Acid | C8H16O2 | 2.307692 | 0.087326 |
| DB01577 | Methamphetamine | C10H15N | 2.307692 | 0.087326 |
| DB06204 | Tapentadol | C14H23NO | 2.307692 | 0.087326 |
| DB06709 | Methacholine | C8H18NO2 | 2.310345 | 0.087669 |
| DB08887 | Icosapent ethyl | C22H34O2 | 2.310345 | 0.087669 |
| DB01187 | Iophendylate | C19H29IO2 | 2.313725 | 0.088098 |
| DB01337 | Pancuronium | C35H60N2O4 | 2.316832 | 0.088483 |
| DB00947 | Fulvestrant | C32H47F5O3S | 2.318182 | 0.088648 |
| DB01083 | Orlistat | C29H53NO5 | 2.318182 | 0.088648 |
| DB00387 | Procyclidine | C19H29NO | 2.32 | 0.088868 |
| DB00942 | Cycrimine | C19H29NO | 2.32 | 0.088868 |
| DB08804 | Nandrolone decanoate | C28H44O3 | 2.32 | 0.088868 |
| DB00818 | Propofol | C12H18O | 2.322581 | 0.089174 |
| DB01463 | Fencamfamine | C15H21N | 2.324324 | 0.089378 |
| DB00137 | Xanthophyll | C40H56O2 | 2.326531 | 0.089632 |
| DB01616 | Alverine | C20H27N | 2.333333 | 0.090387 |
| DB06694 | Xylometazoline | C16H24N2 | 2.333333 | 0.090387 |
| DB06439 | Tyloxapol | C51H80O6 | 2.335766 | 0.090648 |
| DB00304 | Desogestrel | C22H30O | 2.339623 | 0.091049 |
| DB01339 | Vecuronium | C34H57N2O4 | 2.340206 | 0.091108 |
| DB00711 | Diethylcarbamazine | C10H21N3O | 2.342857 | 0.091375 |
| DB01338 | Pipecuronium | C35H62N4O4 | 2.342857 | 0.091375 |
| DB00159 | Icosapent | C20H30O2 | 2.346154 | 0.091697 |
| DB06710 | Methyltestosterone | C20H30O2 | 2.346154 | 0.091697 |
| DB00182 | Amphetamine | C9H13N | 2.347826 | 0.091857 |
| DB01576 | Dextroamphetamine | C9H13N | 2.347826 | 0.091857 |
| DB01586 | Ursodeoxycholic acid | C24H40O4 | 2.352941 | 0.092329 |
| DB06777 | Chenodeoxycholic acid | C24H40O4 | 2.352941 | 0.092329 |
| DB00230 | Pregabalin | C8H17NO2 | 2.357143 | 0.092698 |
| DB06718 | Stanozolol | C21H32N2O | 2.357143 | 0.092698 |
| DB01359 | Penbutolol | C18H29NO2 | 2.36 | 0.09294 |
| DB01599 | Probucol | C31H48O2S2 | 2.361446 | 0.093059 |
| DB00728 | Rocuronium | C32H53N2O4 | 2.362637 | 0.093156 |
| DB00847 | Cysteamine | C2H7NS | 2.363636 | 0.093236 |
| DB01036 | Tolterodine | C22H31NO | 2.363636 | 0.093236 |
| DB00297 | Bupivacaine | C18H28N2O | 2.367347 | 0.093525 |
| DB00464 | Sodium Tetradecyl Sulfate | C14H30O4S | 2.367347 | 0.093525 |
| DB00624 | Testosterone | C19H28O2 | 2.367347 | 0.093525 |
| DB01002 | Levobupivacaine | C18H28N2O | 2.367347 | 0.093525 |
| DB01429 | Aprindine | C22H30N2 | 2.37037 | 0.09375 |
| DB08924 | Amfecloral | C11H12Cl3N | 2.37037 | 0.09375 |
| DB02300 | Calcipotriol | C27H40O3 | 2.371429 | 0.093827 |
| DB00608 | Chloroquine | C18H26ClN3 | 2.375 | 0.094079 |
| DB00652 | Pentazocine | C19H27NO | 2.375 | 0.094079 |
| DB00396 | Progesterone | C21H30O2 | 2.377358 | 0.094238 |
| DB00470 | Dronabinol | C21H30O2 | 2.377358 | 0.094238 |
| DB00486 | Nabilone | C24H36O3 | 2.380952 | 0.09447 |
| DB01216 | Finasteride | C23H36N2O2 | 2.380952 | 0.09447 |
| DB01218 | Halofantrine | C26H30Cl2F3NO | 2.380952 | 0.09447 |
| DB00285 | Venlafaxine | C17H27NO2 | 2.382979 | 0.094595 |
| DB00411 | Carbachol | C6H14N2O2.ClH | 2.384615 | 0.094694 |
| DB00621 | Oxandrolone | C19H30O3 | 2.384615 | 0.094694 |
| DB00810 | Biperiden | C21H29NO | 2.384615 | 0.094694 |
| DB00941 | Hexafluronium | C36H42N2.C2H6 | 2.386364 | 0.094796 |
| DB01037 | Selegiline | C13H17N | 2.387097 | 0.094837 |
| DB00219 | Oxyphenonium | C21H34NO3 | 2.389831 | 0.094989 |
| DB01209 | Dezocine | C16H23NO | 2.390244 | 0.095011 |
| DB00296 | Ropivacaine | C17H26N2O | 2.391304 | 0.095067 |
| DB01244 | Bepridil | C24H34N2O | 2.393443 | 0.095177 |
| DB00202 | Succinylcholine | C14H30N2O4 | 2.4 | 0.095485 |
| DB00379 | Mexiletine | C11H17NO | 2.4 | 0.095485 |
| DB00514 | Dextromethorphan | C18H25NO | 2.4 | 0.095485 |
| DB00523 | Alitretinoin | C20H28O2 | 2.4 | 0.095485 |
| DB00755 | Tretinoin | C20H28O2 | 2.4 | 0.095485 |
