Keywords
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Drug toxicity, DOTS, visual field defects, toxic optic neuropathy, Ethambutol, Linezolid
This article is included in the Eye Health gateway.
This article is included in the Manipal Academy of Higher Education gateway.
Tuberculosis is a global health challenge with one-third of the world’s population infected by it. Although ocular side effects of Anti-tubercular drugs are well known, the patients generally report late in the course which can result in irreversible vision loss. The purpose of this study was to study the visual field changes during the time course of anti-tubercular therapy (ATT).
A total of 48 patients were studied in this prospective type of study. All patients newly diagnosed with TB and started on treatment were included in the study. Baseline examination which included visual acuity, color vision, anterior segment, IOP, Amsler grid, fundus, and visual field test were performed before starting ATT and at 6-month follow-up.
The mean age of the study population was 35.90 ± 10.2 years. 35 (72.9%) were males and 13 (27.1%) females. 32(66.6%) had pulmonary TB and the rest 16 (33.3%) had extrapulmonary TB. MDR TB was diagnosed in 27 (56.3%) of the patients with the rest 21 (43.8%) being drug sensitive. The baseline examination was normal in all 48 patients. 3(6.3%) out of 45 patients presented with visual complaints after the treatment initiation. Altogether 7 patients out of 48, had visual field defects at the 6-month follow-up. The incidence of visual field defects in our study was 14.6% with the value being significant (0.016). 8.3% had peripheral constriction of visual fields, 2.1% with Severe generalized depression of visual fields and 2.1% with central scotoma. Out of the 45 patients with no visual complaints at 6-month follow-up, 4 (8.33%) showed peripheral field constriction.
Visual field defects caused by ATT can precede clinical symptoms. Visual field evaluation can be an important tool for the early detection of optic neuropathy in patients receiving ATT in clinical settings where Visual evoked potential testing and RNFL-OCT are not available.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Drug toxicity, DOTS, visual field defects, toxic optic neuropathy, Ethambutol, Linezolid
Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the ancient diseases known to mankind that has co-evolved with humans for many decades1 and is a global health challenge.2 Among the world’s population, one-third are infected by it, and that makes TB, a public health concern.2–4 TB is one of the top three infectious killing diseases in the world1 and is also the leading cause of death from a single infectious agent.2 According to the India TB Report 2022, there is a 19% increase in cases (new and relapse) in 2021 from 2020.5 Interrupting its transmission is central to achieving the reduction in its incidence required to meet the End TB targets.5
DOT (Directly observed therapy) is widely accepted and followed in many other countries and is the most effective.3 It is the fastest expanding and most extensive growing strategy and the second largest based on people initiated on treatment and population coverage, respectively.1 The standard treatment plan for tuberculosis usually is six months however, for resistant cases, it may even extend to 2 years with less potent and less toxic drugs1with treatment change based on the drug resistance.
The first line of drugs includes ethambutol, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and rifampicin, and these are part of DOTS (Directly Observed Treatment Short course). Despite the increased availability of medical treatment, new challenges have developed with the growing incidences of drug-resistant tuberculosis that include DR-TB (drug-resistant), MDR-TB (multidrug-resistant), and XDR-TB (extensively drug-resistant).6
ATT-associated ocular toxicity was first established in the 1960s.7 Ethambutol and linezolid are the most common anti-TB drugs responsible for ocular side effects.4,8 Rare cases of Isoniazid-induced toxic optic neuropathy have also been reported.9,10 The toxic neuropathies associated with Ethambutol and linezolid account for about 1% and normally occur after 4-6 months of treatment.11 Optic nerve head and retinal nerve fiber layer changes are minimal in the early stages.7 The most common visual field defects associated with ethambutol and linezolid are central and centro-caecal scotomas,12 whereas bitemporal hemianopic scotomas with isoniazid.9
Timely detection of ATT-induced optic neuropathy is essential since sight-threatening complications can be reversed if the drug causing the toxicity is discontinued at the earliest. The purpose of this study was to evaluate visual function in patients receiving ATT and to evaluate the visual field changes caused due to ATT.
This was a prospective observational study done in a tertiary health care center, in south India, conducted from December 2020 to October 2022. The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee (Kasturba Medical College, Mangalore affiliated to Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, India Approval No: IEC KMC MLR 12-2020/441) and abided by the tenets of the Helsinki Protocol. Patients above 15 years of age, newly diagnosed with TB who were started on anti-tubercular therapy were included in the study. A written informed consent was taken from all the patients. Patients who were previously on Anti Tubercular Therapy, patients with a previous history of the retina and optic nerve pathologies, and those with previously documented visual field defects were excluded.