| DB00929 | Misoprostol | C22H38O5 | 2.4 | 0.095485 |
| DB00930 | Colesevelam | C22H38O5 | 2.4 | 0.095485 |
| DB00982 | Isotretinoin | C20H28O2 | 2.4 | 0.095485 |
| DB01407 | Clenbuterol | C12H18Cl2N2O | 2.4 | 0.095485 |
| DB08808 | Bupranolol | C14H22ClNO2 | 2.4 | 0.095485 |
| DB00193 | Tramadol | C16H25NO2 | 2.409091 | 0.095841 |
| DB01255 | Lisdexamfetamine | C15H25N3O | 2.409091 | 0.095841 |
| DB06700 | Desvenlafaxine | C16H25NO2 | 2.409091 | 0.095841 |
| DB00281 | Lidocaine | C14H22N2O | 2.410256 | 0.09588 |
| DB00865 | Benzphetamine | C17H21N | 2.410256 | 0.09588 |
| DB00332 | Ipratropium bromide | C20H30NO3.BrH | 2.410714 | 0.095895 |
| DB00937 | Diethylpropion | C13H19NO | 2.411765 | 0.095929 |
| DB01156 | Bupropion | C13H18ClNO | 2.411765 | 0.095929 |
| DB00996 | Gabapentin | C9H17NO2 | 2.413793 | 0.095991 |
| DB01625 | Isopropamide | C23H32N2O | 2.413793 | 0.095991 |
| DB01185 | Fluoxymesterone | C20H29FO3 | 2.415094 | 0.096029 |
| DB00645 | Dyclonine | C18H27NO2 | 2.416667 | 0.096072 |
| DB00726 | Trimipramine | C20H26N2 | 2.416667 | 0.096072 |
| DB00268 | Ropinirole | C16H24N2O | 2.418605 | 0.096121 |
| DB00935 | Oxymetazoline | C16H24N2O | 2.418605 | 0.096121 |
| DB00308 | Ibutilide | C20H36N2O3S | 2.419355 | 0.09614 |
| DB00253 | Medrysone | C22H32O3 | 2.421053 | 0.096178 |
| DB01420 | Testosterone Propionate | C22H32O3 | 2.421053 | 0.096178 |
| DB05812 | Abiraterone | C24H31NO | 2.421053 | 0.096178 |
| DB00857 | Terbinafine | C21H25N | 2.425532 | 0.096267 |
| DB00896 | Rimexolone | C24H34O3 | 2.42623 | 0.096279 |
| DB00854 | Levorphanol | C17H23NO | 2.428571 | 0.096315 |
| DB00195 | Betaxolol | C18H29NO3 | 2.431373 | 0.09635 |
| DB00367 | Levonorgestrel | C21H28O2 | 2.431373 | 0.09635 |
| DB00378 | Dydrogesterone | C21H28O2 | 2.431373 | 0.09635 |
| DB01091 | Butenafine | C23H27N | 2.431373 | 0.09635 |
| DB01256 | Retapamulin | C30H47NO4S | 2.433735 | 0.096374 |
| DB00504 | Levallorphan | C19H25NO | 2.434783 | 0.096382 |
| DB00944 | Demecarium | C32H52N4O4 | 2.434783 | 0.096382 |
| DB01258 | Aliskiren | C30H53N3O6 | 2.434783 | 0.096382 |
| DB04835 | Maraviroc | C29H41F2N5O | 2.435897 | 0.09639 |
| DB00354 | Buclizine | C28H33ClN2 | 2.4375 | 0.096399 |
| DB00866 | Alprenolol | C15H23NO2 | 2.439024 | 0.096405 |
| DB00283 | Clemastine | C21H26ClNO | 2.44 | 0.096408 |
| DB00333 | Methadone | C21H27NO | 2.44 | 0.096408 |
| DB01231 | Diphenidol | C21H27NO | 2.44 | 0.096408 |
| DB00770 | Alprostadil | C20H34O5 | 2.440678 | 0.096409 |
| DB01046 | Lubiprostone | C20H32F2O5 | 2.440678 | 0.096409 |
| DB04575 | Quinestrol | C25H32O2 | 2.440678 | 0.096409 |
| DB00189 | Ethchlorvynol | C7H9ClO | 2.444444 | 0.096407 |
| DB00458 | Imipramine | C19H24N2 | 2.444444 | 0.096407 |
| DB00612 | Bisoprolol | C18H31NO4 | 2.444444 | 0.096407 |
| DB00750 | Prilocaine | C13H20N2O | 2.444444 | 0.096407 |
| DB00852 | Pseudoephedrine | C10H15NO | 2.444444 | 0.096407 |
| DB01010 | Edrophonium | C10H15NO | 2.444444 | 0.096407 |
| DB01019 | Bethanechol | C7H16N2O2 | 2.444444 | 0.096407 |
| DB01242 | Clomipramine | C19H23ClN2 | 2.444444 | 0.096407 |
| DB01364 | Ephedrine | C10H15NO | 2.444444 | 0.096407 |
| DB06804 | Nonoxynol-9 | C33H60O10 | 2.446602 | 0.096399 |
| DB02703 | Fusidic Acid | C31H48O6 | 2.447059 | 0.096397 |
| DB01057 | Echothiophate | C9H23NO3PS | 2.447368 | 0.096395 |
| DB01122 | Ambenonium | C28H40Cl2N4O2 | 2.447368 | 0.096395 |
| DB06702 | Fesoterodine | C26H37NO3 | 2.447761 | 0.096393 |
| DB01611 | Hydroxychloroquine | C18H26ClN3O | 2.44898 | 0.096384 |
| DB00961 | Mepivacaine | C15H22N2O | 2.45 | 0.096376 |
| DB04896 | Milnacipran | C15H22N2O | 2.45 | 0.096376 |
| DB08918 | Levomilnacipran | C15H22N2O | 2.45 | 0.096376 |
| DB00654 | Latanoprost | C26H40O5 | 2.450704 | 0.09637 |
| DB01579 | Phendimetrazine | C12H17NO | 2.451613 | 0.096361 |
| DB00611 | Butorphanol | C21H29NO2 | 2.45283 | 0.096348 |
| DB06713 | Norelgestromin | C21H29NO2 | 2.45283 | 0.096348 |
| DB00149 | L-Leucine | C6H13NO2 | 2.454545 | 0.096326 |
| DB00167 | L-Isoleucine | C6H13NO2 | 2.454545 | 0.096326 |
| DB00264 | Metoprolol | C15H25NO3 | 2.454545 | 0.096326 |
| DB00321 | Amitriptyline | C20H23N | 2.454545 | 0.096326 |
| DB00513 | Aminocaproic Acid | C6H13NO2 | 2.454545 | 0.096326 |
| DB00780 | Phenelzine | C8H12N2 | 2.454545 | 0.096326 |
| DB00783 | Estradiol | C18H24O2 | 2.454545 | 0.096326 |
| DB00934 | Maprotiline | C20H23N | 2.454545 | 0.096326 |
| DB06698 | Betahistine | C8H12N2 | 2.454545 | 0.096326 |
| DB01227 | Levomethadyl Acetate | C23H31NO2 | 2.45614 | 0.096304 |
| DB01433 | Methadyl Acetate | C23H31NO2 | 2.45614 | 0.096304 |
| DB00717 | Norethindrone | C20H26O2 | 2.458333 | 0.096268 |
| DB01012 | Cinacalcet | C22H22F3N | 2.458333 | 0.096268 |
| DB01186 | Pergolide | C19H26N2S | 2.458333 | 0.096268 |
| DB00184 | Nicotine | C10H14N2 | 2.461538 | 0.096207 |
| DB00294 | Etonogestrel | C22H28O2 | 2.461538 | 0.096207 |
| DB00302 | Tranexamic Acid | C8H15NO2 | 2.461538 | 0.096207 |
| DB00176 | Fluvoxamine | C15H21F3N2O2 | 2.465116 | 0.096125 |
| DB00925 | Phenoxybenzamine | C18H22ClNO | 2.465116 | 0.096125 |
| DB01173 | Orphenadrine | C18H23NO | 2.465116 | 0.096125 |
| DB00185 | Cevimeline | C10H17NOS | 2.466667 | 0.096085 |
| DB01107 | Methyprylon | C10H17NO2 | 2.466667 | 0.096085 |
| DB01196 | Estramustine | C23H31Cl2NO3 | 2.466667 | 0.096085 |
| DB01550 | Fenproporex | C12H16N2 | 2.466667 | 0.096085 |
| DB00207 | Azithromycin | C38H72N2O12 | 2.467742 | 0.096056 |
| DB00429 | Carboprost Tromethamine | C21H36O5.C4H11NO3 | 2.469136 | 0.096017 |
| DB00641 | Simvastatin | C25H38O5 | 2.470588 | 0.095974 |
| DB08823 | Spinosad | C42H67NO9 | 2.470588 | 0.095974 |
| DB00291 | Chlorambucil | C14H19Cl2NO2 | 2.473684 | 0.095874 |
| DB00405 | Dexbrompheniramine | C16H19BrN2 | 2.473684 | 0.095874 |
| DB00835 | Brompheniramine | C16H19BrN2 | 2.473684 | 0.095874 |
| DB01035 | Procainamide | C13H21N3O | 2.473684 | 0.095874 |
| DB01114 | Chlorphenamine | C16H19ClN2 | 2.473684 | 0.095874 |
| DB01620 | Pheniramine | C16H20N2 | 2.473684 | 0.095874 |
| DB00473 | Hexylcaine | C16H23NO2 | 2.47619 | 0.095785 |
| DB00752 | Tranylcypromine | C9H11N | 2.47619 | 0.095785 |
| DB01151 | Desipramine | C18H22N2 | 2.47619 | 0.095785 |
| DB01176 | Cyclizine | C18H22N2 | 2.47619 | 0.095785 |
| DB08936 | Chlorcyclizine | C18H21ClN2 | 2.47619 | 0.095785 |
| DB00905 | Bimatoprost | C25H37NO4 | 2.477612 | 0.095732 |
| DB00938 | Salmeterol | C25H37NO4 | 2.477612 | 0.095732 |
| DB01126 | Dutasteride | C27H30F6N2O2 | 2.477612 | 0.095732 |
| DB06708 | Lumefantrine | C30H32Cl3NO | 2.477612 | 0.095732 |
| DB08801 | Dimetindene | C20H24N2 | 2.478261 | 0.095707 |
| DB08824 | Ioflupane I 123 | C18H23FINO2 | 2.478261 | 0.095707 |
| DB00091 | Cyclosporine | C62H111N11O12 | 2.479592 | 0.095654 |
| DB00677 | Isoflurophate | C6H14FO3P | 2.48 | 0.095637 |
| DB00892 | Oxybuprocaine | C17H28N2O3 | 2.48 | 0.095637 |
| DB00921 | Buprenorphine | C29H41NO4 | 2.48 | 0.095637 |
| DB01626 | Pargyline | C11H13N | 2.48 | 0.095637 |
| DB08834 | Tauroursodeoxycholic acid | C26H45NO6S | 2.481013 | 0.095595 |
| DB00280 | Disopyramide | C21H29N3O | 2.481481 | 0.095576 |
| DB00647 | Dextropropoxyphene | C22H29NO2 | 2.481481 | 0.095576 |
| DB00531 | Cyclophosphamide | C7H15Cl2N2O2P | 2.482759 | 0.095521 |
| DB01103 | Quinacrine | C23H30ClN3O | 2.482759 | 0.095521 |
| DB01181 | Ifosfamide | C7H15Cl2N2O2P | 2.482759 | 0.095521 |
| DB00603 | Medroxyprogesterone Acetate | C24H34O4 | 2.483871 | 0.095471 |
| DB01050 | Ibuprofen | C13H18O2 | 2.484848 | 0.095427 |
| DB01104 | Sertraline | C17H17Cl2N | 2.486486 | 0.09535 |
| DB08803 | Tymazoline | C14H20N2O | 2.486486 | 0.09535 |