The following tests were done at baseline (beginning of ATT) and at 6 months from the date of starting ATT. Baseline ocular examination which included best corrected visual acuity using Snellen chart and Jaeger chart, color vision using Ishihara plates, Slit amp examination, IOP with Goldman Applanation Tonometer, Amsler grid, Dilated fundus examination using slit lamp biomicroscopy and indirect ophthalmoscopy, and Humphrey visual field analysis 30-2 were done. Patients were advised to continue with their ATT and to review immediately in case of any visual symptoms. At the onset of visual symptoms, the drug responsible was identified and stopped.
The data was analyzed using IBM SPSS version 25. The nominal variables-type of color vision and fields at baseline and follow-up were compared using the Mc Nemer test for nominal variables; whereas the visual acuity was compared at baseline and follow-up using the Wilcoxon sign rank test for ordinal variables. A p-value of <0.05 was considered significant for all analyses.
A total of 48 patients were part of this study. The mean age of the study population was 35.90 years ± 10.2 years. Among the 48 patients, 4 (8.3%) were 15-20 years of age, 13 (27%) in the age group of 21-30 years, and 8 (16.6%) in the age group of 31-40. Rest 23 (47.9%) patients are in the age group of 41-50 years.35 (72.9%) out of 48 were male and 13 (27.1%) were female.
Of the total 48 patients included, 32(66.6%) patients had a diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis. Out of the 15 patients with extrapulmonary tuberculosis 4(8.3%) had disseminated tuberculosis, 4(8.3%) with TB lymphadenitis, 6(12.5%) with pleural effusion, 1(2.1%) with abdominal tuberculosis and 1(2.1%) with pott’s spine (Figure 1).
TB REGIMEN: MDR tuberculosis, mainly rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis was found in 27(56.3%) at the time of their diagnosis and the rest 21 (43.8%) were drug-sensitive.
Of the 27 with drug resistance, 2(4.2%) were initiated on a shorter bedaquiline regimen and 3(6.3%) on all oral longer MDR TB regimens (Table 1).
| Sensitivity | Drug sensitive | MDR TB Rifampicin resistant | Shorter bedaquiline | Longer MDR TB regimen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 21 | 22 | 2 | 3 |
| Percentage | 43.8% | 45.8% | 4.2% | 6.3% |
Visual acuity at baseline for all the 48 patients included in the study was 6/6. 3(6.3%) out of 45 patients presented with visual complaints after the treatment initiation. 1 patient (2.1%) had vision of 6/18 with the other two patients (4.2%) below 6/60 (Table 2).
| Visual acuity | baseline | 6 month follow-up | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6/6 | 48 (100%) | 45 (93.8%) | .102 |
| 6/18-6/9 | 0 | 0 | |
| 6/36-6/18 | 0 | 1 (2.1%) | |
| <6/60 | 0 | 2 (4.2%) |
Color vision examination was normal in all 48 patients during baseline evaluation. 3(6.3%) developed color vision abnormalities at follow-up with all of them being red-green deficient (Table 3). P value was 0.250 which is not significant.
| Color vision | baseline | 6-month follow-up | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 48 (100%) | 45 (93.8%) | .250 (NS) |
| Red-green deficit | 0 | 3 (6.3%) |
Anterior segment examination findings and IOP were normal in all patients at baseline and follow-up. Fundus examination was found to be within normal limits in all 48 patients at baseline. However, 3(6.3%) had abnormal findings at follow-up. 1(2.1%) had bilateral temporal disc pallor with the other two patients (4.2%) having bilateral hyperaemic disc (Figure 2).