| DB01160 | Dinoprost Tromethamine | C20H34O5.C4H11NO3 | 2.487179 | 0.095316 |
| DB00344 | Protriptyline | C19H21N | 2.487805 | 0.095286 |
| DB00540 | Nortriptyline | C19H21N | 2.487805 | 0.095286 |
| DB00725 | Homatropine Methylbromide | C17H24NO3.BrH | 2.489362 | 0.095208 |
| DB01357 | Mestranol | C21H26O2 | 2.489796 | 0.095185 |
| DB06730 | Gestodene | C21H26O2 | 2.489796 | 0.095185 |
| This is a portion of the data; to view all the data, please download the file. |
Dataset 2.Approved and experimental drugs selected as candidate for treatment of EVD.
AQVN: average quasivalence number; EIIP: electron-ion interaction potentialDataset 3.Experimental drugs selected as candidate for treatment of EVD.
AQVN: average quasivalence number; EIIP: electron-ion interaction potentialMadrid and co-workers selected 24 drugs by in vitro screening of 1012 FDA-approved drugs, which are effective against Ebola virus infection2. They also showed that among these compounds, four antimalarial drugs (chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, amodiaquine and aminoquinoline-13) also are effective against Ebola virus infection in vivo2. Among 53 compounds which effectively inhibit Ebola virus infection in vitro, which Kouznetsova and co-workers selected from 2816 approved drugs, are also three anti-malarial drugs (mefloquione, chloroquine, amodiaquine)3. It was also suggested that application of chloroquine for prevention of virus transmission should be considered because this compound significantly inhibits Ebola virus infection13. Our analysis showed that 15 of 22 approved ant-malarial drugs (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antimalarial_medication) are located in EVIIS (Table 3). Six 2-alkylquinolines have been also included in this study. This chemical series is promising as some derivatives exhibited antiviral activity such as 2PQ, and 2QQ32,33 antimalarial activity such as 2PQ and 2PentQ234, antileishmanial activity such as 2PQ35,36 and neurotrophin-like activity on dopaminergic neurons such as 2QI1537. These compounds exhibit some advantages in regard to their chemical synthesis with few steps and good yields as well as their chemical stability in tropical conditions of storage. Their combined effects against virus and Leishmania parasites suggested they could be an advantage for the treatment of Leishmania/HIV co-infections and they were considered as attractive enough to enter the pipeline of DNDi on 2010.
All these data strongly suggest that this class of drugs should be further investigated as a promising source of therapeutics for treatment of EVD. Anti-malarial drugs with dual activity should be of special interest because malaria represents the highest health-related disease in African countries with EVD.
Among 3828 FDA-approved drugs screened for anti-Ebola activity were six antibiotics which inhibit Ebola virus infection (azthromycin, erythromycin, spiramycin, dirithromycin, maduramicin, charitromycin)2,3. All these antibiotics are within EVIIS and four of them are in cEVIIS. Analysis of 184 approved antibiotics (Dataset 4) showed that only 32 (17.4%) have AQVN and EIIP values in EVIIS, and that 11 of them are located within cEVIIS. Previously we reported domains of AQVN and EIIP which characterize different classes of antibiotics (Table 4)6. According to these data, among antibiotics some macrolides, pleuromutilins and aminoglycosides have the highest chance for inhibition of Ebola virus infection. Of note is that five of six antibiotics with experimentally proved activity against Ebola virus infection (azthromycin, erythromycin, spiramycin, dirithromycin, charitromycin) are macrolides. Antibiotics representing candidate Ebola virus infection inhibitors selected by EIIP/AQVN criterion are given in Table 5.
Table 3. Approved anti-malarial drugs selected as candidate drugs for EVD.
| Compound | Formula | AQVN | EIIP [Ry] |
|---|
| Quinine | C20H24N2O2 | 2.625 | 0.0784 |
| Chloroquinine | C18H26ClN3 | 2.375 | 0.0941 |
| Amodiquinine | C20H22ClN3O | 2.638 | 0.0756 |
| Proguanil | C11H16ClN5 | 2.606 | 0.0819 |
| Mefloquine | C17H16F6N2O | 2.524 | 0.0928 |
| Primaquine | C15H21NO3 | 2.600 | 0.0829 |
| Halofantrine | C26H30Cl2F3NO | 2.381 | 0.0945 |
| Clindamycin | C18H33ClN2O5S | 2.533 | 0.0919 |
| Artemether | C16H26O5 | 2.553 | 0.0897 |
| Piperaquine | C29H32Cl2N6 | 2.609 | 0.0814 |
| Artemotil | C17H28O5 | 2.520 | 0.0931 |
| Dihydroartemisin | C15H24O5 | 2.591 | 0.0844 |
| Quinidine | C20H24N2O2 | 2.625 | 0.0784 |
| Cinchonidine | C19H22N2O | 2.591 | 0.0844 |
| Artemisin | C15H22O5 | 2.667 | 0.0693 |
Table 4. AQVN and EIIP range of different antibiotics classes6.
| Antibiotic class | AQVN | EIIP [Ry] |
|---|
| Penicillins | 2.975 - 3.180 | 0.035 - 0.124 |
| Cephalosporins | 3.071 - 3.473 | 0.070 - 0.130 |
| Carbapenems & Penems | 2.973 - 3.059 | 0.022 - 0.066 |
| Monobactams | 3.166 - 3.581 | 0.100 - 0.134 |
| Quinolines | 2.760 - 3.060 | 0.003 - 0.065 |
| Aminoglycosides | 2.552 - 2.820 | 0.024 - 0.084 |
| Tetracyclines | 2.933 - 3.111 | 0.018 - 0.084 |
| Macrolides | 2.467 - 2.630 | 0.077 - 0.096 |
| Pleuromutilins | 2.395 - 2.473 | 0.095 - 0.096 |
| Nitrofurans | 3.652 - 3.826 | 0.010 - 0.086 |
| Antibiotics | Formula | AQVN | EIIP [Ry] |
|---|
| Teicoplanins | C77H77Cl2N9O13 -R | 2.75 | 0.046 |
| Telavancin | C80H106Cl2N11O27P | 2.863 | 0.008 |
| Vancomycin | C66H75Cl2N9O24 | 3.011 | 0.048 |
| Cefpodoxime | C15H17N5O6S2 | 3.333 | 0.132 |
| Tiamulin | C28H47NO4S | 2.395 | 0.095 |
| Retapamulin | C30H47NO4S | 2.434 | 0.096 |
| Valnemulin | C31H52N2O5S | 2.440 | 0.096 |
| Azithromycin | C38H72N2O12 | 2.468 | 0.096 |
| BC-3205 | C32H51N2O5S | 2.472 | 0.096 |
| Dirithromycin | C42H78N2O14 | 2.500 | 0.095 |
| Clarithromycin | C38H69NO13 | 2.512 | 0.094 |
| Surfactin | C53H93N7O13 | 2.518 | 0.093 |
| Erythromycin | C37H67NO13 | 2.525 | 0.093 |
| Clindamycin | C18H33ClN2O5S | 2.533 | 0.092 |
| Roxithromycin | C41H76N2O15 | 2.537 | 0.092 |
| Oleandomycin | C35H61NO12 | 2.550 | 0.090 |
| Gentamicin | C21H43N5O7 | 2.553 | 0.090 |
| Spiramycin | C43H74N2O14 | 2.556 | 0.089 |
| Mupirocin | C26H44O9 | 2.557 | 0.089 |
| Lincomycin | C18H34N2O6S | 2.590 | 0.085 |
| Netilmicin | C21H41N5O7 | 2.595 | 0.084 |
| Astromicin | C17H35N5O6 | 2.603 | 0.082 |
| Tylosin | C46H77NO17 | 2.610 | 0.081 |
| Kitasamycin | C35H59NO13 | 2.611 | 0.081 |
| Josamycin | C42H69NO15 | 2.614 | 0.080 |
| Telithromycin | C43H65N5O10 | 2.618 | 0.080 |
| Telithromycin | C43H65N5O10 | 2.618 | 0.080 |
| Verdamicin | C20H39N5O7 | 2.620 | 0.080 |
| Midecamycin | C41H67NO15 | 2.629 | 0.078 |
| Troleandomycin | C41H67NO15 | 2.629 | 0.078 |
| Sisomicin | C19H37N5O7 | 2.647 | 0.074 |
| Cethromycin | C42H59N3O10 | 2.649 | 0.073 |
| Carbomycin A | C42H67NO16 | 2.667 | 0.069 |
| Dibekacin | C18H37N5O8 | 2.676 | 0.067 |
| Echinocandin B | C52H81N7O16 | 2.692 | 0.063 |
| Rifabutin | C46H62N4O11 | 2.699 | 0.061 |
| Arbekacin | C22H44N6O10 | 2.707 | 0.059 |
| Rifapentine | C47H64N4O12 | 2.709 | 0.059 |
| Herbimycin | C30H42N2O9 | 2.723 | 0.055 |
| Tobramycin | C18H37N5O9 | 2.725 | 0.054 |
| Grepafloxacin | C19H22FN3O3 | 2.750 | 0.047 |