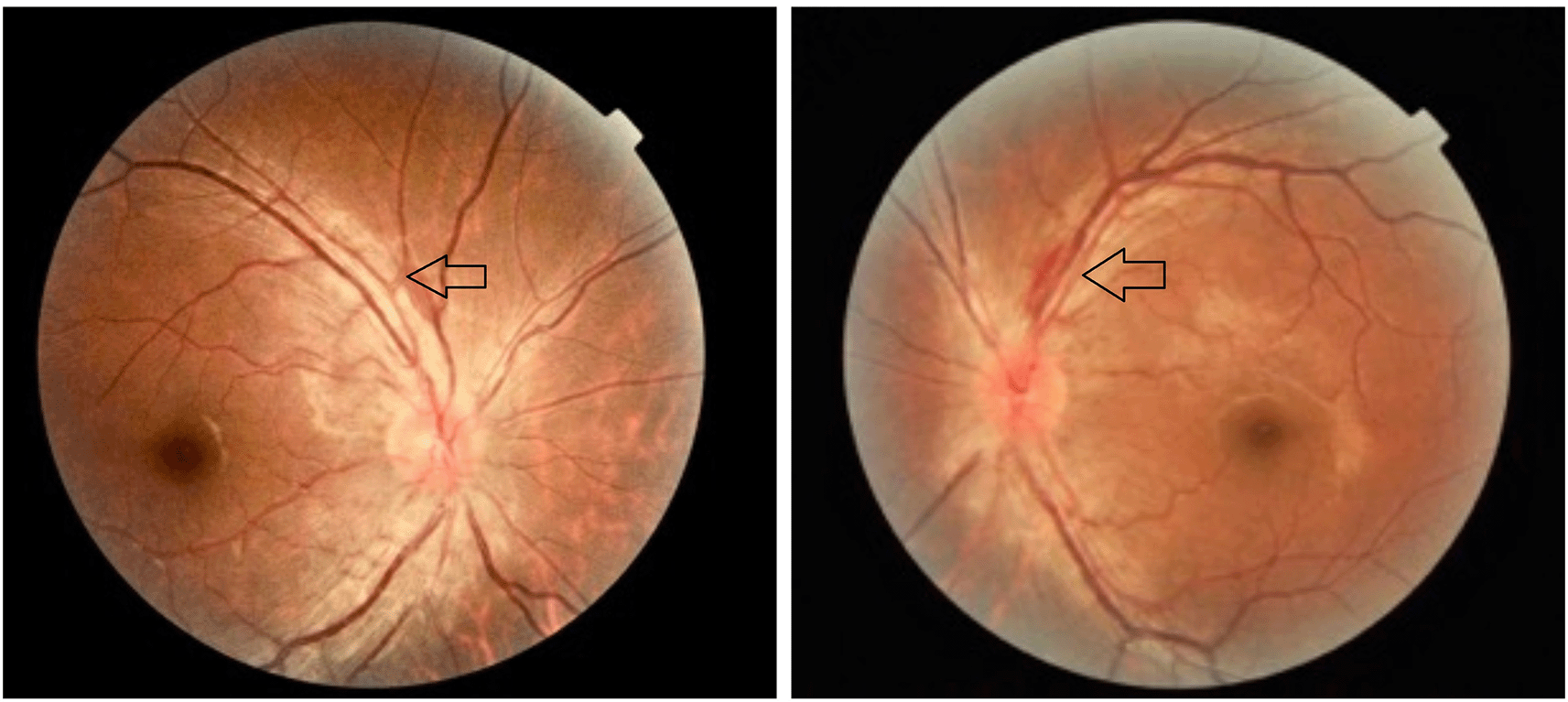
Visual fields at baseline for all 48 patients were normal. Out of the 45 patients with no visual complaints at 6-month follow-up, 4 (8.33%) showed peripheral field constriction. Out of the 8.33%, Constriction in one quadrant was observed in 2.1% whereas constriction in 2 quadrants was observed in 6.3%. 3(6.3%) patients developed visual symptoms during the treatment course, out of them, peripheral field constriction was noted in one patient (2.1%), one showed severe generalized depression of visual fields (2.1%) and the other patient had central scotoma (2.1%). p-value of 0.16 was calculated which was found to be significant (Table 4).
All three of these patients with visual complaints were on linezolid as part of their all-oral long bedaquiline regimen. The three patients with visual symptoms were immediately advised to stop the linezolid and even the TB center had been notified of the same.
To confirm the diagnosis in the three patients with visual symptoms VEP and RNFL OCT was done which showed prolonged P100 latency and thinning of the RNFL layer.
The visual acuity, color vision, and visual field defects improved in two of the three patients within 1-2 months with the average being 1.5 months post-stopping linezolid. Visual symptoms of one patient however did not improve even after stopping linezolid which can be attributed to a longer duration of drug intake.