| Geldanamycin | C29H40N2O9 | 2.750 | 0.047 |
| Rifampicin | C43H58N4O12 | 2.752 | 0.046 |
| Sparfloxacin | C19H22F2N4O3 | 2.760 | 0.044 |
| Balofloxacin | C20H24FN3O4 | 2.769 | 0.041 |
| Bekanamycin | C18H37N5O10 | 2.771 | 0.040 |
| Fleroxacin | C17H18F3N3O3 | 2.773 | 0.039 |
| Lomefloxacin | C17H19F2N3O3 | 2.773 | 0.039 |
| Pefloxacin | C17H20FN3O3 | 2.773 | 0.039 |
| Isepamicin | C22H43N5O12 | 2.780 | 0.037 |
| Paromomycin | C23H47N5O14 | 2.786 | 0.035 |
| Quinupristin/dalfopristin | C53H67N9O10S | 2.786 | 0.035 |
| Moxifloxacin | C21H24FN3O4 | 2.792 | 0.033 |
| Pristinamycin IIA | C28H35N3O7 | 2.794 | 0.032 |
| Neomycin | C23H46N6O13 | 2.796 | 0.032 |
| Nadifloxacin | C19H21FN2O4 | 2.808 | 0.028 |
| Spectinomycin | C14H24N2O7 | 2.808 | 0.028 |
| Kanamycin | C18H36N4O11 | 2.812 | 0.026 |
| Tigecycline | C29H39N5O8 | 2.815 | 0.025 |
| Gatifloxacin | C19H22FN3O4 | 2.816 | 0.025 |
| Linezolid | C16H20FN3O4 | 2.818 | 0.024 |
| Amikacin | C22H43N5O13 | 2.819 | 0.024 |
| Meropenem | C17H25N3O5S | 2.824 | 0.022 |
| Sitafloxacin | C19H18ClF2N3O3 | 2.826 | 0.021 |
| Norfloxacin | C16H18FN3O3 | 2.829 | 0.020 |
| Pristinamycin IA | C45H54N8O10 | 2.855 | 0.011 |
| Ciprofloxacin | C17H18FN3O3 | 2.857 | 0.010 |
| Clinafloxacin | C17H17ClFN3O3 | 2.857 | 0.010 |
| Eperezolid | C18H23FN4O5 | 2.863 | 0.008 |
| Ofloxacin | C18H20FN3O4 | 2.870 | 0.006 |
| Levofloxacin | C18H20FN3O4 | 2.870 | 0.006 |
| Trimethoprim | C14H18N4O3 | 2.872 | 0.005 |
| Trimethoprim | C14H18N4O3 | 2.872 | 0.005 |
| Rolitetracycline | C27H33N3O8 | 2.873 | 0.004 |
| Temafloxacin | C21H18F3N3O3 | 2.875 | 0.004 |
| Hygromycin B | C20H37N3O13 | 2.877 | 0.003 |
| Virginiamycin S1 | C43H49N7O10 | 2.899 | 0.005 |
| Enoxacin | C15H17FN4O3 | 2.900 | 0.006 |
| Radezolid | C22H23FN6O3 | 2.909 | 0.009 |
| Streptomycin | C21H39N7O12 | 2.911 | 0.010 |
| Daptomycin | C72H101N17O26 | 2.917 | 0.012 |
| Rufloxacin | C17H18FN3O3S | 2.930 | 0.017 |
| Minocycline | C23H27N3O7 | 2.933 | 0.018 |
| Nimorazole | C9H14N4O3 | 2.933 | 0.019 |
| Gemifloxacin | C18H20FN5O4 | 2.958 | 0.028 |
| Flumequine | C14H12FNO3 | 2.968 | 0.032 |
| Sulfadicramide | C11H14N2O3S | 2.968 | 0.032 |
| Imipenem | C12H17N3O4S | 2.973 | 0.034 |
| Piromidic acid | C14H16N4O3 | 2.973 | 0.034 |
| Pipemidic acid | C14H17N5O3 | 2.974 | 0.034 |
| Benzylpenicillin | C16H18N2O4S | 2.976 | 0.035 |
| Ampicillin | C16H19N3O4S | 2.977 | 0.035 |
| Nafcillin | C21H22N2O5S | 2.980 | 0.036 |
| Doripenem | C15H24N4O6S2 | 2.980 | 0.036 |
| Pazufloxacin | C16H15FN2O4 | 3.000 | 0.044 |
| Tosufloxacin | C19H15F3N4O3 | 3.000 | 0.044 |
| Mafenide | C7H10N2O2S | 3.000 | 0.044 |
| Ornidazole | C7H10ClN3O3 | 3.000 | 0.044 |
| Secnidazole | C7H11N3O3 | 3.000 | 0.044 |
| Trovafloxacin | C20H15F3N4O3 | 3.022 | 0.052 |
| Sulfadimidine | C12H14N4O2S | 3.030 | 0.055 |
| Sulfisomidine | C12H14N4O2S | 3.030 | 0.055 |
| Ertapenem | C22H25N3O7S | 3.034 | 0.057 |
| Nalidixic acid | C12H12N2O3 | 3.034 | 0.057 |
| Tetracycline | C22H24N2O8 | 3.036 | 0.057 |
| Chlortetracycline | C22H23ClN2O8 | 3.036 | 0.057 |
| Doxycycline | C22H24N2O8 | 3.036 | 0.057 |
| Lymecycline | C22H23ClN2O8 | 3.036 | 0.057 |
| Posizolid | C21H21F2N3O7 | 3.037 | 0.058 |
| Meticillin | C17H20N2O6S | 3.043 | 0.060 |
| Amoxicillin | C16H19N3O5S | 3.046 | 0.061 |
| Phenoxymethylpenicillin | C16H18N2O5S | 3.048 | 0.062 |
| Piperacillin | C23H27N5O7S | 3.048 | 0.062 |
| Rosoxacin | C17H14N2O3 | 3.056 | 0.064 |
| Faropenem | C12H15NO5S | 3.059 | 0.066 |
| Chloramphenicol | C11H12Cl2N2O5 | 3.062 | 0.067 |
| Cefepime | C19H24N6O5S2 | 3.071 | 0.070 |
| Cefalexin | C16H17N3O4S | 3.073 | 0.071 |
| Oxytetracycline | C22H24N2O9 | 3.088 | 0.076 |
| Azlocillin | C20H23N5O6S | 3.091 | 0.077 |
| Demeclocycline | C21H21ClN2O8 | 3.094 | 0.078 |
| Sulfafurazole | C11H13N3O3S | 3.097 | 0.079 |
| Sulfamoxole | C11H13N3O3S | 3.097 | 0.079 |
| Tinidazole | C8H13N3O4S | 3.103 | 0.081 |
| Oxacillin | C19H19N3O5S | 3.106 | 0.082 |
| Cloxacillin | C19H18ClN3O5S | 3.106 | 0.082 |
| Dicloxacillin | C19H17Cl2N3O5S | 3.106 | 0.082 |
| Flucloxacillin | C19H17ClFN3O5S | 3.106 | 0.082 |
| Meclocycline | C22H21ClN2O8 | 3.111 | 0.084 |
| Metacycline | C22H22N2O8 | 3.111 | 0.084 |
| Sulfaphenazole | C15H14N4O2S | 3.111 | 0.084 |
| Prulifloxacin | C21H20FN3O6S | 3.115 | 0.085 |
| Sulfametomidine | C12H14N4O3S | 3.118 | 0.086 |
| Sulfaperin | C11H12N4O2S | 3.133 | 0.090 |
| Carbenicillin | C17H18N2O6S | 3.136 | 0.091 |
| Sulfapyridine | C11H11N3O2S | 3.143 | 0.093 |
| Metronidazole | C6H9N3O3 | 3.143 | 0.093 |
| Torezolid | C17H15FN6O3 | 3.143 | 0.093 |
| Prontosil | C12H13N5O2S | 3.152 | 0.096 |
| Cefaclor | C15H14ClN3O4S | 3.158 | 0.098 |
| Nocardicin A | C23H24N4O9 | 3.167 | 0.100 |
| Sulfacetamide | C8H10N2O3S | 3.167 | 0.100 |
| Sulfaguanidine | C7H10N4O2S | 3.167 | 0.100 |
| Mezlocillin | C21H25N5O8S2 | 3.180 | 0.104 |
| Propenidazole | C11H13N3O5 | 3.188 | 0.106 |
| Cefpirome | C22H22N6O5S2 | 3.193 | 0.107 |
| Sulfadimethoxine | C12H14N4O4S | 3.200 | 0.109 |
| Sulfaquinoxaline | C14H12N4O2S | 3.212 | 0.112 |
| Sulfamethoxazole | C10H11N3O3S | 3.214 | 0.113 |
| Sulfamazone | C23H24N6O7S2 | 3.226 | 0.115 |
| Sulfametoxydiazine | C11H12N4O3S | 3.226 | 0.115 |
| Temocillin | C16H18N2O7S2 | 3.244 | 0.119 |
| Sulfadiazine | C10H10N4O2S | 3.259 | 0.122 |
| Oxolinic acid | C13H11NO5 | 3.267 | 0.123 |
| Ticarcillin | C15H16N2O6S2 | 3.268 | 0.123 |
| Cefalotin | C16H16N2O6S2 | 3.286 | 0.126 |
| Azanidazole | C10H10N6O2 | 3.286 | 0.126 |
| Ceftazidime | C22H22N6O7S2 | 3.288 | 0.127 |
| Clavulanic acid | C8H9NO5 | 3.304 | 0.129 |
| Clavulanic acid | C8H9NO5 | 3.304 | 0.129 |
| Sulfathiourea | C7H9N3O2S2 | 3.304 | 0.129 |
| Cefamandole | C18H18N6O5S2 | 3.306 | 0.129 |
| Aldesulfone | C14H16N2O6S3 | 3.317 | 0.130 |
| Sulfamethizole | C9H10N4O2S2 | 3.333 | 0.132 |
| Sulfathiazole | C9H9N3O2S2 | 3.360 | 0.134 |
| Tazobactam | C10H12N4O5S | 3.375 | 0.134 |
| Cinoxacin | C12H10N2O5 | 3.379 | 0.134 |
| Sulfasalazine | C18H14N4O5S | 3.381 | 0.134 |
| Succinylsulfathiazole | C13H13N3O5S2 | 3.389 | 0.134 |
| Cefotaxime | C16H17N5O7S2 | 3.404 | 0.134 |
| Cefuroxime | C16H16N4O8S | 3.422 | 0.134 |
| Aztreonam | C13H17N5O8S2 | 3.422 | 0.134 |
| Phthalylsulfathiazole | C17H13N3O5S2 | 3.450 | 0.132 |
| Ceftibuten | C15H14N4O6S2 | 3.463 | 0.131 |
| Ceftaroline | C24H25N8O10PS4 | 3.472 | 0.130 |
| Nifuroxazide | C12H9N3O5 | 3.517 | 0.123 |
| Ceftriaxone | C18H18N8O7S3 | 3.518 | 0.123 |
| Cefazolin | C14H14N8O4S3 | 3.535 | 0.120 |
| Tigemonam | C12H15N5O9S2 | 3.581 | 0.108 |
| Furazolidone | C8H7N3O5 | 3.652 | 0.086 |
| Nitrofurazone | C6H6N4O4 | 3.700 | 0.068 |
| Nifurtoinol | C9H8N4O6 | 3.704 | 0.066 |
| Nifurzide | C12H8N4O6S | 3.806 | 0.020 |
Dataset 4.Approved antibiotics screened for candidate anti-Ebola drugs.