Baseline visual acuity was normal in all patients, however, 3 (6.3%) patients complained of visual symptoms with 2 reported vision less than 6/60. This is similar to Garg et a13 at 8.69%, Ashraf et al,14 at 10.6%, Panchal et al,4 7.44%, and Goyal et al,15 at 3.3% incidence of visual complaints. However, no patient in studies done by Saxena et al,16 Menon et al,17 Kandel et al,18 Kim et al,19 Jin et al,8 had any visual complaints.
Color vision abnormality was noted in 6.3% of our patients similar to 5.32% as seen in a study done by Panchal et al.4 All our patients had Red-Green deficiency in contrast to the study by Ashraf et al,14 who had 23.23% of people with color vision abnormalities with the maximum being blue-yellow deficient.
Out of 48 people in our study on fundus examination, 4.2% had disc edema and 2.1% had temporal disc pallor. The findings in these patients were bilateral. Similar findings were noted by Panchal et al4 who had 2.12% with bilateral disc edema and 2.12% with bilateral disc pallor. A study done by Ambika et al,20 showed 44.14% with disc pallor and <1% showed disc edema.
The incidence of visual field defects in our study was 14.6% with the value being significant (0.016). 2.1% had a peripheral constriction in all 4 quadrants, 2.1% with Severe generalized depression of visual fields, and 2.1% with central scotoma. In our study, 4 patients (8.3%) showed Peripheral field constriction in different quadrants making it the most common field defect similar to the study done by Ashraf et al,14 in which 13.3% had field defects with 8.15% being peripheral field defects in different quadrants. However, visual field defects in patients receiving anti-tubercular therapy varied in different studies. Bitemporal field defects were observed by Kho et al12 in his study, centro-caecal scotomas (2.12%) were observed by Panchal et al.4 Garg et al13 in their study concluded that 8.69% (8 eyes of 4 patients) with visual field defects with centro-caecal scotoma in one patient and the rest with peripheral constriction. Few studies like Kandel et al,18 Kim et al,19 Jin et al,8Saxena et al,16 observed no visual field changes in any of their patients on anti-tubercular therapy. The limitations of this study include that reaching a definite conclusion by extrapolation of results to the general population was not possible due to the small sample size. the patients were not followed up at shorter intervals, the accurate time of onset of the side effects could not be studied. Incidence of visual field defects was 14.6% in our study with 6.25% of them reporting visual symptoms.
Visual field defects caused by ATT can precede clinical symptoms. Visual field evaluation can be an important tool for the early detection of optic neuropathy in patients receiving ATT in clinical settings where visual evoked potential testing and RNFL-OCT are not available. Patients on ATT should be regularly screened for ocular adverse effects preferably every month. Routine examinations like visual acuity, color vision, and fundus examination must be carried out to look for any subclinical effects of the treatment and monitor their progression.
Chest physicians, ophthalmologists, and Health care workers need to be aware of potentially sight-threatening side effects of ATT. Prompt diagnosis and timely intervention are the keys to optimal visual outcomes in patients with toxic optic neuropathy due to ATT.
Open Science Framework: Visual field changes in patients receiving antitubercular therapy, https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/SAQMC. 21
Data are available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license (CC-BY 4.0).
| Views | Downloads | |
|---|---|---|
| F1000Research | - | - |
|
PubMed Central
Data from PMC are received and updated monthly.
|
- | - |
Is the work clearly and accurately presented and does it cite the current literature?
Partly
Is the study design appropriate and is the work technically sound?
Yes
Are sufficient details of methods and analysis provided to allow replication by others?
Partly
If applicable, is the statistical analysis and its interpretation appropriate?
Partly
Are all the source data underlying the results available to ensure full reproducibility?
No
Are the conclusions drawn adequately supported by the results?
Partly
Competing Interests: No competing interests were disclosed.
Reviewer Expertise: Areas of intrest is Neurology. Neuro-ophthalmology and neuroinfections
Alongside their report, reviewers assign a status to the article:
| Invited Reviewers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|
Version 4 (revision) 30 Jul 25 |
read | read | |
|
Version 3 (revision) 26 Feb 25 |
read | ||
|
Version 2 (revision) 01 Aug 24 |
read | ||
|
Version 1 01 Jul 24 |
read | ||
Provide sufficient details of any financial or non-financial competing interests to enable users to assess whether your comments might lead a reasonable person to question your impartiality. Consider the following examples, but note that this is not an exhaustive list:
Sign up for content alerts and receive a weekly or monthly email with all newly published articles
Already registered? Sign in
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here.
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here.
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
Comments on this article Comments (0)