AQVN: average quasivalence number; EIIP: electron-ion interaction potentialPrevious, we determined AQVN and EIIP domains characterizing different classes of anti-HIV drugs4–9. As can be seen in Table 6, the EIIP/AQVN domain of CCR5 HIV entry inhibitors is within EVIIS, and domains of CXCR4 HIV entry inhibitors and HIV protease inhibitors partially overlaps EVIIS. The EIIP/AQVN domains of other classes of anti-HIV agents are located outside EVIIS. This indicates that some HIV entry inhibitors and HIV protease inhibitors could also be effective drugs against Ebola virus infection.
Table 5. Antibiotics selected as candidate drugs for EVD.
| Antibiotics | Formula | AQVN | EIIP [Ry] |
|---|
| Tiamulin | C28H47NO4S | 2.395 | 0.095 |
| Retapamulin | C30H47NO4S | 2.434 | 0.096 |
| Valnemulin | C31H52N2O5S | 2.440 | 0.096 |
| Azithromycin | C38H72N2O12
| 2.468 | 0.096 |
| BC-3205 | C32H51N2O5S | 2.472 | 0.096 |
| Dirithromycin | C42H78N2O14
| 2.500 | 0.095 |
| Clarithromycin | C38H69NO13
| 2.512 | 0.094 |
| Surfactin | C53H93N7O13
| 2.518 | 0.093 |
| Erythromycin | C37H67NO13
| 2.525 | 0.093 |
| Clindamycin | C18H33ClN2O5S | 2.533 | 0.092 |
| Roxithromycin | C41H76N2O15
| 2.537 | 0.092 |
| Oleandomycin | C35H61NO12
| 2.550 | 0.090 |
| Gentamicin | C21H43N5O7
| 2.553 | 0.090 |
| Spiramycin | C43H74N2O14
| 2.556 | 0.089 |
| Mupirocin | C26H44O9
| 2.557 | 0.089 |
| Lincomycin | C18H34N2O6S | 2.590 | 0.085 |
| Netilmicin | C21H41N5O7
| 2.595 | 0.084 |
| Astromicin | C17H35N5O6
| 2.603 | 0.082 |
| Tylosin | C46H77NO17
| 2.610 | 0.081 |
| Kitasamycin | C35H59NO13
| 2.611 | 0.081 |
| Josamycin | C42H69NO15
| 2.614 | 0.080 |
| Telithromycin | C43H65N5O10
| 2.618 | 0.080 |
| Telithromycin | C43H65N5O10
| 2.618 | 0.080 |
| Verdamicin | C20H39N5O7
| 2.620 | 0.080 |
| Midecamycin | C41H67NO15
| 2.629 | 0.078 |
| Troleandomycin | C41H67NO15
| 2.629 | 0.078 |
| Sisomicin | C19H37N5O7
| 2.647 | 0.074 |
| Cethromycin | C42H59N3O10
| 2.649 | 0.073 |
| Carbomycin A | C42H67NO16
| 2.667 | 0.069 |
| Dibekacin | C18H37N5O8
| 2.676 | 0.067 |
| Echinocandin B | C52H81N7O16
| 2.692 | 0.063 |
| Rifabutin | C46H62N4O11
| 2.699 | 0.061 |
Table 6. AQVN and EIIP range of anti-HIV drugs6.
| Target | AQVN | EIIP [Ry] |
|---|
| CXCR4 | 2.16 - 2.53 | 0.062 - 0.096 |
| CCR5 | 2.42 - 2.63 | 0.079 - 0.099 |
| PI | 2.61 - 2.78 | 0.040 - 0.080 |
| NRTI/NtRTI | 2.92 - 3.20 | 0.040 - 0.100 |
| INI | 3.00 - 3.20 | 0.044 - 0.116 |
| Anti-HIV flavonoids | 3.34 - 3.59 | 0.110 - 0.135 |
In conclusion, the presented results show that the EIIP/AQVN criterion can be used as an efficient filter in virtual screening of molecular libraries for candidate inhibitors of Ebola virus infection. Approved (Dataset 2) and experimental drugs (Dataset 3), anti-malarial drugs (Table 3) and antibiotics (Table 5) selected by this criterion represents a valuable source of candidate therapeutics for treatment of EVD, some of which are already approved by FDA for treatment of other diseases which can be repurposed for use in EVD. We hope that these data, obtained by an in silico drug repurposing screen, will accelerate discovery of drugs for treatment of EVD, which are necessary in this ongoing emergency situation caused by the current unprecedented Ebola virus outbreak. To enable other researchers working on online EIIP/AQVN-based screening of different sources of small molecules for candidate Ebola drugs, we established an open web server (http://www.biomedconsulting.info/ebola_screen.php).
Data availability
The virtual screen for candidate inhibitors of EBOLA virus infection web tool is available at: http://www.biomedconsulting.info/tools/ebolascreen.php. An archived version can be accessed at: http://www.webcitation.org/6Vxtuojgx38
F1000Research: Dataset 1. FDA-approved drugs which are active against Ebola virus infection2,3, 10.5256/f1000research.6110.d4287639
F1000Research: Dataset 2. Approved and experimental drugs selected as candidate for treatment of EVD, 10.5256/f1000research.6110.d4287740
F1000Research: Dataset 3. Experimental drugs selected as candidate for treatment of EVD, 10.5256/f1000research.6110.d4287841
F1000Research: Dataset 4. Approved antibiotics screened for candidate anti-Ebola drugs, 10.5256/f1000research.6110.d4287942

Comments on this article Comments (0)